5G offers extensive coverage and higher mobility, making it ideal for outdoor and large-scale deployments, while Wi-Fi 6 excels in providing fast, reliable connections within localized environments such as homes or offices. Both technologies leverage advanced antenna configurations and optimized spectrum efficiency to deliver enhanced speeds and reduced latency. Choosing between 5G and Wi-Fi 6 depends on specific use cases, with 5G prioritizing broad network access and Wi-Fi 6 focusing on dense device connectivity indoors.
Table of Comparison
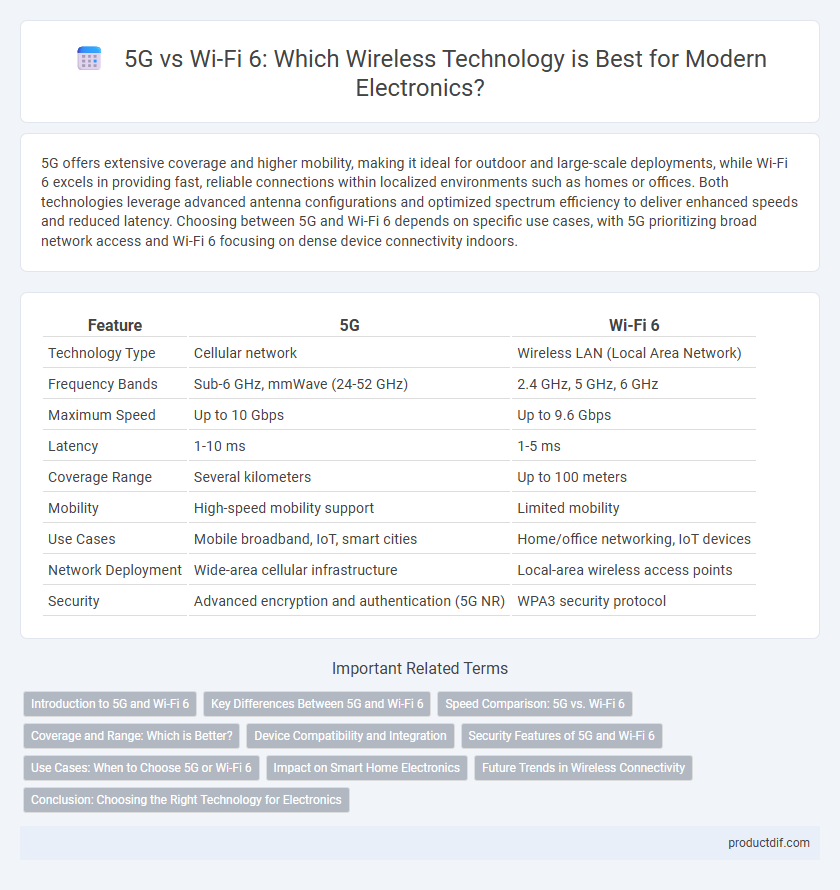
| Feature | 5G | Wi-Fi 6 |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Type | Cellular network | Wireless LAN (Local Area Network) |
| Frequency Bands | Sub-6 GHz, mmWave (24-52 GHz) | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz |
| Maximum Speed | Up to 10 Gbps | Up to 9.6 Gbps |
| Latency | 1-10 ms | 1-5 ms |
| Coverage Range | Several kilometers | Up to 100 meters |
| Mobility | High-speed mobility support | Limited mobility |
| Use Cases | Mobile broadband, IoT, smart cities | Home/office networking, IoT devices |
| Network Deployment | Wide-area cellular infrastructure | Local-area wireless access points |
| Security | Advanced encryption and authentication (5G NR) | WPA3 security protocol |
Introduction to 5G and Wi-Fi 6
5G technology offers ultra-fast mobile internet with enhanced bandwidth, low latency, and massive device connectivity, targeting widespread adoption across smart cities and IoT applications. Wi-Fi 6, or 802.11ax, enhances wireless local area networks by improving speed, capacity, and efficiency in dense environments like offices and homes. Both technologies complement each other by addressing different connectivity needs: 5G for wide-area mobile access and Wi-Fi 6 for localized, high-performance wireless networking.
Key Differences Between 5G and Wi-Fi 6
5G offers broader coverage and higher mobility with speeds up to 10 Gbps, making it ideal for outdoor and large-scale wireless connectivity, while Wi-Fi 6 provides ultra-fast local network speeds of up to 9.6 Gbps with lower latency, optimized for indoor environments and dense device networks. 5G operates on licensed cellular spectrum bands, ensuring reliable mobile connectivity, whereas Wi-Fi 6 uses unlicensed spectrum, primarily the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, with support for the new 6 GHz band in Wi-Fi 6E. Energy efficiency and enhanced capacity are featured in both technologies, but 5G targets IoT scalability and broad network infrastructure, while Wi-Fi 6 focuses on improving wireless performance for local-area networks and smart home devices.
Speed Comparison: 5G vs. Wi-Fi 6
5G technology offers peak speeds up to 10 Gbps, significantly enhancing mobile connectivity and enabling ultra-fast downloads and low latency. Wi-Fi 6 delivers maximum speeds around 9.6 Gbps, optimized for dense environments and multiple device connections within localized networks. While both support high-speed data transmission, 5G excels in broader coverage and mobility, whereas Wi-Fi 6 provides superior performance in controlled, indoor scenarios.
Coverage and Range: Which is Better?
5G offers significantly broader coverage and longer range compared to Wi-Fi 6, as it operates on licensed cellular bands designed for wide-area connectivity. Wi-Fi 6 provides high-speed, low-latency connections but is limited to short-range coverage within buildings or small outdoor areas. For extensive outdoor or mobile use, 5G excels, while Wi-Fi 6 is optimal for localized high-performance networking.
Device Compatibility and Integration
5G offers broader network coverage and is natively supported by many modern smartphones and IoT devices, ensuring seamless mobility and consistent connectivity across wide areas. Wi-Fi 6, optimized for local network environments, excels in high-density settings like offices and homes, with compatibility primarily reliant on device hardware and router support. Integrating both technologies enhances device ecosystem performance, leveraging 5G for outdoor and wide-area connectivity and Wi-Fi 6 for faster speeds and lower latency within localized networks.
Security Features of 5G and Wi-Fi 6
5G enhances security by incorporating end-to-end encryption, improved subscriber identity protection, and robust network slicing capabilities, making it highly resilient to cyber threats in mobile environments. Wi-Fi 6 introduces WPA3 encryption, individualized data encryption, and enhanced authentication protocols, which significantly improve security in local wireless networks. Both technologies prioritize data integrity and confidentiality, but 5G's architecture provides stronger protection for large-scale, mobile broadband applications.
Use Cases: When to Choose 5G or Wi-Fi 6
5G excels in wide-area mobile connectivity, making it ideal for autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and remote healthcare applications requiring seamless, high-speed internet on the move. Wi-Fi 6 is suited for high-density indoor environments like offices, stadiums, and airports, offering low latency and enhanced capacity for numerous connected devices within a confined space. Choosing between 5G and Wi-Fi 6 depends on the need for mobility and coverage versus localized, high-speed network performance.
Impact on Smart Home Electronics
5G delivers ultra-low latency and broader coverage, enabling seamless connectivity for smart home devices beyond traditional Wi-Fi boundaries. Wi-Fi 6 enhances in-home network capacity and efficiency with higher data rates and better device management, crucial for densely populated smart environments. Both technologies complement each other, with 5G supporting mobility and long-range connections while Wi-Fi 6 optimizes local network performance for smart appliances and IoT ecosystems.
Future Trends in Wireless Connectivity
5G technology is set to drive future wireless connectivity with ultra-low latency and massive device density, enabling seamless IoT integration and smart city infrastructure. Wi-Fi 6 enhances local network performance through higher data rates and improved spectral efficiency, optimizing indoor environments such as offices and homes. Emerging trends indicate a complementary relationship where 5G supports widespread outdoor coverage while Wi-Fi 6 excels in secure, high-capacity indoor networks.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Technology for Electronics
Selecting between 5G and Wi-Fi 6 depends on the use case, with 5G offering superior mobile connectivity and broader coverage for electronics in outdoor or large-area environments. Wi-Fi 6 excels in providing higher data throughput, low latency, and enhanced capacity ideal for indoor electronics like smart homes and office networks. Balancing factors such as device compatibility, network infrastructure, and specific performance needs ensures optimal technology choice for seamless electronic communication.
5G vs Wi-Fi 6 Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com