Solid-State Drives (SSDs) offer faster data access speeds and enhanced durability compared to Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), as they use flash memory without moving parts. HDDs provide larger storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte but are more prone to mechanical failures and slower data transfer rates. Choosing between SSD and HDD depends on prioritizing speed and reliability versus storage size and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
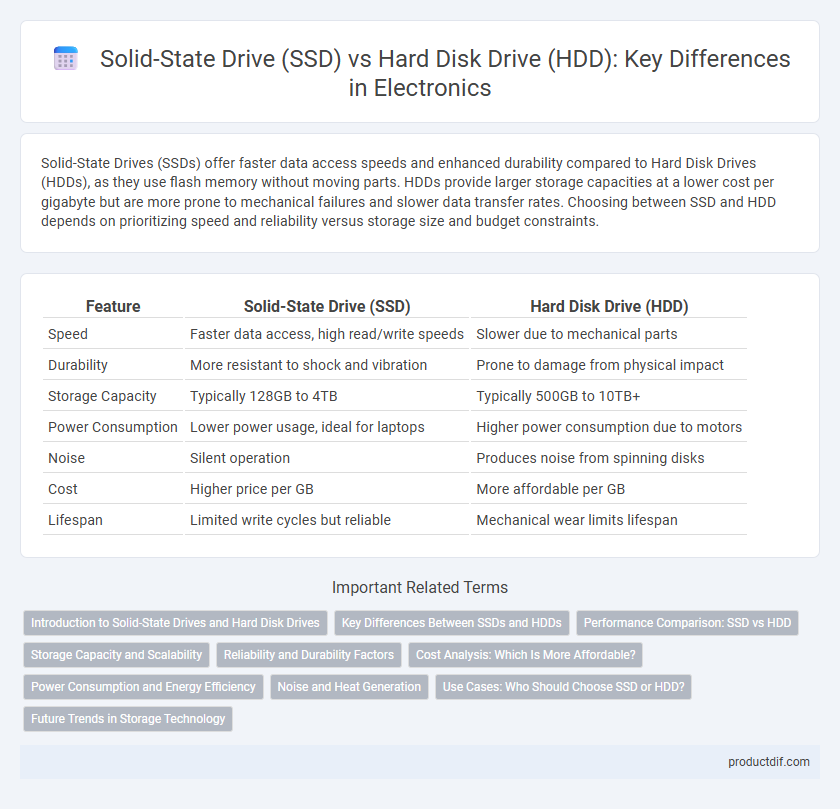
| Feature | Solid-State Drive (SSD) | Hard Disk Drive (HDD) |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Faster data access, high read/write speeds | Slower due to mechanical parts |
| Durability | More resistant to shock and vibration | Prone to damage from physical impact |
| Storage Capacity | Typically 128GB to 4TB | Typically 500GB to 10TB+ |
| Power Consumption | Lower power usage, ideal for laptops | Higher power consumption due to motors |
| Noise | Silent operation | Produces noise from spinning disks |
| Cost | Higher price per GB | More affordable per GB |
| Lifespan | Limited write cycles but reliable | Mechanical wear limits lifespan |
Introduction to Solid-State Drives and Hard Disk Drives
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) use flash memory to store data, offering faster read/write speeds and lower power consumption compared to Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), which rely on spinning magnetic platters for data storage. SSDs provide enhanced durability due to the absence of moving parts, reducing the risk of mechanical failure, while HDDs typically offer larger storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte. Both SSDs and HDDs serve essential roles in computing, with SSDs preferred for speed-sensitive applications and HDDs favored for bulk storage.
Key Differences Between SSDs and HDDs
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) offer faster data access speeds and improved durability compared to Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), which rely on spinning magnetic platters and mechanical read/write heads. SSDs consume less power and produce less heat, making them ideal for laptops and portable devices, whereas HDDs provide higher storage capacity at a lower cost per gigabyte. The absence of moving parts in SSDs results in quieter operation and greater resistance to physical shock, enhancing overall system reliability.
Performance Comparison: SSD vs HDD
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) offer significantly faster read and write speeds compared to Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), with typical SSDs reaching up to 550 MB/s for sequential reads, while HDDs often peak around 150 MB/s. SSDs leverage NAND flash memory, enabling near-instant data access and reduced latency, which dramatically improves boot times and application load speeds. In contrast, HDDs rely on mechanical spinning disks and read/write heads, resulting in slower data transfer rates and increased susceptibility to physical wear and mechanical failure.
Storage Capacity and Scalability
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) typically offer lower maximum storage capacities compared to Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), with consumer SSDs reaching up to 8TB while HDDs can scale beyond 20TB for enterprise models. HDDs use magnetic storage platters, allowing cost-effective scalability for large-scale data storage, making them preferable for archival and bulk storage solutions. SSDs prioritize speed and reliability but face higher costs per gigabyte, limiting their scalability for extensive capacity needs.
Reliability and Durability Factors
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) offer superior reliability and durability compared to Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) due to their lack of moving parts, reducing the risk of mechanical failure caused by shocks or vibrations. SSDs are less susceptible to data corruption from physical impacts and have a longer lifespan in extreme conditions, while HDDs rely on spinning platters and read/write heads that wear out over time. The Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) for SSDs typically exceeds that of HDDs, making SSDs a preferable choice for environments demanding high durability and consistent performance.
Cost Analysis: Which Is More Affordable?
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) typically have higher initial costs per gigabyte compared to Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), with SSD prices averaging around $0.10-$0.15 per GB, while HDDs range from $0.03-$0.05 per GB. Despite the higher upfront cost, SSDs offer lower total cost of ownership through reduced power consumption and faster data access speeds, which can enhance productivity and system lifespan. HDDs remain more affordable for large storage needs but may incur higher maintenance and energy costs over time.
Power Consumption and Energy Efficiency
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) consume significantly less power than Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) due to their lack of moving mechanical parts, resulting in improved energy efficiency for laptops and desktop computers. SSDs typically use 2 to 5 watts during active operation, compared to HDDs which often draw 6 to 15 watts, making SSDs ideal for energy-conscious applications. This lower power consumption not only extends battery life in portable devices but also reduces heat generation, contributing to overall system longevity and operational cost savings.
Noise and Heat Generation
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) operate silently due to the absence of moving parts, producing negligible heat even under heavy workloads. In contrast, Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) generate noticeable noise from spinning disks and read/write heads, coupled with higher heat output due to mechanical friction. This noise and heat generation affect system cooling requirements and overall device longevity.
Use Cases: Who Should Choose SSD or HDD?
Solid-State Drives (SSD) are ideal for users requiring fast data access, such as gamers, video editors, and professionals working with large files, due to their high-speed performance and durability. Hard Disk Drives (HDD) suit budget-conscious consumers who need ample storage capacity for backups, media libraries, or archival purposes, offering larger space at a lower price per gigabyte. Enterprises with frequent read/write cycles and mission-critical applications often prefer SSDs to benefit from their reliability and reduced latency.
Future Trends in Storage Technology
Future trends in storage technology emphasize the rapid adoption of Solid-State Drives (SSDs) due to their superior speed, durability, and energy efficiency compared to traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). Innovations in NAND flash memory and emerging technologies like NVMe and 3D XPoint are significantly enhancing SSD performance and storage capacity. While HDDs remain cost-effective for large-scale data storage, market shifts toward cloud computing and data-intensive applications drive the growing preference for SSDs in both consumer and enterprise environments.
Solid-State Drive vs Hard Disk Drive Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com