USB-C offers faster data transfer speeds and broader compatibility across devices compared to Lightning, making it a versatile choice for charging and connectivity. Lightning connectors are primarily used in Apple's ecosystem, providing a compact design but limited interoperability with non-Apple products. The gradual industry shift towards USB-C aims to unify charging standards and enhance user convenience.
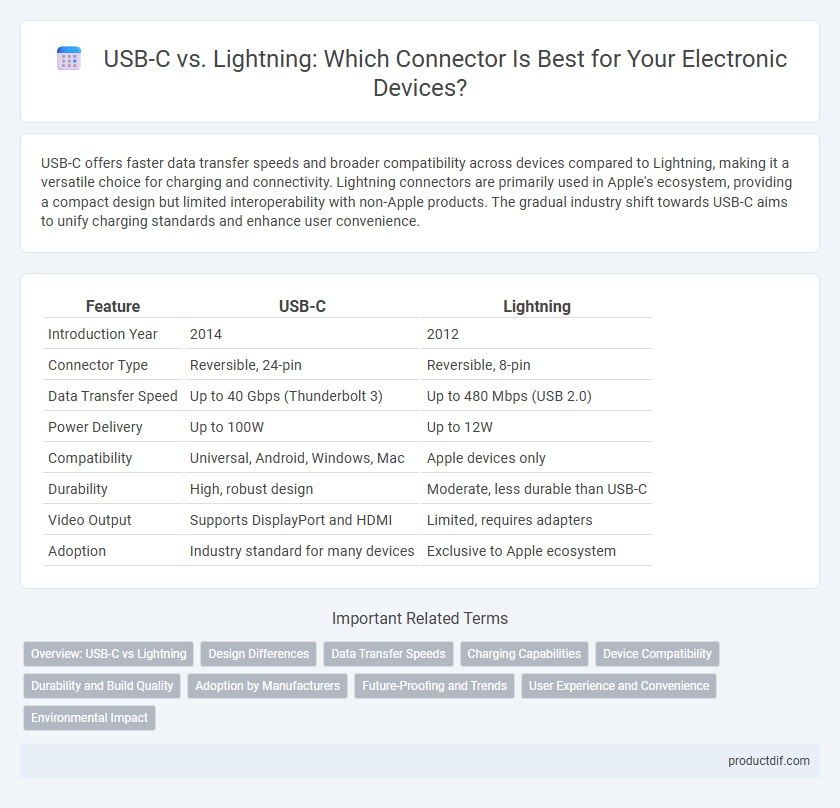
Table of Comparison
| Feature | USB-C | Lightning |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction Year | 2014 | 2012 |
| Connector Type | Reversible, 24-pin | Reversible, 8-pin |
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 40 Gbps (Thunderbolt 3) | Up to 480 Mbps (USB 2.0) |
| Power Delivery | Up to 100W | Up to 12W |
| Compatibility | Universal, Android, Windows, Mac | Apple devices only |
| Durability | High, robust design | Moderate, less durable than USB-C |
| Video Output | Supports DisplayPort and HDMI | Limited, requires adapters |
| Adoption | Industry standard for many devices | Exclusive to Apple ecosystem |
Overview: USB-C vs Lightning
USB-C and Lightning are two prevalent charging and data transfer standards in modern electronics, with USB-C offering a universal interface compatible with numerous devices, including laptops, smartphones, and tablets. Lightning, designed exclusively by Apple, remains integral to iPhones and some iPad models, featuring a compact 8-pin connector optimized for Apple's ecosystem. USB-C supports faster data transfer rates up to 40 Gbps via Thunderbolt 3 and higher power delivery up to 100W, whereas Lightning's maximum power delivery and data rates are considerably lower, influencing device charging and accessory compatibility.
Design Differences
USB-C features a symmetrical, oval-shaped connector supporting reversible plug orientation and a universal design compatible with multiple device types. Lightning connectors are smaller, proprietary to Apple devices, and also reversible but have a narrower pin layout optimized for thinner device profiles. USB-C's robust design accommodates higher power delivery and faster data transfer rates, while Lightning prioritizes compactness and device-specific integration.
Data Transfer Speeds
USB-C supports data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps with Thunderbolt 3 or 4, significantly outperforming Lightning ports that max out at 480 Mbps with USB 2.0 standards. USB-C's faster transfer rates benefit large file transfers, high-resolution video streaming, and improved overall device synchronization. Devices using USB-C provide enhanced performance for professional and multimedia applications compared to the slower Lightning interface.
Charging Capabilities
USB-C supports higher power delivery with up to 100W, enabling faster charging for a wide range of devices including laptops and smartphones. Lightning cables typically deliver up to 20W, primarily optimized for Apple devices like iPhones and iPads. The USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) protocol in USB-C allows dynamic power adjustment, enhancing safety and efficiency during the charging process.
Device Compatibility
USB-C offers broader device compatibility, supporting smartphones, tablets, laptops, and peripherals across multiple brands, including Android devices, Apple MacBooks, and Windows PCs. Lightning connectors are proprietary to Apple, compatible primarily with iPhones, iPads, and certain Apple accessories, limiting cross-device use. As USB-C becomes a universal standard, it enhances user convenience by reducing the need for multiple cables and adapters.
Durability and Build Quality
USB-C connectors typically offer enhanced durability compared to Lightning ports due to their reversible design and robust metal casing, which withstands frequent plugging and unplugging. Lightning connectors, while compact and efficient, often feature a thinner, smaller port that is more prone to wear and physical damage over extended use. High-quality USB-C cables often utilize reinforced stress points and braided materials, contributing to superior longevity in demanding electronic environments.
Adoption by Manufacturers
USB-C has seen widespread adoption by leading electronics manufacturers, including Apple, Samsung, and Dell, due to its versatility and universal compatibility across devices. Lightning remains exclusive primarily to Apple products, limiting its adoption to iPhones, iPads, and select accessories. The global push for standardized charging ports has accelerated USB-C integration in smartphones, laptops, and peripherals, increasing cross-brand interoperability.
Future-Proofing and Trends
USB-C offers superior future-proofing due to its universal adoption across multiple device categories, including smartphones, laptops, and tablets, supporting faster data transfer rates up to 40 Gbps with Thunderbolt 3 compatibility. Lightning remains limited to Apple devices, with slower data speeds and diminishing support as Apple gradually transitions to USB-C in new iPhone models. Industry trends indicate USB-C's dominance driven by regulatory mandates and consumer demand for a single, versatile charging and data interface.
User Experience and Convenience
USB-C offers faster data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps with Thunderbolt 3 support, enabling swift file sharing and seamless connectivity across diverse devices. Its reversible design and universal compatibility reduce cable confusion, enhancing user convenience during charging and syncing. Lightning cables, while compact and Apple-optimized, limit cross-platform use and slower charging speeds, often requiring multiple accessories for non-Apple devices.
Environmental Impact
USB-C cables generally have a lower environmental impact than Lightning cables due to their universal compatibility, reducing electronic waste by minimizing the need for multiple chargers. The widespread adoption of USB-C encourages manufacturers to standardize production, leading to less resource consumption and improved recyclability. Lightning cables, being proprietary, contribute to greater electronic waste as their usage is limited to specific Apple devices, resulting in higher production and disposal demands.
USB-C vs Lightning Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com