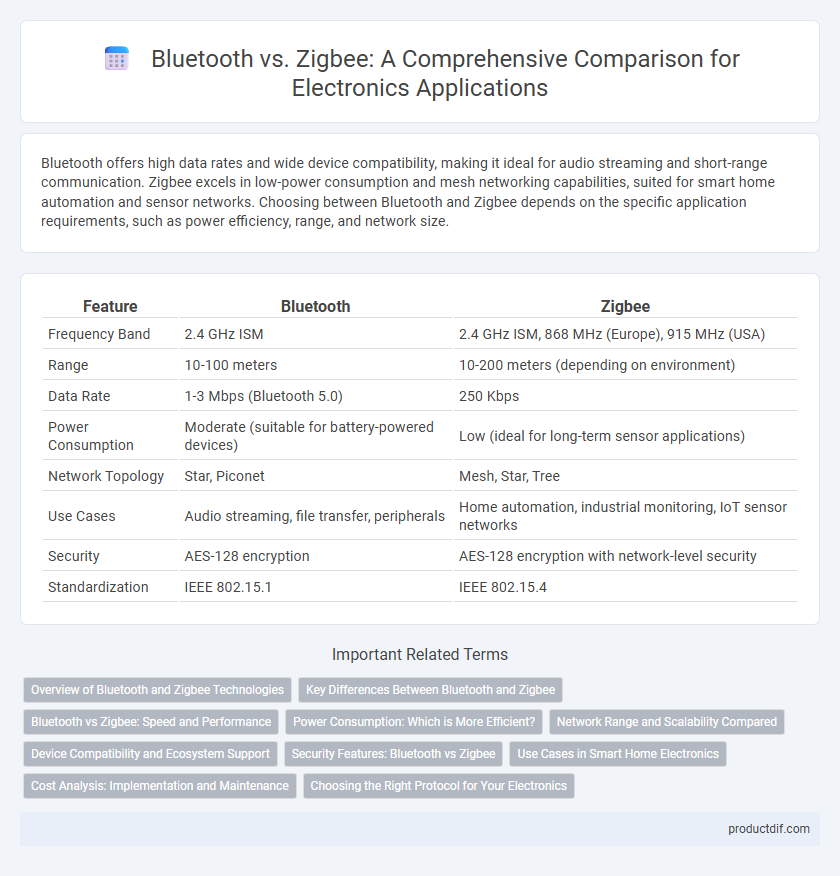
Bluetooth offers high data rates and wide device compatibility, making it ideal for audio streaming and short-range communication. Zigbee excels in low-power consumption and mesh networking capabilities, suited for smart home automation and sensor networks. Choosing between Bluetooth and Zigbee depends on the specific application requirements, such as power efficiency, range, and network size.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bluetooth | Zigbee |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Band | 2.4 GHz ISM | 2.4 GHz ISM, 868 MHz (Europe), 915 MHz (USA) |
| Range | 10-100 meters | 10-200 meters (depending on environment) |
| Data Rate | 1-3 Mbps (Bluetooth 5.0) | 250 Kbps |
| Power Consumption | Moderate (suitable for battery-powered devices) | Low (ideal for long-term sensor applications) |
| Network Topology | Star, Piconet | Mesh, Star, Tree |
| Use Cases | Audio streaming, file transfer, peripherals | Home automation, industrial monitoring, IoT sensor networks |
| Security | AES-128 encryption | AES-128 encryption with network-level security |
| Standardization | IEEE 802.15.1 | IEEE 802.15.4 |
Overview of Bluetooth and Zigbee Technologies
Bluetooth and Zigbee are wireless communication protocols designed for short-range data exchange, with Bluetooth widely used for high-speed audio and data streaming between devices such as smartphones, headphones, and computers. Zigbee excels in low-power, low-data-rate applications ideal for home automation, industrial monitoring, and sensor networks, supporting mesh networking to extend range and reliability. Both operate in the 2.4 GHz ISM band, but Bluetooth prioritizes high throughput and device interoperability, while Zigbee emphasizes energy efficiency and scalable network topologies.
Key Differences Between Bluetooth and Zigbee
Bluetooth operates on the 2.4 GHz ISM band with typical ranges up to 100 meters, prioritizing high data rates of up to 3 Mbps for audio and file transfer applications. Zigbee also uses the 2.4 GHz band but emphasizes low power consumption and longer battery life, supporting mesh networking with ranges typically around 10-20 meters per node, ideal for home automation and IoT devices. Bluetooth excels in device pairing and streaming, while Zigbee provides robust scalability and network reliability for sensor and control networks.
Bluetooth vs Zigbee: Speed and Performance
Bluetooth offers faster data transfer rates, typically up to 3 Mbps with Bluetooth 4.0 and higher versions reaching even greater speeds, making it suitable for applications requiring quick data exchange. Zigbee, designed for low-power, low-data-rate applications, operates at a maximum speed of 250 kbps, prioritizing energy efficiency and reliability over raw speed. In terms of performance, Bluetooth excels in high-throughput tasks like audio streaming, while Zigbee is optimized for stable, long-range communication in automation and sensor networks.
Power Consumption: Which is More Efficient?
Bluetooth typically consumes more power than Zigbee, with Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) designed to minimize energy usage for short-range communication and frequent data transmission. Zigbee excels in ultra-low power consumption, often operating on coin-cell batteries for extended periods, making it ideal for IoT devices requiring long battery life and infrequent data transfer. Zigbee's mesh networking capability further enhances power efficiency by allowing devices to relay data, reducing the need for direct high-power transmissions.
Network Range and Scalability Compared
Bluetooth typically offers a network range of up to 100 meters, suitable for personal area networks and short-distance communication. Zigbee supports extended network ranges of up to 300 meters per node and enables mesh networking, allowing devices to relay data and expand coverage beyond individual device limits. Scalability is more robust in Zigbee networks, supporting thousands of nodes compared to Bluetooth's limitation of around 7 active connections per device.
Device Compatibility and Ecosystem Support
Bluetooth offers extensive device compatibility with most smartphones, laptops, and tablets, making it widely supported across consumer electronics ecosystems. Zigbee caters primarily to smart home and industrial automation devices, featuring robust mesh networking ideal for low-power IoT applications but with more limited compatibility compared to Bluetooth. Ecosystem support for Bluetooth includes major OS platforms like iOS, Android, and Windows, whereas Zigbee relies heavily on dedicated hubs and gateways to integrate with broader smart home systems.
Security Features: Bluetooth vs Zigbee
Bluetooth employs robust security protocols such as AES-128 encryption, secure simple pairing, and frequency hopping spread spectrum to ensure data integrity and protection against eavesdropping. Zigbee, designed for low-power IoT devices, incorporates AES-128 encryption with network and link-layer security measures, providing strong authentication and key management for secure device communication. Both technologies emphasize secure data transmission, but Zigbee's focus on mesh networks enhances security resilience in multi-node environments.
Use Cases in Smart Home Electronics
Bluetooth excels in smart home electronics requiring short-range, high-bandwidth connections, such as wireless audio streaming and device control through smartphones. Zigbee is ideal for low-power, low-data-rate applications like smart lighting systems, security sensors, and thermostats, supporting mesh networking for extended coverage. Both protocols integrate seamlessly in home automation, with Bluetooth favoring direct device pairing and Zigbee enabling scalable, energy-efficient sensor networks.
Cost Analysis: Implementation and Maintenance
Bluetooth's implementation cost is generally lower due to widespread device compatibility and simpler network setup, making it ideal for consumer electronics. Zigbee requires higher initial investment because of specialized hardware and complex mesh network configurations but offers reduced maintenance costs through enhanced energy efficiency and scalability in smart home systems. Long-term expenses favor Zigbee in large-scale applications, while Bluetooth remains cost-effective for small to medium deployments.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Electronics
Bluetooth offers higher data rates and widespread compatibility, making it ideal for audio streaming and device pairing in consumer electronics. Zigbee excels in low-power applications and mesh networking, suitable for smart home automation and industrial sensor systems. Selecting the right protocol depends on the required range, power consumption, and network complexity of your electronic devices.
Bluetooth vs Zigbee Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com