Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer cycle life, making them ideal for devices requiring extended usage and consistent performance. Li-polymer batteries provide greater flexibility in shape and size, enhancing design options for slim and lightweight electronics. Both types utilize lithium-based chemistry but differ in electrolyte composition, impacting safety, weight, and form factor considerations.
Table of Comparison
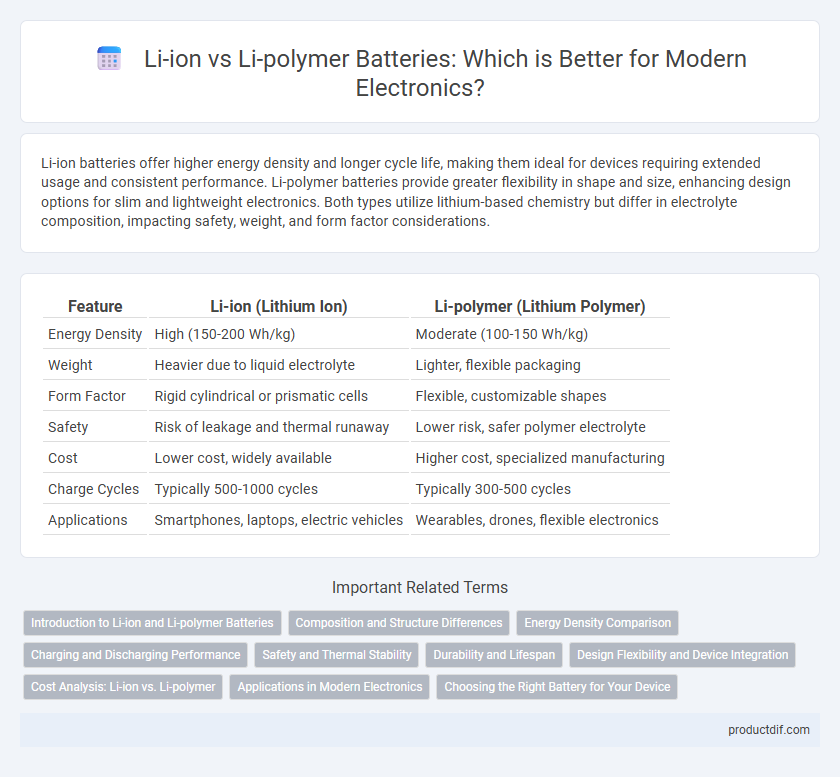
| Feature | Li-ion (Lithium Ion) | Li-polymer (Lithium Polymer) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | High (150-200 Wh/kg) | Moderate (100-150 Wh/kg) |
| Weight | Heavier due to liquid electrolyte | Lighter, flexible packaging |
| Form Factor | Rigid cylindrical or prismatic cells | Flexible, customizable shapes |
| Safety | Risk of leakage and thermal runaway | Lower risk, safer polymer electrolyte |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, specialized manufacturing |
| Charge Cycles | Typically 500-1000 cycles | Typically 300-500 cycles |
| Applications | Smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles | Wearables, drones, flexible electronics |
Introduction to Li-ion and Li-polymer Batteries
Li-ion batteries utilize a liquid electrolyte to facilitate ion movement, providing high energy density and long cycle life, commonly found in smartphones and laptops. Li-polymer batteries use a solid or gel-like polymer electrolyte, enabling flexible shapes and lighter weight while maintaining good energy capacity and safety features. Both technologies deliver rechargeable power sources but differ in form factor, safety, and application-specific advantages.
Composition and Structure Differences
Li-ion batteries use a liquid electrolyte enclosed in a rigid cylindrical or prismatic metal casing, while Li-polymer batteries employ a solid or gel-like polymer electrolyte that allows for flexible, lightweight packaging. The anodes and cathodes in Li-ion cells consist of liquid-infused porous materials, enabling high energy density, whereas Li-polymer cells utilize a solid polymer matrix that improves mechanical stability and reduces leakage risks. Structural differences affect the form factor, with Li-polymer batteries offering thinner profiles and customizable shapes compared to the sturdier, more standardized Li-ion designs.
Energy Density Comparison
Li-ion batteries typically offer higher energy density, ranging from 150 to 250 Wh/kg, compared to Li-polymer batteries, which usually provide around 100 to 200 Wh/kg. The denser energy storage in Li-ion cells results from their use of a liquid electrolyte, allowing more active material per unit volume. Although Li-polymer batteries have slightly lower energy density, their flexible form factor enables custom shapes and sizes for compact electronic devices.
Charging and Discharging Performance
Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density and typically provide consistent charging and discharging rates with stable voltage output, making them suitable for devices requiring steady power. Li-polymer batteries excel in faster charging capabilities and flexible form factors, enabling quicker energy absorption and efficient discharging with lower internal resistance. The choice between Li-ion and Li-polymer largely depends on device design constraints and performance demands related to charge speed and cycle stability.
Safety and Thermal Stability
Li-ion batteries offer high energy density but can pose thermal runaway risks under extreme conditions, causing potential safety hazards like fires or explosions. Li-polymer batteries utilize a gel-like electrolyte, providing better mechanical stability and heat dissipation, which reduces the likelihood of overheating and enhances overall safety. Advanced thermal management systems and robust battery management circuits further improve the safe operation of both battery types in electronic devices.
Durability and Lifespan
Li-ion batteries offer a higher energy density but generally exhibit shorter lifespans due to greater sensitivity to temperature and charging cycles, which can accelerate capacity loss. Li-polymer batteries, while slightly lower in energy density, provide improved durability with a flexible, lightweight design and better resistance to swelling and physical damage, contributing to longer usable life. Optimal battery management systems and proper charging habits can significantly extend the lifespan of both Li-ion and Li-polymer technologies.
Design Flexibility and Device Integration
Li-polymer batteries offer greater design flexibility compared to Li-ion due to their customizable shapes and thinner profile, enabling seamless integration into slim and compact electronic devices. The gel-like electrolyte in Li-polymer cells allows for more versatile packaging options, which is ideal for advanced wearables and curved smartphones. Li-ion batteries, while energy-dense, are limited by rigid metal casing, making them less adaptable for innovative device form factors.
Cost Analysis: Li-ion vs. Li-polymer
Li-ion batteries typically offer a lower cost per watt-hour compared to Li-polymer cells due to their established manufacturing processes and higher energy density. Li-polymer batteries, while more expensive, provide benefits like flexible form factors and enhanced safety, justifying the higher investment in specific applications such as wearables and slim devices. Cost analysis must weigh the trade-offs between upfront battery expenses and long-term performance or design advantages.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Li-ion batteries offer high energy density and long cycle life, making them ideal for smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Li-polymer batteries provide greater flexibility in shape and lighter weight, preferred in wearable devices, drones, and advanced medical equipment. Both technologies drive modern electronics by balancing power efficiency, durability, and device design constraints.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Device
Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer lifespan, making them ideal for devices requiring extended usage, while Li-polymer batteries provide greater flexibility in shape and a lighter weight, beneficial for slim and compact electronics. Consider device design constraints and power demands when choosing between Li-ion and Li-polymer batteries to optimize performance and user experience. Safety features and cost factors also play crucial roles in selecting the appropriate battery type for your specific application.
Li-ion vs Li-polymer Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com