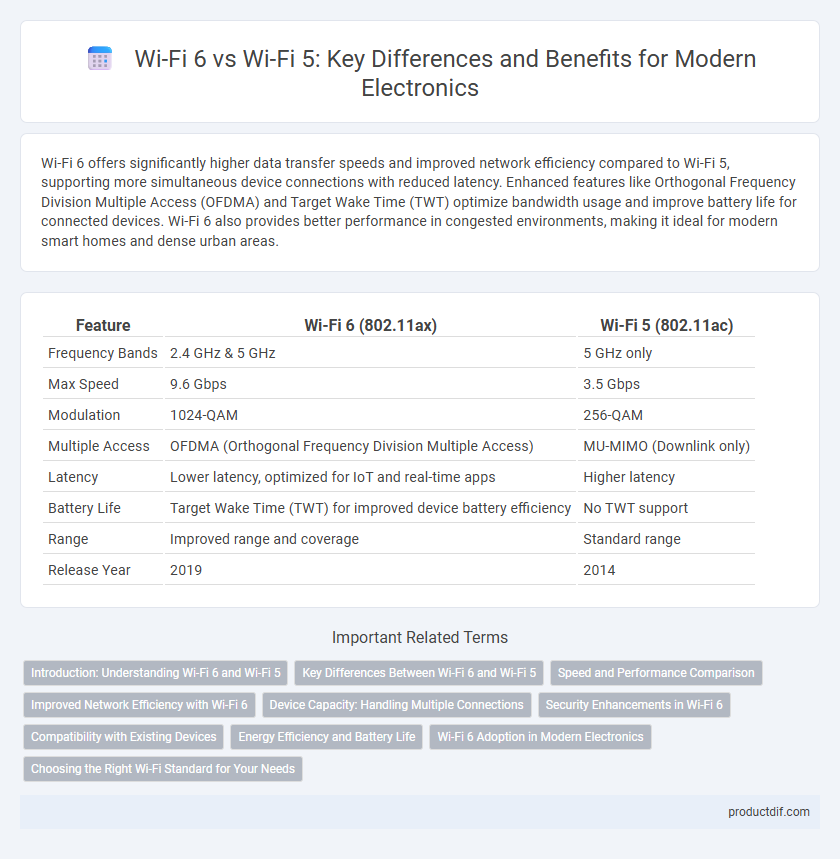
Wi-Fi 6 offers significantly higher data transfer speeds and improved network efficiency compared to Wi-Fi 5, supporting more simultaneous device connections with reduced latency. Enhanced features like Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Target Wake Time (TWT) optimize bandwidth usage and improve battery life for connected devices. Wi-Fi 6 also provides better performance in congested environments, making it ideal for modern smart homes and dense urban areas.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) | Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Bands | 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz | 5 GHz only |
| Max Speed | 9.6 Gbps | 3.5 Gbps |
| Modulation | 1024-QAM | 256-QAM |
| Multiple Access | OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) | MU-MIMO (Downlink only) |
| Latency | Lower latency, optimized for IoT and real-time apps | Higher latency |
| Battery Life | Target Wake Time (TWT) for improved device battery efficiency | No TWT support |
| Range | Improved range and coverage | Standard range |
| Release Year | 2019 | 2014 |
Introduction: Understanding Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 5
Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax, is the latest wireless networking standard designed to improve speed, capacity, and performance in congested environments compared to Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac). Wi-Fi 6 introduces technologies like OFDMA, MU-MIMO enhancements, and Target Wake Time to optimize data transfer and reduce latency across multiple devices. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right Wi-Fi standard for modern smart homes, offices, and high-density scenarios.
Key Differences Between Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 5
Wi-Fi 6 offers significantly higher speeds up to 9.6 Gbps compared to Wi-Fi 5's 3.5 Gbps, improving overall network efficiency in congested environments. It incorporates Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) technology, enhancing simultaneous data transmission for multiple devices and reducing latency. Additionally, Wi-Fi 6 features improved power management with Target Wake Time (TWT), optimizing battery life for connected Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Speed and Performance Comparison
Wi-Fi 6 offers significantly faster speeds than Wi-Fi 5, with a maximum theoretical throughput of 9.6 Gbps compared to Wi-Fi 5's 3.5 Gbps, enabling enhanced performance for high-bandwidth applications. The introduction of OFDMA and improved MU-MIMO in Wi-Fi 6 increases efficiency and reduces latency in dense networks, resulting in smoother connectivity and better overall user experience. These advancements make Wi-Fi 6 ideal for environments with multiple connected devices requiring simultaneous high-speed data transmission.
Improved Network Efficiency with Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 significantly enhances network efficiency through advanced technologies like Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Target Wake Time (TWT), enabling simultaneous data transmission to multiple devices and reducing latency. These improvements allow for better management of bandwidth in dense environments, supporting higher device capacity and minimizing network congestion. Enhanced modulation schemes such as 1024-QAM further increase throughput, making Wi-Fi 6 ideal for high-demand applications and IoT ecosystems.
Device Capacity: Handling Multiple Connections
Wi-Fi 6 significantly outperforms Wi-Fi 5 in device capacity, efficiently supporting up to four times more simultaneous connections. This improvement is enabled by Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO) technologies, which optimize bandwidth allocation per device. Enhanced capacity reduces latency and ensures reliable performance in dense environments like smart homes and crowded public spaces.
Security Enhancements in Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 introduces Enhanced Open and WPA3 security protocols, offering superior encryption and stronger protection against cyber threats compared to Wi-Fi 5's WPA2 standard. The implementation of individualized encryption on open networks and improved password-based authentication significantly mitigates risks of data interception and unauthorized access. These advancements make Wi-Fi 6 a more secure choice for modern wireless communication in both personal and enterprise environments.
Compatibility with Existing Devices
Wi-Fi 6 maintains backward compatibility with Wi-Fi 5 and earlier standards, ensuring seamless connectivity with existing devices. This compatibility allows users to gradually upgrade their network hardware without requiring simultaneous updates to all connected gadgets. Enhanced efficiency in Wi-Fi 6 also optimizes performance in mixed-device environments, improving overall network stability and speed.
Energy Efficiency and Battery Life
Wi-Fi 6 offers significant improvements in energy efficiency compared to Wi-Fi 5 by utilizing Target Wake Time (TWT) technology, which schedules communication times to reduce device power consumption. This results in longer battery life for smartphones, laptops, and IoT devices operating on Wi-Fi 6 networks. Enhanced power management features in Wi-Fi 6 reduce unnecessary transmissions, making it ideal for energy-conscious applications and extended device usage.
Wi-Fi 6 Adoption in Modern Electronics
Wi-Fi 6 adoption in modern electronics significantly enhances network efficiency, offering up to 40% faster speeds and improved capacity for connected devices compared to Wi-Fi 5. Advanced technologies like Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Target Wake Time (TWT) enable better device communication and lower latency in smart homes, IoT devices, and smartphones. Leading manufacturers increasingly integrate Wi-Fi 6 in laptops, routers, and gaming consoles to meet the rising demand for reliable, high-performance wireless connectivity.
Choosing the Right Wi-Fi Standard for Your Needs
Wi-Fi 6 offers higher data rates up to 9.6 Gbps, improved capacity, and better performance in crowded environments compared to Wi-Fi 5's maximum speed of 3.5 Gbps. Devices requiring low latency and greater network efficiency, such as smart home systems and gaming consoles, benefit most from Wi-Fi 6 technology. Selecting the right Wi-Fi standard depends on factors like device compatibility, network congestion, and the need for advanced features such as OFDMA and target wake time supported by Wi-Fi 6.
Wi-Fi 6 vs Wi-Fi 5 Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com