NAND Flash offers higher storage density and faster write/erase speeds, making it ideal for mass storage devices like SSDs and memory cards. NOR Flash provides faster random access and execute-in-place (XIP) capabilities, which are crucial for code storage and embedded system booting. The choice between NAND and NOR Flash depends on the application's need for speed, endurance, and storage capacity in electronic devices.
Table of Comparison
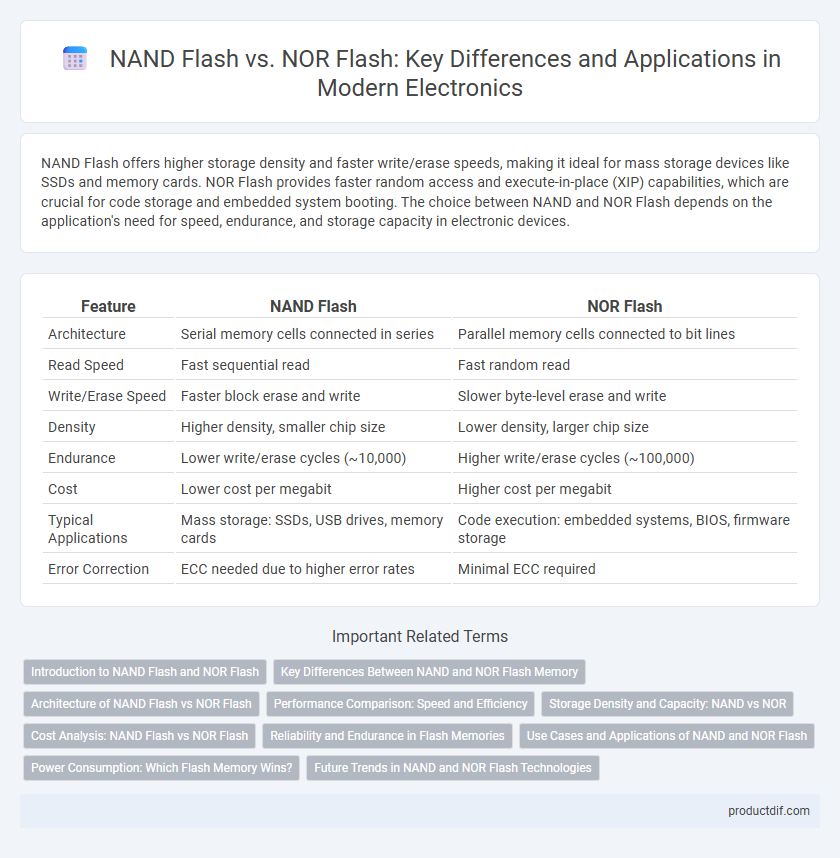
| Feature | NAND Flash | NOR Flash |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Serial memory cells connected in series | Parallel memory cells connected to bit lines |
| Read Speed | Fast sequential read | Fast random read |
| Write/Erase Speed | Faster block erase and write | Slower byte-level erase and write |
| Density | Higher density, smaller chip size | Lower density, larger chip size |
| Endurance | Lower write/erase cycles (~10,000) | Higher write/erase cycles (~100,000) |
| Cost | Lower cost per megabit | Higher cost per megabit |
| Typical Applications | Mass storage: SSDs, USB drives, memory cards | Code execution: embedded systems, BIOS, firmware storage |
| Error Correction | ECC needed due to higher error rates | Minimal ECC required |
Introduction to NAND Flash and NOR Flash
NAND Flash and NOR Flash are two primary types of non-volatile memory used in electronic devices. NAND Flash is favored for data storage applications due to its high density, faster write and erase speeds, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for solid-state drives (SSDs) and memory cards. NOR Flash provides faster read speeds and execute-in-place (XIP) capabilities, commonly used in embedded systems and firmware storage where code execution directly from memory is required.
Key Differences Between NAND and NOR Flash Memory
NAND Flash memory offers higher density and faster write/erase speeds, making it ideal for data storage applications like USB drives and SSDs. NOR Flash provides faster random access and execute-in-place (XIP) capability, suitable for code storage and embedded systems. Key differences include architecture--NAND uses a series-connected cell array optimized for high capacity, while NOR cells connect in parallel for rapid read access and reliability.
Architecture of NAND Flash vs NOR Flash
NAND Flash architecture is designed with memory cells connected in a series, forming strings that optimize density and cost efficiency for large storage applications, whereas NOR Flash features memory cells arranged in parallel, enabling faster random access and execute-in-place capabilities. NAND Flash utilizes a compact cell structure with fewer contacts, resulting in higher storage capacity per chip, while NOR Flash's parallel configuration supports direct code execution but at a higher cost and lower density. The key architectural difference impacts performance, cost, and usage scenarios, with NAND ideal for data storage and NOR suited for code storage and fast read applications.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Efficiency
NAND Flash offers faster write and erase speeds due to its high-density cell architecture, making it ideal for mass storage applications such as SSDs and USB drives. NOR Flash provides quicker read speeds and random access capabilities, which benefit code execution in embedded systems requiring fast instruction fetch. Efficiency-wise, NAND Flash consumes less power during write and erase cycles, enhancing battery life in mobile devices, whereas NOR Flash excels in reliability and data retention for firmware storage.
Storage Density and Capacity: NAND vs NOR
NAND Flash offers significantly higher storage density and capacity compared to NOR Flash, making it the preferred choice for applications requiring large data storage such as solid-state drives and memory cards. NAND cells are densely packed in a grid, allowing for more gigabytes per chip, whereas NOR Flash has a simpler architecture with lower density, favoring faster read speeds but limiting its maximum capacity. The scalability of NAND Flash enables cost-effective mass storage solutions, while NOR Flash is typically used in smaller memory applications where quick access and reliability are prioritized.
Cost Analysis: NAND Flash vs NOR Flash
NAND Flash offers significantly lower cost per bit compared to NOR Flash due to its higher storage density and simpler cell architecture, making it ideal for high-capacity applications. NOR Flash incurs higher manufacturing costs because of its complex cell design and lower density, which is optimized for fast read and random access performance rather than bulk data storage. Cost analysis favors NAND Flash for large-scale memory solutions, while NOR Flash remains cost-effective for smaller, code storage purposes.
Reliability and Endurance in Flash Memories
NAND flash memory offers higher endurance with write/erase cycles typically ranging from 3,000 to 100,000, making it suitable for applications requiring frequent data updates. NOR flash provides greater reliability for code execution due to its faster read speeds and bit-alterability but has lower endurance, generally supporting around 10,000 write/erase cycles. Both technologies use error correction codes (ECC) to enhance data integrity, yet NAND's wear-leveling algorithms significantly extend its lifespan in consumer and industrial electronics.
Use Cases and Applications of NAND and NOR Flash
NAND Flash is widely used in high-capacity storage devices like SSDs, USB drives, and memory cards due to its fast write and erase speeds, making it ideal for bulk data storage in consumer electronics and enterprise servers. NOR Flash excels in applications requiring fast read speeds and execute-in-place capability, such as firmware storage, embedded systems, and automotive control units, where reliable random access to code is critical. The selection between NAND and NOR Flash depends on balancing cost, performance, endurance, and read/write patterns specific to the device's operational needs.
Power Consumption: Which Flash Memory Wins?
NAND Flash memory typically offers lower power consumption compared to NOR Flash due to its efficient page-level read and write architecture, making it ideal for portable and battery-powered devices. NOR Flash, while providing faster random access speeds and byte-level read capabilities, generally consumes more power during read and erase cycles. For applications where energy efficiency is critical, NAND Flash is the preferred choice, delivering superior performance with reduced power usage.
Future Trends in NAND and NOR Flash Technologies
Future trends in NAND Flash technology emphasize higher density and increased storage capacity driven by advancements in 3D stacking and scaling techniques, aiming to meet growing demands for data-centric applications like AI and IoT. NOR Flash development focuses on enhancing read speed, reliability, and execute-in-place (XIP) capabilities, making it ideal for embedded systems and automotive applications requiring fast code execution and robust endurance. Emerging innovations in both NAND and NOR Flash include integrating new materials such as silicon carbide (SiC) and adopting AI-based error correction to improve performance and lifespan in next-generation memory devices.
NAND Flash vs NOR Flash Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com