Ground loop occurs when multiple paths to ground create unwanted current flow, causing noise in audio and video signals. Signal interference arises from external electromagnetic sources disrupting the integrity of the transmitted data. Proper grounding and shielding techniques are essential to minimize both ground loop issues and signal interference in electronic systems.
Table of Comparison
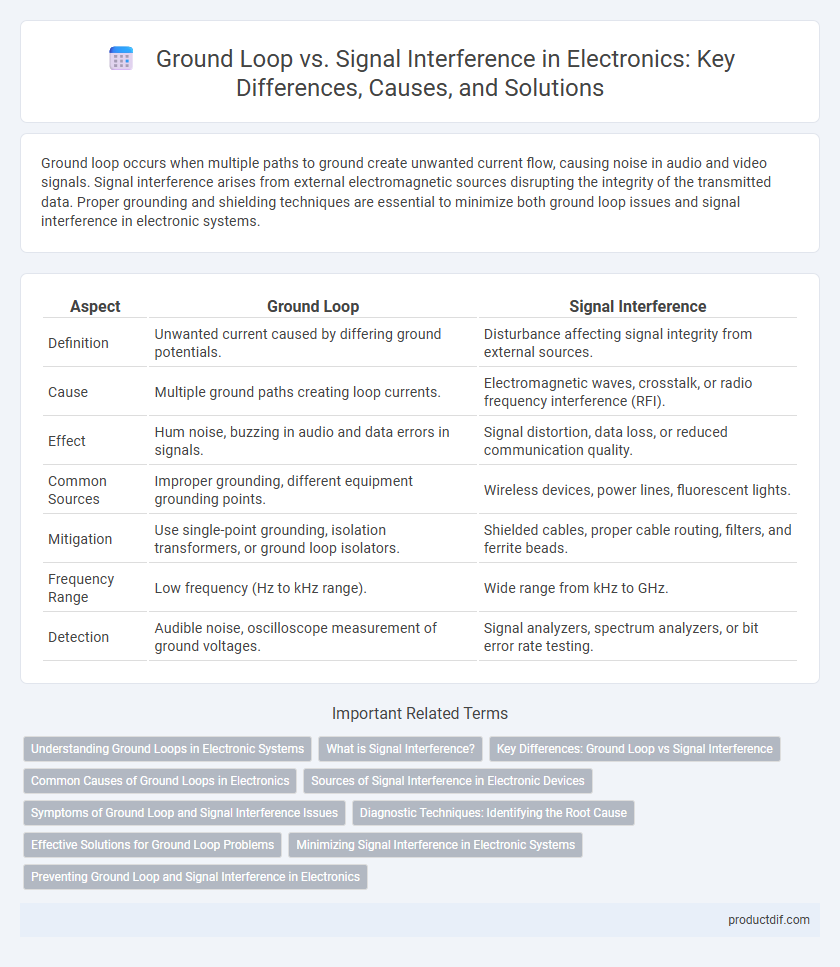
| Aspect | Ground Loop | Signal Interference |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unwanted current caused by differing ground potentials. | Disturbance affecting signal integrity from external sources. |
| Cause | Multiple ground paths creating loop currents. | Electromagnetic waves, crosstalk, or radio frequency interference (RFI). |
| Effect | Hum noise, buzzing in audio and data errors in signals. | Signal distortion, data loss, or reduced communication quality. |
| Common Sources | Improper grounding, different equipment grounding points. | Wireless devices, power lines, fluorescent lights. |
| Mitigation | Use single-point grounding, isolation transformers, or ground loop isolators. | Shielded cables, proper cable routing, filters, and ferrite beads. |
| Frequency Range | Low frequency (Hz to kHz range). | Wide range from kHz to GHz. |
| Detection | Audible noise, oscilloscope measurement of ground voltages. | Signal analyzers, spectrum analyzers, or bit error rate testing. |
Understanding Ground Loops in Electronic Systems
Ground loops occur when multiple grounding paths create a looped circuit, introducing unwanted current that generates noise in electronic systems. This phenomenon often results in hum or buzz in audio and signal interference in sensitive equipment, degrading performance and signal integrity. Effective grounding practices and isolation techniques help mitigate ground loops, ensuring clearer signal transmission and minimizing electromagnetic interference.
What is Signal Interference?
Signal interference refers to unwanted disturbances that degrade the quality of electronic signals, often caused by electromagnetic waves from nearby devices or electrical circuits. It disrupts communication signals by introducing noise, resulting in data loss, reduced clarity, or erratic device performance. Ground loops, a specific type of interference, occur when multiple ground paths create unwanted currents that contribute to signal noise in audio and video systems.
Key Differences: Ground Loop vs Signal Interference
Ground loops occur when multiple grounding paths create unintended current flow, causing hum or noise in audio and video systems, whereas signal interference results from external electromagnetic signals disrupting the desired signal transmission. Ground loops primarily affect signal quality through induced voltage differences in grounding systems, while signal interference is often caused by radio frequency interference (RFI) or electromagnetic interference (EMI) from nearby devices. Understanding the distinct origins of ground loops and signal interference is crucial for applying appropriate mitigation techniques such as proper grounding and shielding in electronic circuits.
Common Causes of Ground Loops in Electronics
Ground loops in electronics often arise due to multiple grounding points connected at different potentials, causing unwanted current flow and signal distortion. Common causes include improper grounding schemes in audio equipment, long cable runs with multiple ground references, and the use of different power sources or grounded devices interconnected in a system. These conditions create a loop where electromagnetic interference induces noise, resulting in degraded signal quality and performance issues.
Sources of Signal Interference in Electronic Devices
Ground loops occur when multiple grounding paths create unintended current flow, generating low-frequency hum in audio and video signals. Signal interference in electronic devices often originates from electromagnetic radiation emitted by nearby power lines, radio transmitters, and switching power supplies. Other common sources include poorly shielded cables, improper grounding, and proximity to high-frequency digital circuits, which induce noise and degrade signal integrity.
Symptoms of Ground Loop and Signal Interference Issues
Ground loop issues often manifest as a persistent humming or buzzing noise in audio systems, especially when multiple devices share a common grounding point. Signal interference typically causes sporadic static, signal dropouts, or distorted data transmission in electronic circuits and communication lines. Identifying these symptoms is crucial for diagnosing audio quality degradation and connectivity problems in electronic devices.
Diagnostic Techniques: Identifying the Root Cause
Diagnostic techniques for ground loop issues involve using multimeters to measure voltage differences between equipment grounds and employing spectrum analyzers to detect low-frequency hums caused by ground currents. Signal interference diagnosis requires oscilloscopes to observe waveform distortions and network analyzers to identify frequency-specific noise coupling into signal paths. Employing isolation transformers and differential probes during testing helps isolate ground loop effects from electromagnetic interference, enabling precise root cause identification.
Effective Solutions for Ground Loop Problems
Effective solutions for ground loop problems include using isolation transformers, which break the unwanted current path between interconnected equipment. Implementing balanced audio connections and maintaining a single, low-resistance grounding point reduce the potential difference causing hum and noise. Proper shielding and careful routing of cables further minimize signal interference caused by ground loops in electronic systems.
Minimizing Signal Interference in Electronic Systems
Minimizing signal interference in electronic systems involves implementing proper grounding techniques to prevent ground loops, which can introduce unwanted noise and degrade signal quality. Utilizing differential signaling and shielding cables effectively reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI), ensuring cleaner signal transmission. Maintaining consistent reference potentials and isolating sensitive circuits further enhances system immunity to external and internal interference sources.
Preventing Ground Loop and Signal Interference in Electronics
Preventing ground loop and signal interference in electronics involves proper grounding techniques, such as using a single-point ground system to eliminate unwanted current paths and minimize noise. Shielded cables and differential signaling help reduce electromagnetic interference by blocking external signals from affecting sensitive electronic components. Implementing isolation transformers and maintaining proper cable routing away from power lines also significantly decrease the risk of signal degradation and ensure optimal device performance.
Ground Loop vs Signal Interference Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com