Raspberry Pi offers a versatile platform with a full operating system, ideal for complex projects that require multitasking and internet connectivity, while Arduino excels in real-time control applications with its simpler microcontroller architecture. The Raspberry Pi supports extensive software libraries and multimedia capabilities, making it suitable for advanced programming and IoT development. Arduino's lower power consumption and ease of hardware interfacing provide an advantage for embedded systems and sensor-based projects.
Table of Comparison
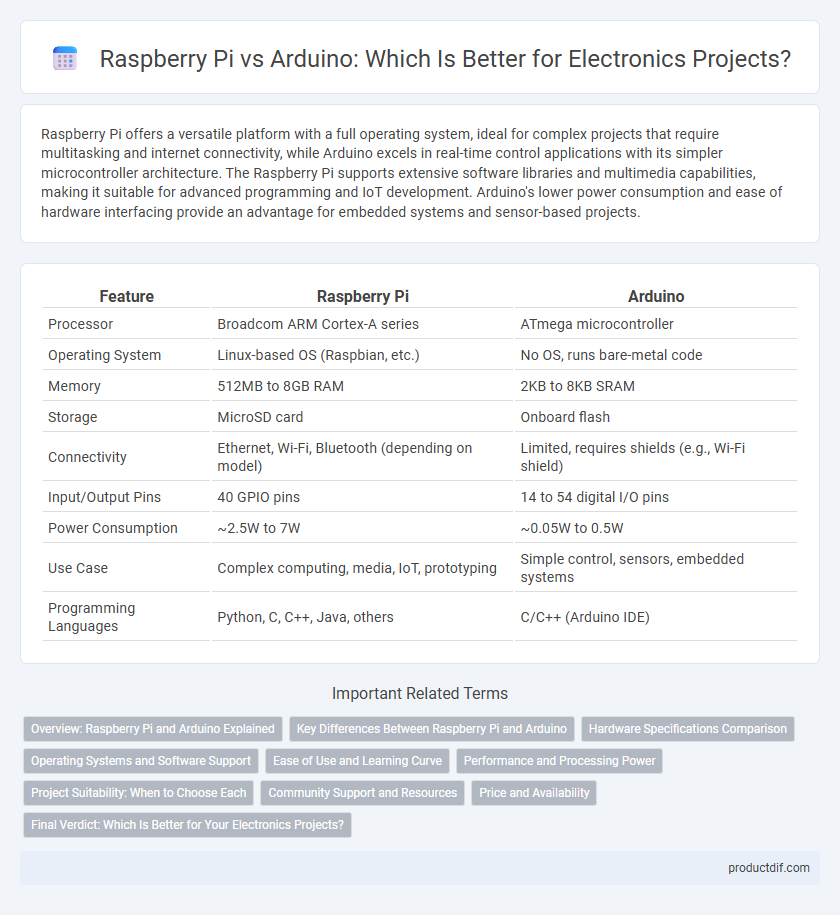
| Feature | Raspberry Pi | Arduino |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Broadcom ARM Cortex-A series | ATmega microcontroller |
| Operating System | Linux-based OS (Raspbian, etc.) | No OS, runs bare-metal code |
| Memory | 512MB to 8GB RAM | 2KB to 8KB SRAM |
| Storage | MicroSD card | Onboard flash |
| Connectivity | Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth (depending on model) | Limited, requires shields (e.g., Wi-Fi shield) |
| Input/Output Pins | 40 GPIO pins | 14 to 54 digital I/O pins |
| Power Consumption | ~2.5W to 7W | ~0.05W to 0.5W |
| Use Case | Complex computing, media, IoT, prototyping | Simple control, sensors, embedded systems |
| Programming Languages | Python, C, C++, Java, others | C/C++ (Arduino IDE) |
Overview: Raspberry Pi and Arduino Explained
Raspberry Pi is a compact, fully functional mini-computer running Linux, ideal for complex projects requiring multitasking and interfacing with various software applications. Arduino is a microcontroller platform designed for straightforward hardware control, excellent for real-time applications like sensor monitoring and robotics. Both platforms excel in electronics prototyping, but Raspberry Pi offers higher processing power and networking capabilities, while Arduino provides simplicity and reliable input/output pin control.
Key Differences Between Raspberry Pi and Arduino
Raspberry Pi is a fully functional single-board computer with a powerful ARM processor, running a full operating system like Linux, ideal for complex projects requiring multitasking and high processing power. Arduino, on the other hand, is a microcontroller-based platform designed for direct hardware control and real-time applications, making it more suitable for simple, low-power embedded projects. Key differences include Raspberry Pi's ability to support multimedia, networking, and user interfaces, while Arduino excels in sensor integration and precise timing control.
Hardware Specifications Comparison
Raspberry Pi features a powerful ARM-based quad-core CPU, up to 8GB RAM, multiple USB ports, HDMI output, and supports Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, making it ideal for complex computing tasks. Arduino uses a simpler microcontroller, typically an 8-bit AVR, with limited memory (2KB to 256KB flash) and lacks native operating system support, optimizing it for real-time control and low-power applications. While Raspberry Pi excels in processing power and multimedia capabilities, Arduino offers robust hardware interfacing with lower latency and predictable performance in embedded systems.
Operating Systems and Software Support
Raspberry Pi supports a wide range of operating systems, including Raspberry Pi OS, Ubuntu, and Windows IoT, enabling complex software development and multitasking capabilities. Arduino operates primarily using its lightweight Arduino IDE and does not support traditional operating systems, focusing instead on real-time control with direct hardware access. This distinction makes Raspberry Pi ideal for software-rich, multi-threaded projects, while Arduino excels in low-level hardware interaction and simplicity.
Ease of Use and Learning Curve
Raspberry Pi offers a more user-friendly experience with a full operating system, making it easier for beginners to navigate and develop projects using familiar programming languages like Python. Arduino features a simplified microcontroller environment requiring less setup but demands a stronger grasp of electronics and coding, which may present a steeper learning curve for newcomers. Both platforms support extensive online communities and resources that significantly ease the learning process depending on user goals.
Performance and Processing Power
Raspberry Pi outperforms Arduino in processing power with its multi-core ARM Cortex-A series processors, enabling complex computing tasks and multitasking. Arduino's microcontrollers offer lower clock speeds and limited RAM, making it ideal for simple, real-time control applications but unsuitable for demanding performance needs. The Raspberry Pi's higher clock speed, advanced GPU, and greater memory capacity provide superior performance for software development, multimedia projects, and networked applications.
Project Suitability: When to Choose Each
Raspberry Pi excels in complex projects requiring high processing power, multimedia capabilities, and running full operating systems, making it ideal for applications like web servers, media centers, and IoT development. Arduino is better suited for real-time control and simple sensor-based projects with limited processing needs, such as robotics, home automation, and embedded systems. For projects demanding extensive networking or computation, Raspberry Pi is preferable, while Arduino is the optimal choice for low-power, hardware-focused tasks.
Community Support and Resources
Raspberry Pi benefits from a vast and active community that offers extensive tutorials, forums, and open-source projects, making it ideal for advanced computing and multimedia applications. Arduino's community excels in beginner-friendly resources, a wide range of hardware shields, and straightforward programming support, which suits electronics prototyping and sensor integration. Both platforms provide comprehensive libraries and user-generated content, ensuring strong support for diverse DIY and educational projects.
Price and Availability
Raspberry Pi offers more computing power but at a higher price point, typically ranging from $35 to $75 depending on the model, while Arduino boards are generally more affordable, starting as low as $10. Availability fluctuates due to supply chain issues, with Raspberry Pi often facing stock shortages because of high demand and component scarcity. Arduino products are usually more consistently available through various distributors and online retailers, making them a budget-friendly option for hobbyists and educational purposes.
Final Verdict: Which Is Better for Your Electronics Projects?
Raspberry Pi offers advanced processing power and a full operating system, ideal for complex projects requiring multitasking and high computational capabilities. Arduino excels in real-time control applications with simple, low-power microcontroller hardware, perfect for sensor integration and basic automation tasks. Choosing between Raspberry Pi and Arduino depends on project needs: Raspberry Pi suits multimedia and networking projects, while Arduino is better for straightforward, hardware-focused electronics.
Raspberry Pi vs Arduino Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com