TFT (Thin Film Transistor) displays are a type of LCD technology known for their fast response times and affordability but often suffer from limited viewing angles and color accuracy. IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels significantly improve upon these limitations by offering wider viewing angles and superior color reproduction, making them ideal for tasks requiring precise color fidelity. While IPS screens tend to be more expensive and consume slightly more power than TFT displays, their enhanced image quality justifies the cost in professional and multimedia applications.
Table of Comparison
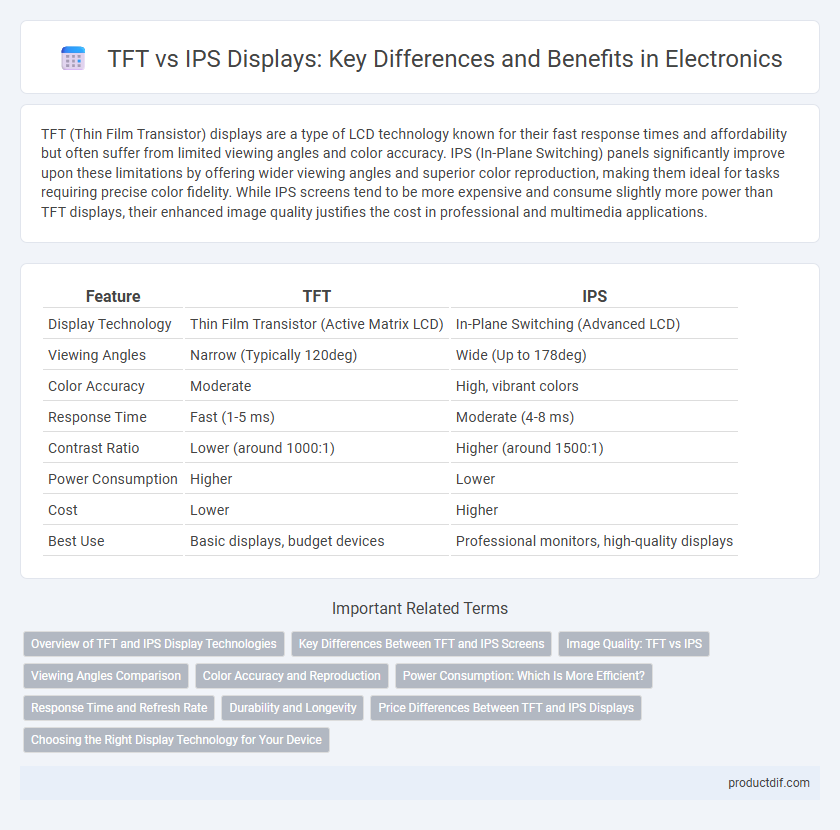
| Feature | TFT | IPS |
|---|---|---|
| Display Technology | Thin Film Transistor (Active Matrix LCD) | In-Plane Switching (Advanced LCD) |
| Viewing Angles | Narrow (Typically 120deg) | Wide (Up to 178deg) |
| Color Accuracy | Moderate | High, vibrant colors |
| Response Time | Fast (1-5 ms) | Moderate (4-8 ms) |
| Contrast Ratio | Lower (around 1000:1) | Higher (around 1500:1) |
| Power Consumption | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best Use | Basic displays, budget devices | Professional monitors, high-quality displays |
Overview of TFT and IPS Display Technologies
TFT (Thin Film Transistor) and IPS (In-Plane Switching) are two prominent display technologies used in electronics to enhance screen quality. TFT is a type of LCD technology that improves image sharpness and response time by using thin film transistor-based active matrix backplanes. IPS, a subtype of TFT, offers superior color accuracy and wider viewing angles by aligning liquid crystals horizontally, making it ideal for devices requiring vibrant visuals and consistent image quality across multiple perspectives.
Key Differences Between TFT and IPS Screens
TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) screens utilize a basic LCD technology with individual transistors controlling pixels, offering faster response times but narrower viewing angles and less accurate color reproduction. IPS (In-Plane Switching) screens feature advanced liquid crystal alignment, providing superior color accuracy, wider viewing angles up to 178 degrees, and better image consistency under diverse lighting conditions. IPS panels generally consume more power than TFT but excel in professional graphics, smartphones, and high-end monitors demanding vibrant visuals and precise color fidelity.
Image Quality: TFT vs IPS
IPS technology delivers superior image quality compared to traditional TFT displays due to its wider viewing angles and more accurate color reproduction, ensuring consistent visuals from different perspectives. TFT panels often suffer from color shifting and reduced contrast when viewed off-center, limiting overall display performance. IPS displays also provide higher brightness and better color saturation, making them ideal for applications requiring vivid and precise imagery.
Viewing Angles Comparison
IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels deliver superior viewing angles up to 178 degrees with minimal color distortion, making them ideal for consistent image quality from wide perspectives. TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) LCDs, often based on TN (Twisted Nematic) technology, generally have narrower viewing angles around 90 to 120 degrees, resulting in noticeable color and contrast shifts when viewed off-center. For applications requiring extensive viewing angles and accurate color reproduction, IPS technology outperforms traditional TFT displays.
Color Accuracy and Reproduction
IPS displays provide superior color accuracy and reproduction compared to traditional TFT panels due to their advanced in-plane switching technology, which enables consistent and vibrant color output across wider viewing angles. TFT panels often suffer from color shifting and reduced accuracy when viewed off-axis, leading to less reliable color representation in professional applications. For tasks requiring precise color fidelity, such as graphic design and photo editing, IPS technology remains the preferred choice.
Power Consumption: Which Is More Efficient?
TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays typically consume more power due to their backlighting and lower light transmission efficiency. IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels, while offering superior color accuracy and viewing angles, often use advanced LED backlighting and better light modulation techniques, resulting in more efficient power consumption. For energy-sensitive applications, IPS technology tends to be more efficient, balancing performance and power usage effectively.
Response Time and Refresh Rate
TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays typically offer faster response times compared to standard IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels, making TFT better suited for gaming and fast-motion videos. However, IPS panels excel in delivering higher refresh rates with superior color accuracy and wider viewing angles, enhancing overall image quality. For applications demanding quick pixel transitions and smooth motion, selecting a TFT display with a high refresh rate is crucial.
Durability and Longevity
IPS displays offer superior durability compared to traditional TFT panels due to their stable liquid crystal alignment, reducing pixel degradation over time. The robust construction of IPS screens enhances longevity, maintaining consistent color accuracy and brightness for extended usage periods. Conversely, TFT displays tend to experience faster wear, leading to color fading and reduced lifespan under prolonged or intense use.
Price Differences Between TFT and IPS Displays
TFT displays generally cost less than IPS screens due to simpler manufacturing processes and lower material expenses. IPS displays offer superior color accuracy and wider viewing angles, which increase production costs and drive prices higher. Consumers often pay a premium for IPS technology to benefit from enhanced image quality despite the price gap compared to TFT panels.
Choosing the Right Display Technology for Your Device
When selecting display technology for your device, TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) offers faster pixel response and cost efficiency, ideal for budget-conscious electronics. IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels deliver superior color accuracy, wider viewing angles, and better image consistency, making them the preferred choice for high-end smartphones, tablets, and monitors. Consider display application requirements such as color fidelity, viewing angle, and power consumption to determine the optimal balance between performance and cost.
TFT vs IPS Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com