OLED displays provide superior contrast and deeper blacks compared to LED screens due to their self-emissive pixels that can turn off individually. LED panels rely on backlighting, which often results in less accurate color reproduction and potential light bleed. For users seeking vibrant visuals with improved energy efficiency and thinner designs, OLED technology offers a clear advantage over traditional LED displays.
Table of Comparison
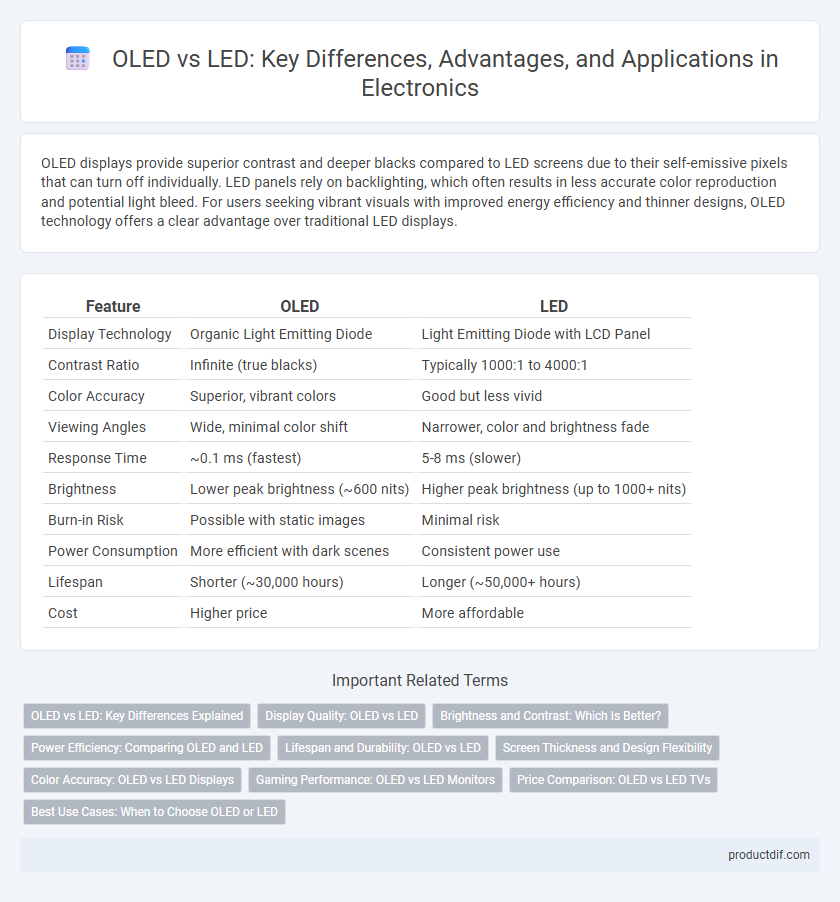
| Feature | OLED | LED |
|---|---|---|
| Display Technology | Organic Light Emitting Diode | Light Emitting Diode with LCD Panel |
| Contrast Ratio | Infinite (true blacks) | Typically 1000:1 to 4000:1 |
| Color Accuracy | Superior, vibrant colors | Good but less vivid |
| Viewing Angles | Wide, minimal color shift | Narrower, color and brightness fade |
| Response Time | ~0.1 ms (fastest) | 5-8 ms (slower) |
| Brightness | Lower peak brightness (~600 nits) | Higher peak brightness (up to 1000+ nits) |
| Burn-in Risk | Possible with static images | Minimal risk |
| Power Consumption | More efficient with dark scenes | Consistent power use |
| Lifespan | Shorter (~30,000 hours) | Longer (~50,000+ hours) |
| Cost | Higher price | More affordable |
OLED vs LED: Key Differences Explained
OLED displays use organic compounds that emit light individually, offering superior contrast ratios and deeper blacks compared to LED screens, which rely on backlit LCD panels. OLED technology provides wider viewing angles and faster response times, enhancing overall picture quality and reducing motion blur. LED displays are generally more energy-efficient and cost-effective, but OLED screens excel in color accuracy and thinness due to their self-emissive design.
Display Quality: OLED vs LED
OLED displays deliver superior contrast ratios and deeper blacks compared to LED screens due to their self-emissive pixels that can turn off individually. LED displays rely on backlighting, which limits black levels and can cause light bleed, affecting overall picture quality. Color accuracy and viewing angles are typically better in OLED technology, making it ideal for high-end visuals and immersive media experiences.
Brightness and Contrast: Which Is Better?
OLED displays deliver superior contrast due to their ability to turn off individual pixels, resulting in true blacks and infinite contrast ratios. LED screens, especially those with local dimming, can achieve high brightness levels, often surpassing OLEDs in peak luminance for HDR content. For environments requiring intense brightness, LED panels perform better, while OLED excels in delivering deep contrast and vibrant colors.
Power Efficiency: Comparing OLED and LED
OLED displays consume less power than LED screens when displaying darker images due to their ability to individually turn off pixels, resulting in significant energy savings. LED displays, however, maintain consistent power usage regardless of image content since their backlight stays on continuously. For devices prioritizing battery life during dark mode or predominantly dark content, OLED technology offers superior power efficiency compared to traditional LED backlit LCDs.
Lifespan and Durability: OLED vs LED
OLED displays typically have a shorter lifespan compared to LED screens, with organic materials prone to degradation after around 30,000 to 50,000 hours of use. LED displays boast greater durability and longer operational life, often exceeding 50,000 to 100,000 hours due to their inorganic components and robust backlighting. While OLED offers superior contrast and flexibility, LED technology remains the more reliable choice for longevity and resistance to screen burn-in.
Screen Thickness and Design Flexibility
OLED screens offer superior design flexibility with their ability to be extremely thin and bendable, allowing for innovative curved or foldable displays. LED panels, while thinner than older LCDs, require backlighting that limits how slim and flexible the screen can be. The organic layers in OLEDs enable ultra-thin profiles, making them ideal for sleek, lightweight electronics where design and portability are critical.
Color Accuracy: OLED vs LED Displays
OLED displays offer superior color accuracy compared to LED displays due to their ability to emit light from individual pixels, resulting in true blacks and vibrant colors with higher contrast ratios. LED displays rely on backlighting, which can cause light bleed and reduce color precision, especially in dark scenes. This pixel-level illumination in OLED technology enhances color fidelity and provides a more immersive viewing experience.
Gaming Performance: OLED vs LED Monitors
OLED monitors deliver superior gaming performance with faster response times and near-instant pixel activation, eliminating motion blur and ghosting for smoother gameplay. LED monitors typically exhibit higher brightness levels but suffer from slower refresh rates and input lag, impacting competitive gaming precision. The deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios of OLED displays enhance visual clarity and immersion, providing a distinct advantage in fast-paced gaming environments.
Price Comparison: OLED vs LED TVs
OLED TVs generally have a higher price point than LED TVs due to the advanced technology and manufacturing costs involved. LED TVs offer more affordable options, with a wide range of models catering to budget-conscious consumers. While OLED provides superior contrast and color accuracy, LED remains popular for its cost-effectiveness and energy efficiency.
Best Use Cases: When to Choose OLED or LED
OLED screens provide superior contrast and true black levels, making them ideal for home theaters and multimedia consumption in dim environments. LED displays excel in bright settings and are more energy-efficient, thus better suited for outdoor signage and office monitors. Choosing OLED benefits users seeking vibrant colors and wide viewing angles, whereas LED is preferred for durability and cost-effective brightness.
OLED vs LED Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com