Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer cycle life compared to NiMH batteries, making them ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles. NiMH batteries are less expensive and more environmentally friendly but suffer from higher self-discharge rates and lower voltage output. Choosing between Li-ion and NiMH depends on the specific application requirements for power, cost, and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
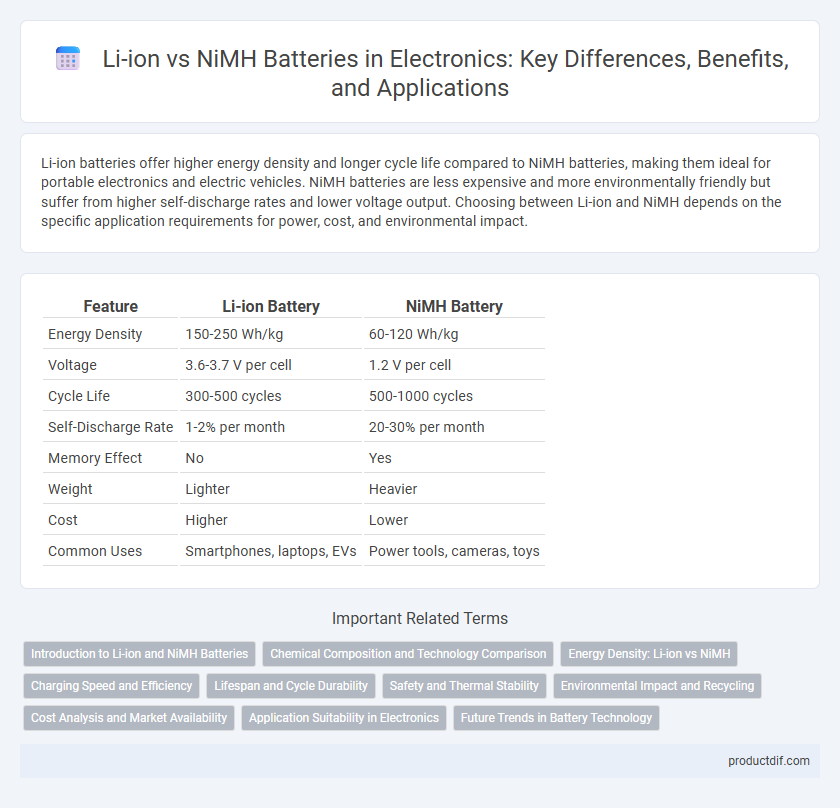
| Feature | Li-ion Battery | NiMH Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 150-250 Wh/kg | 60-120 Wh/kg |
| Voltage | 3.6-3.7 V per cell | 1.2 V per cell |
| Cycle Life | 300-500 cycles | 500-1000 cycles |
| Self-Discharge Rate | 1-2% per month | 20-30% per month |
| Memory Effect | No | Yes |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Uses | Smartphones, laptops, EVs | Power tools, cameras, toys |
Introduction to Li-ion and NiMH Batteries
Li-ion batteries offer high energy density and longer cycle life, making them ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles, while NiMH batteries provide reliable performance and are less prone to memory effect. Li-ion cells use lithium ions to move between the anode and cathode during charge and discharge, resulting in lighter and more compact power sources. NiMH batteries store energy through the reaction between nickel oxyhydroxide and hydrogen in a metal hydride, providing a safer and more environmentally friendly alternative for lower-drain applications.
Chemical Composition and Technology Comparison
Li-ion batteries use lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate, providing higher energy density and longer cycle life compared to NiMH batteries, which rely on nickel oxide hydroxide and metal hydride electrodes. The advanced chemistry of Li-ion enables faster charging and lower self-discharge rates, making them ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles. NiMH technology, while safer and more environmentally friendly, suffers from higher memory effect and less efficient energy storage.
Energy Density: Li-ion vs NiMH
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries exhibit significantly higher energy density, typically ranging from 150 to 250 Wh/kg, compared to nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, which offer around 60 to 120 Wh/kg. This superior energy density in Li-ion cells enables longer device runtimes and greater power storage within compact form factors. As a result, Li-ion technology is preferred in applications requiring lightweight, high-capacity power sources such as smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
Charging Speed and Efficiency
Li-ion batteries offer significantly faster charging speeds compared to NiMH cells, often reaching full charge within 1 to 3 hours, while NiMH batteries typically require 4 to 6 hours. Li-ion technology provides higher energy density and lower self-discharge rates, resulting in improved charging efficiency and longer battery life in electronic devices. NiMH batteries, although safer and less expensive, exhibit lower voltage stability and higher internal resistance, which reduces overall charging speed and efficiency.
Lifespan and Cycle Durability
Li-ion batteries typically offer a longer lifespan with 300 to 500 charge cycles compared to NiMH batteries, which average around 500 to 1,000 cycles but often suffer from capacity loss over time. Li-ion cells maintain consistent energy density throughout their cycle life, while NiMH cells experience gradual voltage drops and self-discharge issues. The superior cycle durability of NiMH makes them suitable for applications requiring frequent charging, but Li-ion's stable performance and longer calendar life dominate in high-energy-demand electronics.
Safety and Thermal Stability
Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density but require sophisticated battery management systems to prevent overheating and thermal runaway, posing greater safety risks compared to NiMH batteries. NiMH batteries exhibit superior thermal stability and are less prone to leakage or combustion under stress, making them safer for consumer electronics in high-temperature environments. Proper usage and charging protocols remain critical for both chemistries to minimize hazards and ensure long-term reliability.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Li-ion batteries have a lower environmental impact compared to NiMH due to higher energy density, resulting in less material usage and waste during production and disposal. Recycling processes for Li-ion batteries are more complex yet critical, recovering valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, while NiMH recycling primarily focuses on nickel recovery with established infrastructure. Proper recycling of both battery types mitigates toxic waste, but improving Li-ion battery recycling technologies is essential to reduce ecological footprint as demand increases in electronics and electric vehicles.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Li-ion batteries generally offer higher energy density and longer lifespan compared to NiMH, but their initial cost is significantly higher, making NiMH a cost-effective choice for budget-sensitive applications. NiMH batteries remain widely available and are often preferred in consumer electronics due to their lower price point and established manufacturing infrastructure. Market trends indicate increasing demand for Li-ion in electric vehicles and portable devices, while NiMH maintains strong presence in power tools and hybrid vehicles due to competitive pricing and availability.
Application Suitability in Electronics
Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer cycle life, making them ideal for portable electronics like smartphones, laptops, and tablets where compact size and extended usage are critical. NiMH batteries provide robust performance in high-drain applications such as digital cameras and power tools, benefiting from better thermal stability and environmental friendliness. Choosing between Li-ion and NiMH depends on specific device requirements, balancing factors like weight, recharge cycles, discharge rates, and cost-efficiency for optimized electronic application performance.
Future Trends in Battery Technology
Li-ion batteries dominate the market due to their high energy density and longer cycle life, but emerging solid-state batteries promise enhanced safety and faster charging times. NiMH batteries, while less energy-dense, are still relevant for specific applications requiring durability and eco-friendliness, especially with ongoing improvements in electrode materials. Future battery technology trends emphasize sustainable materials, improved energy storage capabilities, and integration with smart energy management systems to meet growing demands in electric vehicles and portable electronics.
Li-ion vs NiMH Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com