DC power provides a constant voltage ideal for electronics pets, ensuring stable operation and longer battery life. AC power, with its alternating current, is commonly used for powering charging stations but requires conversion to DC for compatibility with most electronic pet devices. Choosing the right power type optimizes performance and safety for your electronic pet's energy needs.
Table of Comparison
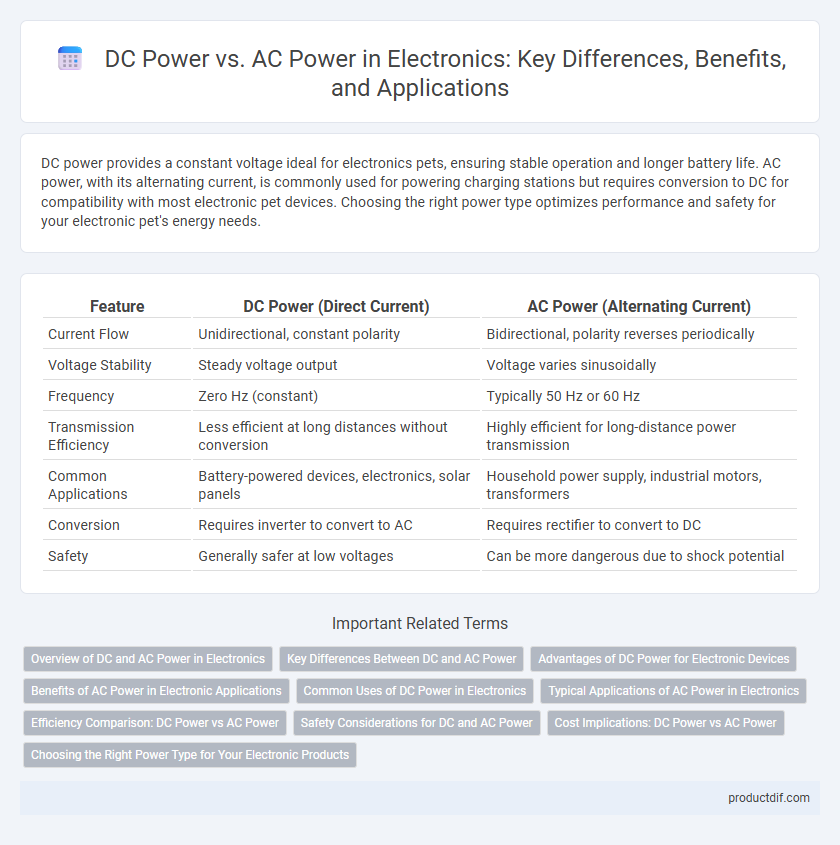
| Feature | DC Power (Direct Current) | AC Power (Alternating Current) |
|---|---|---|
| Current Flow | Unidirectional, constant polarity | Bidirectional, polarity reverses periodically |
| Voltage Stability | Steady voltage output | Voltage varies sinusoidally |
| Frequency | Zero Hz (constant) | Typically 50 Hz or 60 Hz |
| Transmission Efficiency | Less efficient at long distances without conversion | Highly efficient for long-distance power transmission |
| Common Applications | Battery-powered devices, electronics, solar panels | Household power supply, industrial motors, transformers |
| Conversion | Requires inverter to convert to AC | Requires rectifier to convert to DC |
| Safety | Generally safer at low voltages | Can be more dangerous due to shock potential |
Overview of DC and AC Power in Electronics
DC power provides a constant voltage and current flow in a single direction, essential for electronic devices like batteries, LEDs, and integrated circuits. AC power alternates its direction and voltage amplitude, enabling efficient transmission over long distances and powering household appliances. Understanding the fundamental differences between DC and AC power is critical for designing circuits and selecting appropriate power sources in electronics applications.
Key Differences Between DC and AC Power
DC power flows in a single, constant direction with a steady voltage, making it ideal for electronics, batteries, and low-voltage applications. AC power alternates direction and voltage, allowing efficient transmission over long distances and compatibility with household appliances and industrial equipment. Key differences include waveform characteristics, voltage regulation, and typical use cases across power generation and distribution systems.
Advantages of DC Power for Electronic Devices
DC power provides a stable and constant voltage that is ideal for sensitive electronic devices, preventing fluctuations that can cause damage or data loss. Many electronic components, such as microprocessors and LED lights, operate more efficiently and reliably on DC power due to its unidirectional current flow. Furthermore, DC power enables simpler and more compact power supply designs, reducing energy losses in circuits compared to AC power conversion.
Benefits of AC Power in Electronic Applications
AC power offers superior efficiency in electronic applications due to its ability to easily transform voltage levels using transformers, reducing energy loss during transmission. This flexibility enables precise voltage regulation crucial for sensitive electronic devices and large-scale power distribution systems. AC's sinusoidal waveform also improves the performance of electric motors and transformers, enhancing overall system reliability and longevity.
Common Uses of DC Power in Electronics
DC power is essential in electronics for powering devices such as smartphones, laptops, and LED lighting, where a stable and consistent voltage is required. It is commonly used in battery-operated equipment, electronic circuits, and semiconductor devices due to its ability to provide a steady current flow. DC power also plays a critical role in powering microcontrollers, sensors, and digital electronics that demand precise voltage control.
Typical Applications of AC Power in Electronics
AC power is predominantly used in household appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and lighting systems due to its efficient transmission over long distances and compatibility with transformers. Most electronic devices requiring wall power, including computers and televisions, utilize AC power that is converted to DC internally. Industrial equipment like motors and HVAC systems also rely on AC power for its ability to easily change voltage levels and maintain consistent operation.
Efficiency Comparison: DC Power vs AC Power
DC power systems offer higher efficiency in low-voltage applications due to minimal energy loss during transmission and simpler conversion processes. AC power efficiency excels in long-distance distribution because transformers enable voltage regulation that reduces energy dissipation. Overall, the choice between DC and AC power efficiency depends on application scale, voltage level, and infrastructure design.
Safety Considerations for DC and AC Power
DC power systems often pose higher risks of electrical shock due to sustained current flow, requiring stringent insulation and protection measures. AC power, while oscillating, can cause muscle contractions that may prevent release from the source, necessitating circuit breakers and grounding for safety. Proper safety devices and protocols tailored to the distinct characteristics of DC and AC currents are critical to minimize electric shock hazards and equipment damage.
Cost Implications: DC Power vs AC Power
DC power systems often incur higher initial costs due to specialized components and converters required for voltage regulation and storage. AC power infrastructure benefits from widespread standardization and lower equipment expenses, reducing upfront installation costs. Long-term operational expenses for DC can be lower in certain applications like renewable energy systems, where energy efficiency and reduced conversion losses offset initial investments.
Choosing the Right Power Type for Your Electronic Products
DC power provides a stable voltage ideal for sensitive electronic devices such as laptops, smartphones, and LED lights, ensuring consistent performance and longer lifespan. AC power is commonly used for household appliances and industrial equipment due to its efficient transmission over long distances and compatibility with transformers. Selecting between DC and AC power depends on factors like device power requirements, efficiency, conversion needs, and the operational environment of the electronic product.
DC Power vs AC Power Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com