Thunderbolt offers faster data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps compared to USB-C's standard 10 Gbps, making it ideal for high-performance peripherals and video output. USB-C is more widely adopted and supports power delivery and alternate modes but may lack the advanced capabilities and daisy-chaining features found in Thunderbolt. Choosing between Thunderbolt and USB-C depends on the specific requirements for speed, compatibility, and device functionality.
Table of Comparison
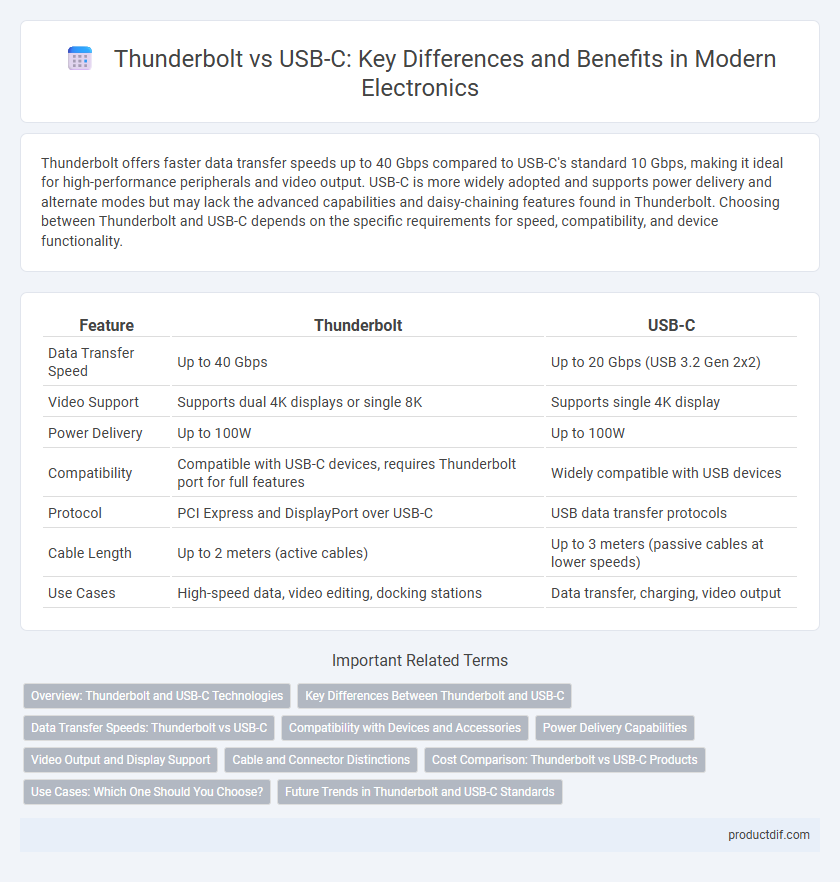
| Feature | Thunderbolt | USB-C |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 40 Gbps | Up to 20 Gbps (USB 3.2 Gen 2x2) |
| Video Support | Supports dual 4K displays or single 8K | Supports single 4K display |
| Power Delivery | Up to 100W | Up to 100W |
| Compatibility | Compatible with USB-C devices, requires Thunderbolt port for full features | Widely compatible with USB devices |
| Protocol | PCI Express and DisplayPort over USB-C | USB data transfer protocols |
| Cable Length | Up to 2 meters (active cables) | Up to 3 meters (passive cables at lower speeds) |
| Use Cases | High-speed data, video editing, docking stations | Data transfer, charging, video output |
Overview: Thunderbolt and USB-C Technologies
Thunderbolt combines data, video, and power in a single connection with speeds up to 40 Gbps, leveraging PCIe and DisplayPort technologies, while USB-C serves as a versatile physical connector supporting USB 3.2, HDMI, and DisplayPort standards. Thunderbolt 4 maintains backward compatibility with USB-C devices and offers enhanced security and daisy-chaining capabilities. USB-C's widespread adoption across devices emphasizes universal charging and data transfer, making it a broadly compatible standard, whereas Thunderbolt excels in high-performance scenarios like external GPU connections and 4K video streaming.
Key Differences Between Thunderbolt and USB-C
Thunderbolt supports data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps, while USB-C maxes out at 20 Gbps in USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 standards, impacting performance for high-bandwidth applications. Thunderbolt integrates PCI Express and DisplayPort protocols, enabling daisy-chaining of multiple devices and support for dual 4K displays, unlike USB-C's more limited video output options. Power delivery varies, with USB-C providing up to 100 watts, whereas Thunderbolt also supports similar power levels but excels in combining data, video, and power through a single versatile port.
Data Transfer Speeds: Thunderbolt vs USB-C
Thunderbolt 4 supports data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps, significantly outperforming USB-C 3.2 Gen 2x2, which offers up to 20 Gbps. This higher bandwidth enables faster file transfers, smoother 4K video streaming, and enhanced peripheral connectivity for Thunderbolt devices. USB-C's versatility is notable, but Thunderbolt's superior transfer speeds are ideal for data-intensive professional applications.
Compatibility with Devices and Accessories
Thunderbolt provides broader compatibility with high-performance devices such as external GPUs, 4K monitors, and PCIe storage, supporting data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps. USB-C offers widespread compatibility across various smartphones, tablets, and peripherals, with speeds ranging from 5 Gbps (USB 3.1) to 20 Gbps (USB 3.2). While USB-C is more commonly adopted for everyday accessories, Thunderbolt's enhanced protocol ensures seamless operation with professional-grade hardware and docking stations.
Power Delivery Capabilities
Thunderbolt supports power delivery up to 100W, enabling fast charging for laptops and other high-power devices through a single cable. USB-C also delivers up to 100W, but actual power delivery depends on the device's implemented USB Power Delivery (USB PD) profile. Thunderbolt's integration with USB-C ports ensures universal compatibility while providing enhanced data transfer speeds alongside robust power delivery capabilities.
Video Output and Display Support
Thunderbolt supports dual 4K displays at 60Hz or a single 8K display, utilizing PCIe data transfer for superior video bandwidth compared to USB-C's DisplayPort Alternate Mode, which typically supports a single 4K display at 60Hz. Thunderbolt's daisy-chaining capability allows multiple high-resolution monitors to connect via one port, enhancing workspace multitasking, while standard USB-C ports vary widely in video output capabilities based on device specifications. For professionals requiring high-resolution, multi-monitor setups with faster refresh rates and robust data throughput, Thunderbolt remains the preferred video output standard within the electronics ecosystem.
Cable and Connector Distinctions
Thunderbolt cables feature active components enabling higher data transfer rates up to 40 Gbps, while USB-C cables can support speeds ranging from 5 Gbps to 20 Gbps depending on the USB specification. Thunderbolt connectors use the USB-C form factor but integrate additional protocols for enhanced power delivery and video output capabilities. USB-C connectors, designed primarily for universal compatibility, support diverse functions including charging, data transfer, and video, but vary in performance based on cable certification and technology standards.
Cost Comparison: Thunderbolt vs USB-C Products
Thunderbolt products typically carry a higher price tag than USB-C counterparts due to advanced data transfer rates and enhanced capabilities such as daisy-chaining multiple devices. USB-C alternatives offer cost-effective solutions with broad compatibility and sufficient speed for everyday tasks, making them ideal for budget-conscious consumers. The cost disparity reflects the premium performance and specialized technology embedded in Thunderbolt devices compared to the more universally adopted USB-C standard.
Use Cases: Which One Should You Choose?
Thunderbolt offers higher data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps, making it ideal for professionals working with 4K video editing, large file transfers, or multiple 4K monitors. USB-C provides widespread compatibility and sufficient speeds up to 10 Gbps, perfect for everyday charging, peripherals, and connecting standard external devices. Choosing between Thunderbolt and USB-C depends on the need for speed, device compatibility, and specific use cases like high-performance workflows or general productivity.
Future Trends in Thunderbolt and USB-C Standards
Future trends in Thunderbolt and USB-C standards emphasize increased data transfer speeds, enhanced power delivery, and broader compatibility with emerging devices like VR headsets and 8K monitors. Thunderbolt 5 promises up to 80 Gbps bandwidth, doubling previous versions, while USB4 continues to unify USB and Thunderbolt protocols, improving versatility and adoption. Industry momentum toward seamless USB-C integration highlights ongoing innovation to support AI-driven peripherals and faster charging technologies.
Thunderbolt vs USB-C Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com