Thunderbolt 4 builds on Thunderbolt 3 by offering improved minimum performance requirements, including support for dual 4K displays or one 8K display and mandatory PCIe data transfer speeds of 32Gbps, twice that of Thunderbolt 3. Thunderbolt 4 also enhances security with Intel VT-d-based DMA protection and provides a more consistent user experience with universal cables up to 2 meters without signal degradation. While Thunderbolt 3 remains widely capable, Thunderbolt 4 delivers greater reliability and future-proofing for advanced electronics and peripherals.
Table of Comparison
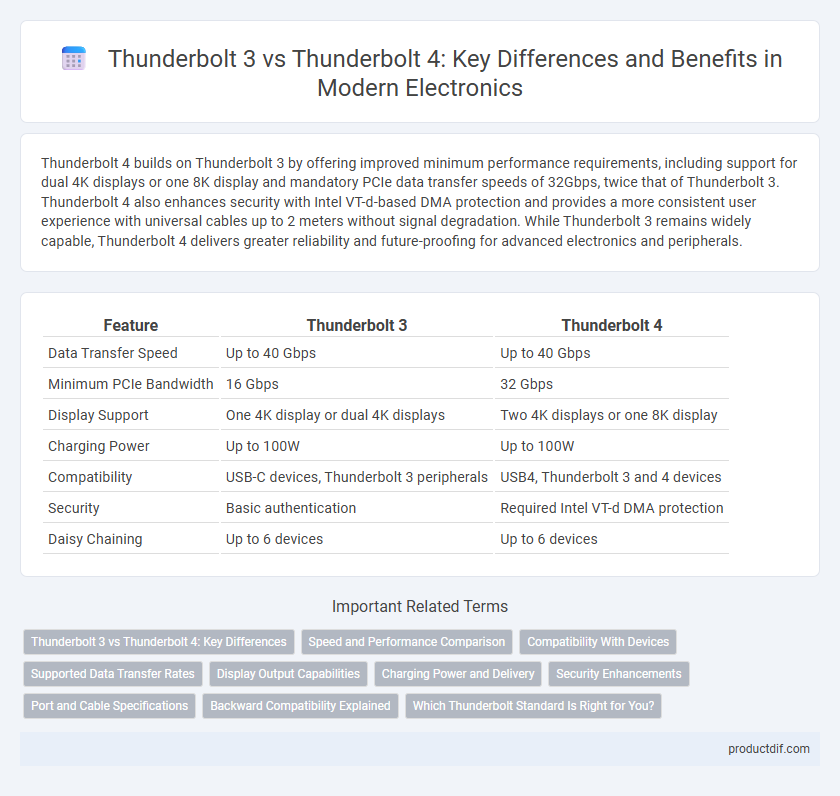
| Feature | Thunderbolt 3 | Thunderbolt 4 |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 40 Gbps | Up to 40 Gbps |
| Minimum PCIe Bandwidth | 16 Gbps | 32 Gbps |
| Display Support | One 4K display or dual 4K displays | Two 4K displays or one 8K display |
| Charging Power | Up to 100W | Up to 100W |
| Compatibility | USB-C devices, Thunderbolt 3 peripherals | USB4, Thunderbolt 3 and 4 devices |
| Security | Basic authentication | Required Intel VT-d DMA protection |
| Daisy Chaining | Up to 6 devices | Up to 6 devices |
Thunderbolt 3 vs Thunderbolt 4: Key Differences
Thunderbolt 4 offers improved minimum performance requirements compared to Thunderbolt 3, including support for dual 4K displays or a single 8K display and mandatory PCIe data transfer speeds of 32 Gbps. Unlike Thunderbolt 3, Thunderbolt 4 guarantees USB4 compatibility, enhanced security with Intel VT-d based DMA protection, and requires cables up to 2 meters that support full 40 Gbps speeds. Power delivery remains at 100W for both, but Thunderbolt 4 enforces stricter certification standards ensuring wider device compatibility and connectivity reliability.
Speed and Performance Comparison
Thunderbolt 3 supports data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps with PCIe bandwidth of 32 Gbps, enabling fast file transfers and seamless 4K video streaming. Thunderbolt 4 maintains the same 40 Gbps speed but improves minimum PCIe data rate to 32 Gbps for consistent performance across devices, enhancing reliability and support for dual 4K displays or a single 8K display. Thunderbolt 4 also features stricter certification requirements, ensuring faster wake-from-sleep times and better overall device compatibility compared to Thunderbolt 3.
Compatibility With Devices
Thunderbolt 4 ensures full compatibility with all Thunderbolt 3 devices, offering universal support for docks, displays, and peripherals without performance limitations. It mandates support for dual 4K displays and PCIe data transfer speeds up to 32 Gbps, which Thunderbolt 3 supports only partially depending on the device. Thunderbolt 4 also expands compatibility by requiring USB4 support, enhancing interoperability with a wider range of USB-C devices.
Supported Data Transfer Rates
Thunderbolt 4 maintains the same maximum data transfer rate of 40 Gbps as Thunderbolt 3, ensuring high-speed connectivity for data-intensive tasks. Both standards support PCIe data transfer speeds up to 32 Gbps, but Thunderbolt 4 requires support for dual 4K displays or one 8K display, enhancing its overall bandwidth utilization. The primary difference lies in Thunderbolt 4's improved minimum performance requirements rather than a higher raw transfer rate.
Display Output Capabilities
Thunderbolt 4 supports dual 4K displays or a single 8K display, while Thunderbolt 3 typically supports a single 4K display or dual 4K at lower refresh rates. Thunderbolt 4 ensures minimum display requirements, offering more consistent multi-display performance and greater compatibility with advanced monitors. Both standards use the USB-C connector, but Thunderbolt 4 enhances video output capabilities for professional and high-resolution setups.
Charging Power and Delivery
Thunderbolt 3 supports power delivery up to 100 watts, enabling fast charging for laptops and other devices through a single USB-C cable. Thunderbolt 4 maintains the same maximum charging power of 100 watts but enforces stricter minimum power delivery requirements to ensure consistent charging performance across compatible devices. Both standards utilize USB Power Delivery protocols, but Thunderbolt 4 guarantees compliance for improved compatibility and charging reliability.
Security Enhancements
Thunderbolt 4 introduces advanced security features such as Intel VT-d-based DMA protection to prevent direct memory access attacks, enhancing system defense compared to Thunderbolt 3. The incorporation of stricter authorization requirements and mandatory Intel hardware DMA protection significantly reduces vulnerabilities exploited by malicious devices. These enhancements ensure a more secure data transfer environment, making Thunderbolt 4 the preferred choice for users prioritizing robust threat mitigation in high-speed connectivity.
Port and Cable Specifications
Thunderbolt 4 maintains the same port design as Thunderbolt 3, using the USB-C connector, ensuring full compatibility with existing devices. Thunderbolt 4 cables must support 40Gbps data transfer, USB4, and PCIe at 32Gbps, while Thunderbolt 3 cables vary in capabilities and can be passive or active with different performance levels. The stricter cable specifications of Thunderbolt 4 guarantee consistent high-speed performance and support for dual 4K displays or a single 8K display.
Backward Compatibility Explained
Thunderbolt 4 maintains full backward compatibility with Thunderbolt 3, USB-C, and previous Thunderbolt versions, ensuring seamless connection with older devices and peripherals. It supports the same USB4 specification, providing enhanced data transfer speeds of up to 40 Gbps and improved video output capabilities while preserving older protocols. This backward compatibility guarantees users can upgrade to Thunderbolt 4 without losing functionality with existing Thunderbolt 3 accessories and cables.
Which Thunderbolt Standard Is Right for You?
Thunderbolt 4 offers improved minimum performance requirements over Thunderbolt 3, including support for dual 4K displays or a single 8K display, 32 Gbps PCIe data transfer, and enhanced security features like VT-d DMA protection. Thunderbolt 3 supports up to 40 Gbps data transfer and a single 4K display but lacks some of Thunderbolt 4's stricter certification guarantees and mandatory features. Choose Thunderbolt 4 for guaranteed performance, better multitasking capabilities, and future-proof connectivity, while Thunderbolt 3 remains suitable for users with less demanding display and data transfer needs.
Thunderbolt 3 vs Thunderbolt 4 Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com