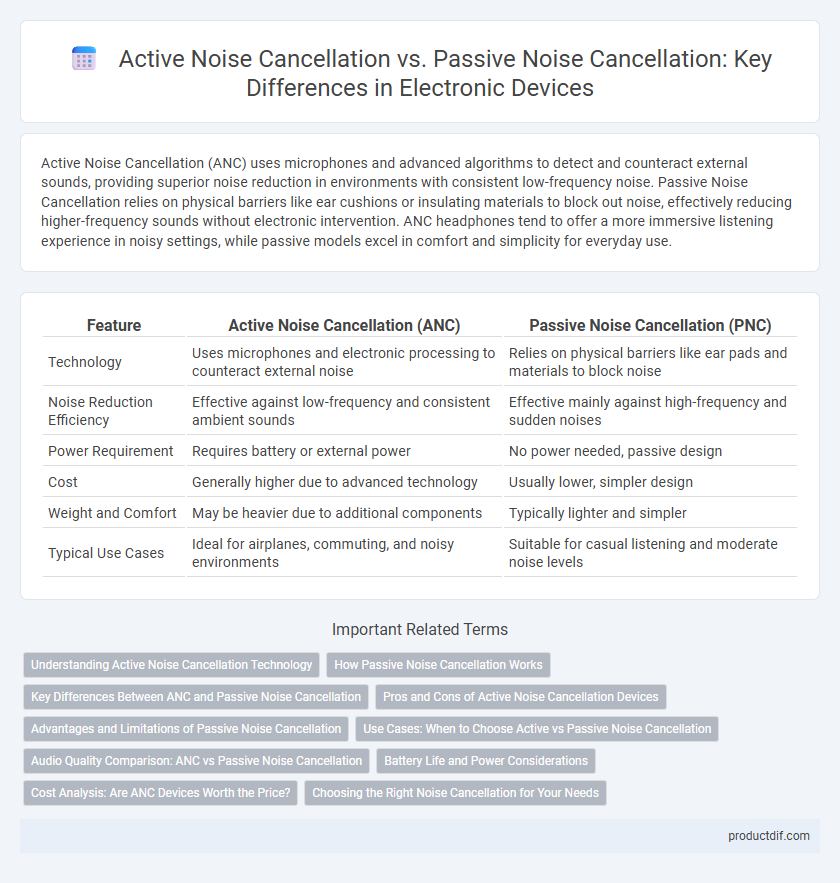
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) uses microphones and advanced algorithms to detect and counteract external sounds, providing superior noise reduction in environments with consistent low-frequency noise. Passive Noise Cancellation relies on physical barriers like ear cushions or insulating materials to block out noise, effectively reducing higher-frequency sounds without electronic intervention. ANC headphones tend to offer a more immersive listening experience in noisy settings, while passive models excel in comfort and simplicity for everyday use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) | Passive Noise Cancellation (PNC) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Uses microphones and electronic processing to counteract external noise | Relies on physical barriers like ear pads and materials to block noise |
| Noise Reduction Efficiency | Effective against low-frequency and consistent ambient sounds | Effective mainly against high-frequency and sudden noises |
| Power Requirement | Requires battery or external power | No power needed, passive design |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced technology | Usually lower, simpler design |
| Weight and Comfort | May be heavier due to additional components | Typically lighter and simpler |
| Typical Use Cases | Ideal for airplanes, commuting, and noisy environments | Suitable for casual listening and moderate noise levels |
Understanding Active Noise Cancellation Technology
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) technology uses microphones and advanced signal processing algorithms to detect and produce sound waves that cancel out ambient noise, significantly reducing unwanted background sounds. Unlike Passive Noise Cancellation, which relies on physical barriers like ear pads and insulation to block noise, ANC actively targets low-frequency sounds for enhanced auditory clarity. This technology is prevalent in headphones and earbuds, offering improved listening experiences in noisy environments such as airplanes and urban settings.
How Passive Noise Cancellation Works
Passive noise cancellation works by physically blocking external sound waves through materials like foam, rubber, or thick padding integrated into headphones or earplugs. These materials absorb and dampen ambient noise, reducing the amount of sound that reaches the ear without requiring any electronic components or power source. This method is effective against higher-frequency sounds but is less efficient at filtering low-frequency noises compared to active noise cancellation technology.
Key Differences Between ANC and Passive Noise Cancellation
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) uses built-in microphones and electronic processing to detect and counteract external sounds with inverse sound waves, effectively reducing low-frequency noise. Passive Noise Cancellation relies on physical barriers such as ear cup padding and seal design to block out external noise, primarily targeting higher-frequency sounds. ANC delivers superior noise reduction in environments with consistent, low-frequency sounds like airplane engines, while passive methods excel in isolating ambient noise without the need for power or electronics.
Pros and Cons of Active Noise Cancellation Devices
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) devices use microphones and speakers to generate sound waves that cancel out ambient noise, significantly improving audio clarity in noisy environments such as airplanes or urban streets. Pros of ANC include enhanced sound quality, reduced listening fatigue, and the ability to customize noise reduction levels, but cons involve higher cost, increased battery consumption, and occasional sound distortion or pressure sensation for sensitive users. ANC technology is most effective against consistent, low-frequency sounds, whereas it may struggle with sudden, high-frequency noises compared to Passive Noise Cancellation.
Advantages and Limitations of Passive Noise Cancellation
Passive Noise Cancellation offers the advantage of blocking ambient sounds through physical barriers like thick ear cups and snug-fitting ear tips, providing uninterrupted audio without the need for batteries or electronic components. It effectively reduces high-frequency noise but has limitations in attenuating low-frequency sounds such as engine hum or traffic noise. Passive noise isolation performance often depends on the quality of materials and ear seal, making it less versatile compared to Active Noise Cancellation in noisy environments.
Use Cases: When to Choose Active vs Passive Noise Cancellation
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) is ideal for environments with consistent, low-frequency noise such as airplane cabins or busy offices, offering superior sound isolation through electronic noise reduction technology. Passive Noise Cancellation excels in settings with sudden, high-frequency sounds like city traffic or public transportation, relying on physical barriers such as ear cup design and materials to block external noise. For commuting or casual listening, passive noise cancellation provides a lightweight, battery-free solution, while ANC is preferable for immersive audio experiences during long flights or work-from-home setups requiring concentration.
Audio Quality Comparison: ANC vs Passive Noise Cancellation
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) enhances audio quality by electronically reducing ambient noise, allowing for clearer sound at lower volumes compared to Passive Noise Cancellation, which relies solely on physical barriers like ear pads or materials to block external sounds. ANC provides a more immersive listening experience by minimizing low-frequency background noise, whereas Passive Noise Cancellation is more effective against higher-frequency sounds but may not eliminate consistent hums or engine noise. The effectiveness of ANC depends on the quality of the microphones and signal processing algorithms, while Passive Noise Cancellation benefits from dense, well-sealed materials that improve comfort and sound isolation.
Battery Life and Power Considerations
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) technology consumes significantly more battery power due to its need for microphones, processors, and amplifiers to analyze and counteract ambient noise in real-time, often reducing battery life by 20-30% compared to non-ANC modes. Passive Noise Cancellation relies on physical barriers such as earcup design and padding to block sound, requiring no electrical power and thus preserving battery life entirely. When prioritizing extended battery life in wireless headphones or earbuds, passive noise cancellation proves more energy-efficient, while ANC demands frequent recharging but offers superior noise reduction in noisy environments.
Cost Analysis: Are ANC Devices Worth the Price?
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) devices typically cost significantly more than passive noise cancellation headphones due to advanced technology and additional components such as microphones and processors. While ANC headphones offer superior noise reduction in dynamic environments, passive models provide effective isolation at a fraction of the price, relying on physical barriers like padded ear cups. Evaluating cost versus benefit depends on usage patterns; frequent travelers or office workers in noisy spaces may find ANC investment justified, whereas casual listeners may prefer the affordability and simplicity of passive options.
Choosing the Right Noise Cancellation for Your Needs
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) uses microphones and advanced electronics to reduce ambient sounds by producing inverse sound waves, ideal for environments with consistent low-frequency noise like airplanes or public transport. Passive Noise Cancellation relies on physical barriers, such as ear padding and insulation, to block external sound and is effective for high-frequency noise in quieter settings or short listening sessions. Selecting the right noise cancellation depends on your typical environment, noise frequency, and budget, with ANC providing superior performance in noisy spaces and passive offering simplicity and no battery dependency.
Active Noise Cancellation vs Passive Noise Cancellation Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com