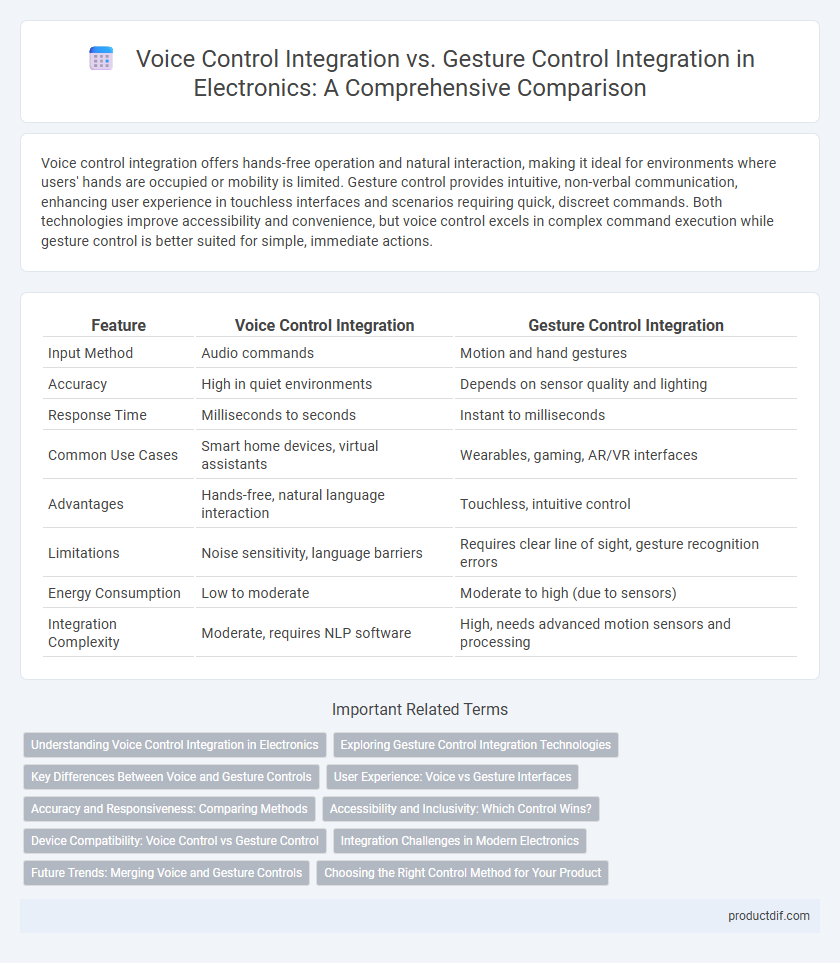
Voice control integration offers hands-free operation and natural interaction, making it ideal for environments where users' hands are occupied or mobility is limited. Gesture control provides intuitive, non-verbal communication, enhancing user experience in touchless interfaces and scenarios requiring quick, discreet commands. Both technologies improve accessibility and convenience, but voice control excels in complex command execution while gesture control is better suited for simple, immediate actions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Voice Control Integration | Gesture Control Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Input Method | Audio commands | Motion and hand gestures |
| Accuracy | High in quiet environments | Depends on sensor quality and lighting |
| Response Time | Milliseconds to seconds | Instant to milliseconds |
| Common Use Cases | Smart home devices, virtual assistants | Wearables, gaming, AR/VR interfaces |
| Advantages | Hands-free, natural language interaction | Touchless, intuitive control |
| Limitations | Noise sensitivity, language barriers | Requires clear line of sight, gesture recognition errors |
| Energy Consumption | Low to moderate | Moderate to high (due to sensors) |
| Integration Complexity | Moderate, requires NLP software | High, needs advanced motion sensors and processing |
Understanding Voice Control Integration in Electronics
Voice control integration in electronics enables users to operate devices through natural language commands, enhancing hands-free interaction and accessibility. This technology relies on advanced speech recognition algorithms and natural language processing to interpret and respond accurately to user instructions. Compared to gesture control, voice control offers more precise and context-aware functionality, especially in environments where physical gestures might be impractical or less intuitive.
Exploring Gesture Control Integration Technologies
Gesture control integration technologies utilize sensors such as infrared, ultrasonic, and camera-based systems to interpret human movements into electronic device commands, enhancing user interaction without physical contact. Advanced algorithms in machine learning and computer vision process complex gestures in real time, offering higher accuracy and responsiveness compared to traditional voice control systems that rely on speech recognition and natural language processing. The integration of gesture control in electronics facilitates hands-free operation in environments with noise interference or privacy concerns, expanding accessibility and user experience beyond voice-dependent interfaces.
Key Differences Between Voice and Gesture Controls
Voice control integration relies on speech recognition technology to interpret user commands through audio input, enabling hands-free operation ideal for environments where mobility or glove use impedes physical contact. Gesture control integration employs motion sensors and cameras to detect hand or body movements, providing an intuitive, touch-free interface best suited for applications requiring silent or discreet interactions. Key differences include voice control's dependence on clear audio and language processing versus gesture control's sensitivity to lighting and spatial constraints, impacting precision and usability in varied electronic devices.
User Experience: Voice vs Gesture Interfaces
Voice control integration enhances user experience by enabling hands-free operation and intuitive interaction, particularly beneficial in smart home devices and wearable technology. Gesture control integration offers a tactile and natural interface, allowing users to perform commands through simple hand or body movements, which can improve accessibility in environments where voice recognition faces challenges. Both technologies prioritize ease of use, but voice interfaces excel in noisy or complex command scenarios, while gesture interfaces shine in visually driven and silent application contexts.
Accuracy and Responsiveness: Comparing Methods
Voice control integration offers high accuracy in recognizing complex commands due to advanced natural language processing algorithms, making it suitable for hands-free device operation. Gesture control integration provides rapid responsiveness through real-time motion detection sensors but may suffer from lower accuracy in distinguishing subtle or overlapping gestures. Combining voice and gesture inputs can enhance overall system performance by compensating for individual limitations in accuracy and responsiveness.
Accessibility and Inclusivity: Which Control Wins?
Voice control integration offers superior accessibility by enabling hands-free operation for users with mobility impairments or limited dexterity, making devices more inclusive across diverse user groups. Gesture control integration, while intuitive and useful in situational contexts, may exclude individuals with limited motor skills due to its reliance on physical movement accuracy. Overall, voice control provides broader inclusivity by accommodating a wider range of disabilities and environmental conditions.
Device Compatibility: Voice Control vs Gesture Control
Voice control integration offers broader device compatibility, supporting smartphones, smart speakers, TVs, and home automation systems across multiple platforms like Android, iOS, and Windows. Gesture control integration, while innovative, tends to have more limited compatibility, primarily requiring specialized sensors or cameras and is mostly found in gaming consoles, VR devices, and select smart home gadgets. The wider ecosystem support makes voice control more versatile for diverse electronics environments.
Integration Challenges in Modern Electronics
Voice control integration in modern electronics faces challenges such as accurately recognizing diverse accents and filtering ambient noise, requiring advanced natural language processing algorithms and robust microphone arrays. Gesture control integration demands precise motion sensing and interpretation, often hindered by variable lighting conditions and limited sensor resolution, complicating reliable user interaction. Both technologies necessitate seamless hardware-software integration and optimized processing power to ensure real-time responsiveness and user experience consistency.
Future Trends: Merging Voice and Gesture Controls
Future trends in electronics emphasize the convergence of voice control integration and gesture control integration, creating hybrid systems that enhance user experience through multimodal interaction. Advances in AI-powered sensors and natural language processing enable seamless switching and combined inputs, improving device responsiveness and accessibility. This integration supports smarter environments in smart homes, wearable devices, and automotive interfaces, driving innovation in human-computer interaction.
Choosing the Right Control Method for Your Product
Voice control integration offers seamless hands-free operation and natural user interaction, ideal for smart home devices and automotive systems where convenience and accessibility are priorities. Gesture control integration provides intuitive, touchless navigation suited for environments requiring hygiene or when hands are occupied, such as medical devices and wearable technology. Selecting the right control method depends on the product's usage context, user preferences, and environmental constraints to maximize usability and enhance the overall user experience.
Voice Control Integration vs Gesture Control Integration Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com