AMOLED displays offer superior contrast ratios and deeper blacks compared to LCD screens due to their self-emissive pixels, resulting in vibrant and energy-efficient visuals. LCDs rely on backlighting, which can lead to lower contrast and less accurate color reproduction but typically provide higher brightness levels suitable for well-lit environments. Choosing between AMOLED and LCD depends on priorities like power consumption, display quality, and usage conditions.
Table of Comparison
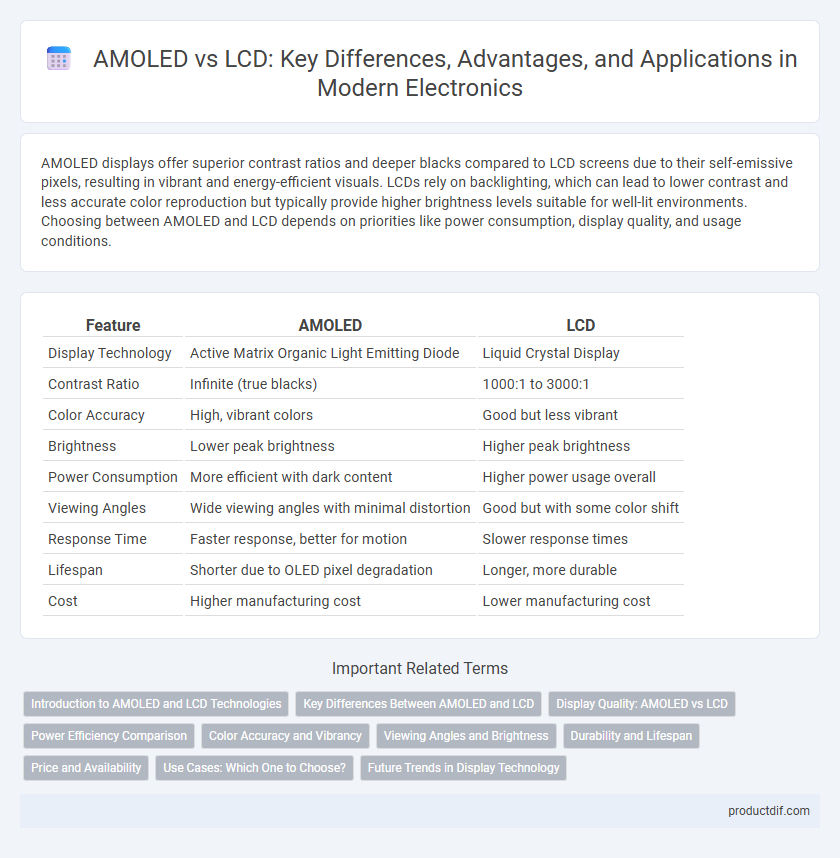
| Feature | AMOLED | LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Display Technology | Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode | Liquid Crystal Display |
| Contrast Ratio | Infinite (true blacks) | 1000:1 to 3000:1 |
| Color Accuracy | High, vibrant colors | Good but less vibrant |
| Brightness | Lower peak brightness | Higher peak brightness |
| Power Consumption | More efficient with dark content | Higher power usage overall |
| Viewing Angles | Wide viewing angles with minimal distortion | Good but with some color shift |
| Response Time | Faster response, better for motion | Slower response times |
| Lifespan | Shorter due to OLED pixel degradation | Longer, more durable |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower manufacturing cost |
Introduction to AMOLED and LCD Technologies
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) technology uses organic compounds that emit light when electric current passes through, creating self-illuminating pixels for deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios compared to LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) which relies on a backlight shining through liquid crystals to generate images. AMOLED displays typically offer faster response times and better energy efficiency, especially when displaying darker images, while LCDs generally have better brightness levels and color accuracy under direct sunlight due to their transmissive nature. The distinct manufacturing processes and underlying pixel structures of AMOLED and LCD influence their applications in smartphones, televisions, and wearable devices, driving consumer choice based on performance and visual quality requirements.
Key Differences Between AMOLED and LCD
AMOLED displays use organic light-emitting diodes that emit light individually, providing deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios compared to LCDs, which rely on a backlight for illumination. LCD screens typically consume more power due to their constant backlight, whereas AMOLED panels offer better energy efficiency, especially when displaying darker images. Color accuracy and viewing angles in AMOLED technology generally surpass LCDs, making AMOLED the preferred choice for vibrant and immersive visual experiences.
Display Quality: AMOLED vs LCD
AMOLED displays deliver superior contrast ratios and deeper blacks compared to LCD screens due to individual pixel illumination, enhancing visual clarity and color vibrancy. LCDs rely on backlighting that can cause light bleed, which reduces contrast and affects overall display sharpness. In terms of color accuracy and dynamic range, AMOLED technology generally provides richer hues and more responsive performance for high-quality visual experiences in electronic devices.
Power Efficiency Comparison
AMOLED displays consume less power than LCDs when showing dark or black images because each pixel emits its own light and can turn off completely. LCDs rely on a constant backlight, resulting in higher power consumption regardless of image brightness. Power efficiency in AMOLED screens decreases with bright, white backgrounds due to increased pixel illumination, whereas LCD power use remains relatively stable across different content.
Color Accuracy and Vibrancy
AMOLED displays offer superior color accuracy and vibrancy compared to LCDs due to their ability to emit light individually from each pixel, resulting in deeper blacks and more saturated colors. LCD panels rely on backlighting, which often causes color washout and reduced contrast, impacting overall image quality. Advances in AMOLED technology have further enhanced color gamut coverage, making them ideal for applications requiring precise color reproduction and vivid visuals.
Viewing Angles and Brightness
AMOLED displays offer superior viewing angles compared to LCDs due to their self-emissive pixel technology, which maintains consistent color and contrast at wide angles. LCDs rely on backlighting, often resulting in color shifting and brightness reduction when viewed off-axis. Furthermore, AMOLED screens typically achieve higher peak brightness levels, enhancing visibility in bright environments and improving overall display vibrancy.
Durability and Lifespan
AMOLED displays generally have a shorter lifespan compared to LCDs due to organic materials that degrade over time, causing potential burn-in and color shift. In contrast, LCD screens typically offer longer durability and resistance to screen burn-in, making them more suitable for prolonged static image use. However, advancements in AMOLED technology are improving longevity, narrowing the gap with traditional LCD durability.
Price and Availability
AMOLED displays typically cost more than LCDs due to advanced organic light-emitting diode technology, impacting their availability primarily in premium smartphones and high-end devices. LCD panels benefit from widespread manufacturing and lower production costs, making them more affordable and widely available in budget to mid-range electronics. Price sensitivity and market demand drive the preference for LCDs in cost-conscious consumer segments, while AMOLED remains favored for superior color accuracy and contrast at a premium price.
Use Cases: Which One to Choose?
AMOLED displays offer superior contrast ratios and energy efficiency, making them ideal for smartphones and wearable devices with predominantly dark user interfaces. LCD screens deliver consistent brightness and color accuracy in brightly lit environments, favoring applications like outdoor monitors and budget-friendly laptops. Choosing between AMOLED and LCD depends on prioritizing power consumption and image quality versus cost and visibility under direct sunlight.
Future Trends in Display Technology
AMOLED displays are expected to dominate future trends in display technology due to their superior color accuracy, energy efficiency, and flexibility compared to LCD panels. Innovations such as micro-LED and quantum dot enhancements aim to further improve brightness and lifespan, addressing current limitations of AMOLED. Meanwhile, LCD technology will continue evolving with mini-LED backlighting to offer better contrast and lower costs, maintaining relevance in budget-friendly devices.
AMOLED vs LCD Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com