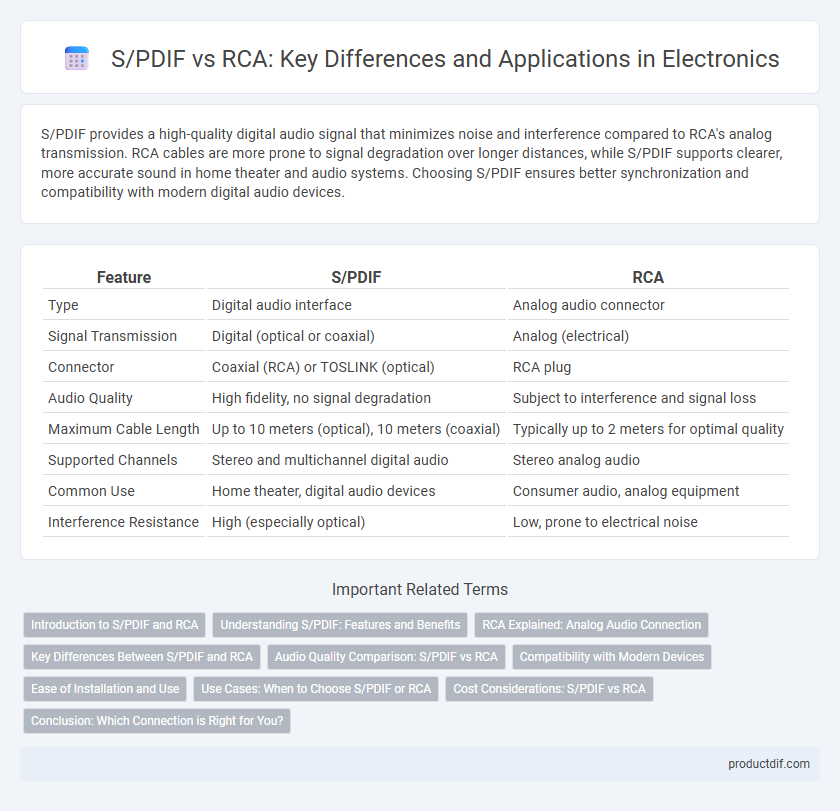
S/PDIF provides a high-quality digital audio signal that minimizes noise and interference compared to RCA's analog transmission. RCA cables are more prone to signal degradation over longer distances, while S/PDIF supports clearer, more accurate sound in home theater and audio systems. Choosing S/PDIF ensures better synchronization and compatibility with modern digital audio devices.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | S/PDIF | RCA |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Digital audio interface | Analog audio connector |
| Signal Transmission | Digital (optical or coaxial) | Analog (electrical) |
| Connector | Coaxial (RCA) or TOSLINK (optical) | RCA plug |
| Audio Quality | High fidelity, no signal degradation | Subject to interference and signal loss |
| Maximum Cable Length | Up to 10 meters (optical), 10 meters (coaxial) | Typically up to 2 meters for optimal quality |
| Supported Channels | Stereo and multichannel digital audio | Stereo analog audio |
| Common Use | Home theater, digital audio devices | Consumer audio, analog equipment |
| Interference Resistance | High (especially optical) | Low, prone to electrical noise |
Introduction to S/PDIF and RCA
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) is a digital audio interface used to transmit high-quality audio signals without analog conversion, commonly employed in home theater systems and professional audio equipment. RCA connectors, typically color-coded red and white, are analog audio interfaces that carry stereo signals and are widely found in consumer audio devices such as DVD players and amplifiers. While RCA transmits analog signals prone to noise and degradation, S/PDIF provides clear digital audio transmission via coaxial or optical cables, preserving sound fidelity across connections.
Understanding S/PDIF: Features and Benefits
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface Format) delivers high-quality digital audio transmission, reducing signal degradation compared to analog RCA connections. It supports stereo and multichannel audio formats with reduced electrical interference thanks to its optical or coaxial cabling. This digital interface ensures clearer sound reproduction, essential for home theater systems and professional audio equipment requiring precise audio fidelity.
RCA Explained: Analog Audio Connection
RCA connectors transmit analog audio signals through distinct left and right channels, providing a simple and widely compatible method for connecting audio devices. Unlike S/PDIF, which carries digital audio data, RCA cables rely on electrical voltage variations to produce sound, making them ideal for vintage and consumer audio equipment. Their analog nature results in signal degradation over long distances, but they remain a staple in home audio systems due to their ease of use and universal presence.
Key Differences Between S/PDIF and RCA
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) transmits digital audio signals using coaxial or optical cables, ensuring minimal signal degradation and supporting multi-channel audio formats like Dolby Digital and DTS. RCA connectors, typically used for analog audio, transmit unbalanced signals prone to noise and interference, limiting audio fidelity compared to digital transmission. The key differences lie in S/PDIF's digital precision and format versatility versus RCA's analog simplicity and vulnerability to signal loss.
Audio Quality Comparison: S/PDIF vs RCA
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) transmits audio signals in a digital format, preserving sound fidelity by minimizing interference and noise compared to analog RCA connections, which convert signals into voltage variations prone to degradation. High-resolution audio formats benefit significantly from S/PDIF's digital transmission, offering clearer sound reproduction with reduced jitter and distortion. RCA cables, while widely compatible and cost-effective, exhibit limitations in bandwidth and susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, impacting overall audio quality.
Compatibility with Modern Devices
S/PDIF interfaces, available in both optical and coaxial forms, provide high-quality digital audio connections compatible with most modern AV receivers, soundbars, and gaming consoles supporting digital audio inputs. RCA connectors, primarily analog, remain widely used for older or entry-level audio and video equipment but often require adapters to connect with newer devices lacking analog inputs. Modern electronics increasingly favor S/PDIF due to its ability to maintain audio fidelity and compatibility with high-resolution audio formats across contemporary home theater and audio systems.
Ease of Installation and Use
S/PDIF connections offer straightforward digital audio transmission with simple plug-and-play setup, minimizing signal degradation common in analog RCA cables. RCA connectors provide versatile compatibility with a wide range of audio devices but may require careful cable management and calibration for optimal analog sound quality. Users seeking hassle-free installation often prefer S/PDIF for its clear digital signal and simplified interface.
Use Cases: When to Choose S/PDIF or RCA
S/PDIF is ideal for digital audio connections requiring high fidelity and minimal interference, commonly used in home theater systems, digital audio interfaces, and high-end sound equipment. RCA cables suit analog audio transmission, perfect for older devices like vintage amplifiers, turntables, and consumer electronics without digital outputs. Choose S/PDIF for superior sound quality and compatibility with modern digital devices, while RCA remains practical for simplicity and legacy analog setups.
Cost Considerations: S/PDIF vs RCA
S/PDIF connectors typically incur higher costs due to their need for specialized optical or coaxial cables and digital-to-analog conversion equipment, which increases overall system expenses. RCA connectors, widely available and simpler in design, offer a budget-friendly analog audio solution with lower cable costs and easier integration into existing setups. When prioritizing cost-effectiveness, RCA remains the more economical choice for analog audio transmission, while S/PDIF caters to higher-quality digital connections with a premium price point.
Conclusion: Which Connection is Right for You?
Choosing between S/PDIF and RCA connections depends on your audio setup and quality preferences. S/PDIF, whether optical or coaxial, provides superior digital audio transfer with minimal interference, ideal for high-fidelity systems and surround sound configurations. RCA connections, offering analog signals, are simpler and more compatible with older or basic audio equipment but may introduce signal degradation compared to digital alternatives.
S/PDIF vs RCA Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com