Consumer electronics prioritize user-friendly design and aesthetic appeal, catering to everyday personal use with devices like smartphones, laptops, and wearable technology. Industrial electronics emphasize durability, high performance, and precision, supporting complex applications in manufacturing, automation, and heavy machinery. The distinction lies in their target environments and reliability standards, with consumer electronics balancing cost and convenience while industrial electronics focus on robustness and long-term functionality.
Table of Comparison
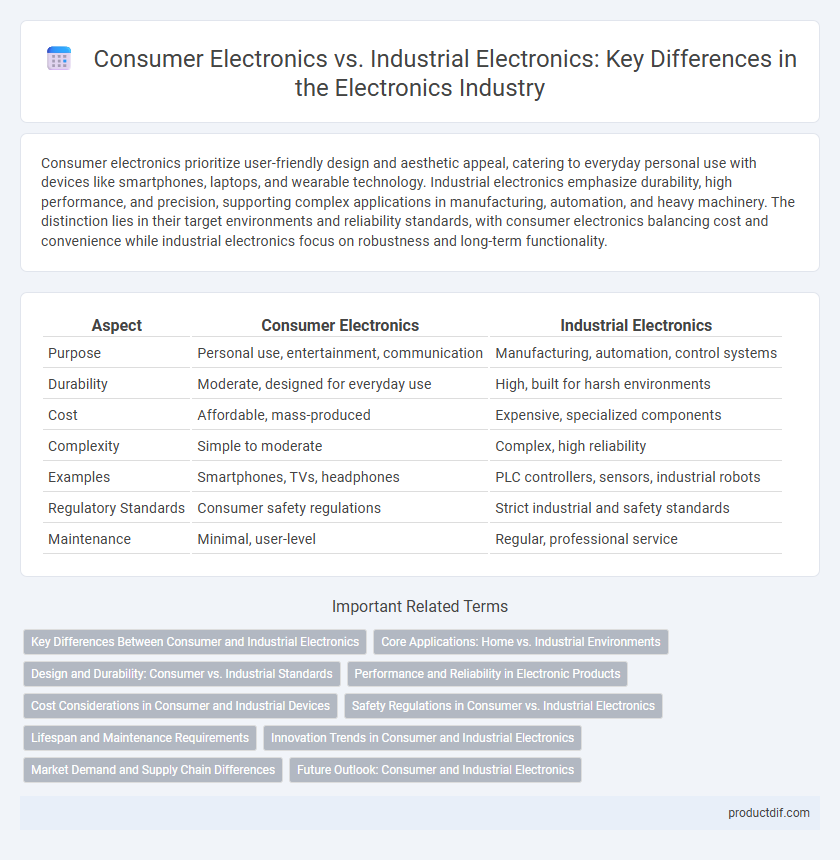
| Aspect | Consumer Electronics | Industrial Electronics |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Personal use, entertainment, communication | Manufacturing, automation, control systems |
| Durability | Moderate, designed for everyday use | High, built for harsh environments |
| Cost | Affordable, mass-produced | Expensive, specialized components |
| Complexity | Simple to moderate | Complex, high reliability |
| Examples | Smartphones, TVs, headphones | PLC controllers, sensors, industrial robots |
| Regulatory Standards | Consumer safety regulations | Strict industrial and safety standards |
| Maintenance | Minimal, user-level | Regular, professional service |
Key Differences Between Consumer and Industrial Electronics
Consumer electronics are designed for everyday personal use, emphasizing user-friendly interfaces, aesthetic appeal, and affordability, whereas industrial electronics prioritize durability, reliability, and functionality in harsh environments. Key differences include build quality, with industrial electronics featuring rugged construction and enhanced thermal management to withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stress. Furthermore, consumer electronics typically follow rapid product cycles driven by trends, while industrial electronics demand long-term availability and compliance with stringent safety and industry standards.
Core Applications: Home vs. Industrial Environments
Consumer electronics primarily serve entertainment, communication, and personal convenience within home environments, including devices like smartphones, TVs, and home automation systems. Industrial electronics focus on robust, high-performance equipment designed for manufacturing processes, automation control, and heavy machinery monitoring in demanding industrial settings. Core applications in industrial electronics emphasize reliability, durability, and real-time data processing critical for optimizing production efficiency.
Design and Durability: Consumer vs. Industrial Standards
Consumer electronics prioritize sleek design and user-friendly interfaces to enhance everyday usability, often incorporating lightweight materials and aesthetic appeal. Industrial electronics demand robust construction with high durability standards, built to withstand harsh environments, extreme temperatures, and continuous operation. The contrast in design philosophies reflects the need for longevity and reliability in industrial applications versus the emphasis on style and convenience in consumer products.
Performance and Reliability in Electronic Products
Consumer electronics prioritize user-friendly design and affordability while offering moderate performance and reliability suited for everyday use. Industrial electronics emphasize high performance, durability, and reliability to withstand harsh environments and continuous operation in critical applications. Enhanced quality control and robust materials in industrial electronics ensure consistent functionality and extended product lifespan compared to consumer-grade devices.
Cost Considerations in Consumer and Industrial Devices
Consumer electronics typically prioritize affordability and mass production, resulting in lower-cost components optimized for short product life cycles and frequent upgrades. Industrial electronics emphasize durability, reliability, and performance under harsh conditions, leading to higher initial costs but reduced maintenance expenses over time. Cost considerations in these sectors reflect differing priorities: consumer devices balance cost with trend-driven features, while industrial devices invest in robustness and long-term operational efficiency.
Safety Regulations in Consumer vs. Industrial Electronics
Consumer electronics are subject to stringent safety regulations focused on user protection, including limits on electrical shock, fire hazards, and electromagnetic interference, ensuring safe everyday use. Industrial electronics must comply with rigorous standards addressing harsher environments, such as extreme temperatures, chemical exposure, and mechanical stresses, to prevent operational failures and protect workers. Compliance with certifications like UL for consumer products and IEC for industrial equipment is crucial for market approval and safety assurance.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Consumer electronics typically have a shorter lifespan, averaging 3 to 5 years, due to frequent technological updates and lighter-duty usage, which results in higher replacement rates. Industrial electronics are designed for durability and reliability, often lasting 10 to 15 years with regular preventive maintenance to minimize downtime and extend operational life. Maintenance requirements for consumer electronics are minimal and usually limited to software updates, whereas industrial electronics demand routine inspections, calibration, and component replacements to ensure optimal performance.
Innovation Trends in Consumer and Industrial Electronics
Innovation trends in consumer electronics emphasize miniaturization, smart connectivity, and enhanced user interfaces, driven by advancements in IoT, AI integration, and wearable technology. Industrial electronics focus on robust automation, predictive maintenance through AI analytics, and edge computing to improve operational efficiency and safety in manufacturing. Both sectors leverage semiconductor innovation and energy-efficient components to meet evolving market demands and sustainability goals.
Market Demand and Supply Chain Differences
Consumer electronics market demand emphasizes rapid product innovation and high-volume production, driven by evolving user preferences and shorter product life cycles. Industrial electronics require robust, durable components tailored for specialized applications, resulting in lower volume but higher value production with strict quality standards. Supply chains for consumer electronics are complex and global, focusing on cost efficiency and speed, while industrial electronics supply chains prioritize reliability, traceability, and long-term supplier relationships.
Future Outlook: Consumer and Industrial Electronics
The future outlook for consumer electronics emphasizes advancements in smart home devices, wearable technology, and augmented reality, driven by increasing connectivity and user-centric innovations. Industrial electronics are poised for growth through the integration of IoT, automation, and AI, enhancing manufacturing efficiency, predictive maintenance, and real-time data analytics. Both sectors will benefit from advancements in semiconductor technology and sustainable materials, pushing the boundaries of performance and environmental responsibility.
Consumer electronics vs Industrial electronics Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com