Wi-Fi 6E extends Wi-Fi 6 by operating in the newly allocated 6 GHz band, offering faster speeds and reduced latency for electronic pet devices that require reliable connectivity. This expansion alleviates congestion found in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, ensuring seamless streaming and real-time communication for smart pet collars and feeders. Enhanced bandwidth in Wi-Fi 6E supports multiple devices simultaneously, improving performance in busy home environments with numerous connected pet gadgets.
Table of Comparison
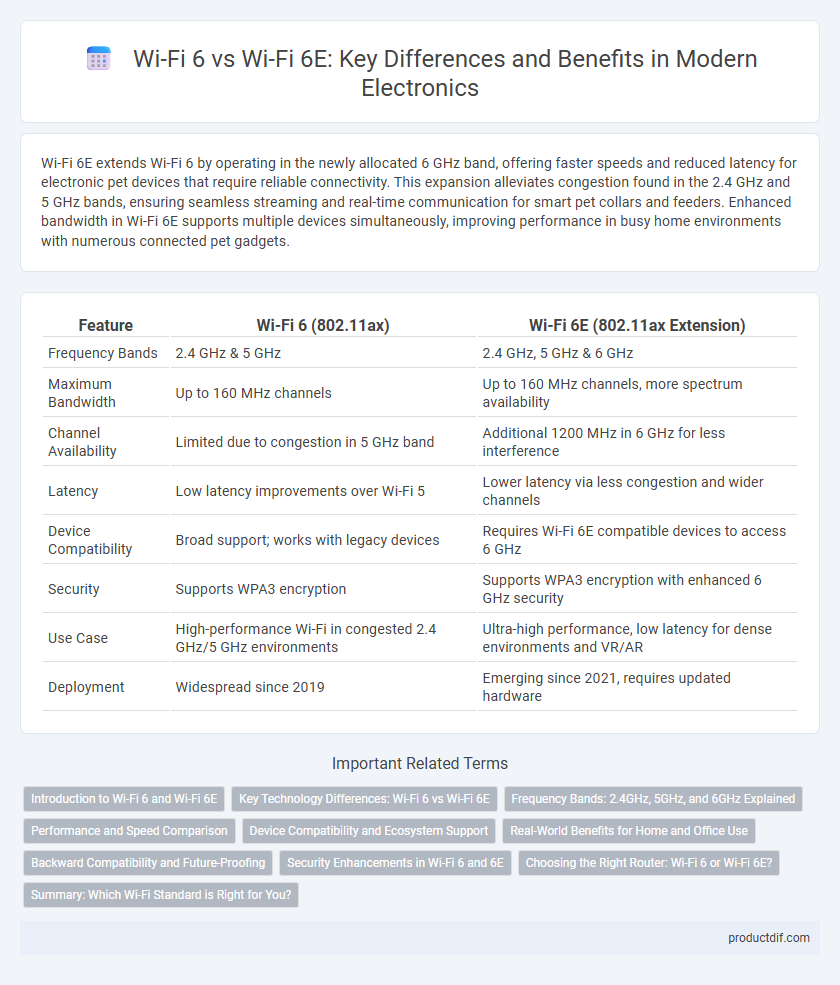
| Feature | Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) | Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax Extension) |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Bands | 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz & 6 GHz |
| Maximum Bandwidth | Up to 160 MHz channels | Up to 160 MHz channels, more spectrum availability |
| Channel Availability | Limited due to congestion in 5 GHz band | Additional 1200 MHz in 6 GHz for less interference |
| Latency | Low latency improvements over Wi-Fi 5 | Lower latency via less congestion and wider channels |
| Device Compatibility | Broad support; works with legacy devices | Requires Wi-Fi 6E compatible devices to access 6 GHz |
| Security | Supports WPA3 encryption | Supports WPA3 encryption with enhanced 6 GHz security |
| Use Case | High-performance Wi-Fi in congested 2.4 GHz/5 GHz environments | Ultra-high performance, low latency for dense environments and VR/AR |
| Deployment | Widespread since 2019 | Emerging since 2021, requires updated hardware |
Introduction to Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E
Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax, is the latest wireless standard designed to improve speed, capacity, and performance in congested environments by utilizing technologies such as OFDMA and MU-MIMO. Wi-Fi 6E extends Wi-Fi 6 capabilities by operating in the newly allocated 6 GHz frequency band, offering additional spectrum for faster speeds, lower latency, and reduced interference. The inclusion of the 6 GHz band in Wi-Fi 6E supports a growing number of connected devices and bandwidth-intensive applications in smart homes and enterprise settings.
Key Technology Differences: Wi-Fi 6 vs Wi-Fi 6E
Wi-Fi 6E extends Wi-Fi 6 by operating in the newly opened 6 GHz frequency band, providing increased bandwidth, reduced latency, and less interference compared to the traditional 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands used by Wi-Fi 6. Key technological differences include Wi-Fi 6E's support for up to 160 MHz channels exclusively in the 6 GHz band, enabling faster data rates and improved network capacity in dense environments. Wi-Fi 6 utilizes OFDMA, MU-MIMO, and Target Wake Time, which Wi-Fi 6E inherits, but the additional spectrum availability in Wi-Fi 6E significantly enhances overall wireless performance and efficiency.
Frequency Bands: 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz Explained
Wi-Fi 6 operates primarily on the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands, providing improved speed and efficiency in congested environments. Wi-Fi 6E extends these capabilities by adding access to the 6GHz band, offering wider channels and reduced interference for ultra-fast, low-latency wireless connections. The 6GHz spectrum in Wi-Fi 6E enables higher throughput and better performance in dense networks compared to the dual-band operation of Wi-Fi 6.
Performance and Speed Comparison
Wi-Fi 6E extends Wi-Fi 6 by operating in the 6 GHz band, offering more spectrum and less interference, which significantly boosts performance and speed compared to Wi-Fi 6's 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The wider channels in Wi-Fi 6E enable higher data rates, reaching up to 9.6 Gbps under optimal conditions, enhancing throughput in congested environments. Wi-Fi 6E also supports lower latency and improved network efficiency, making it ideal for high-demand applications like VR, streaming, and gaming.
Device Compatibility and Ecosystem Support
Wi-Fi 6 offers broad device compatibility with a well-established ecosystem supporting most current smartphones, laptops, and IoT devices. Wi-Fi 6E extends this compatibility by operating in the 6 GHz band, requiring new chipsets and firmware updates, limiting its usage to the latest devices. The adoption of Wi-Fi 6E is growing, but full ecosystem support depends on widespread hardware upgrades and regulatory approval in various regions.
Real-World Benefits for Home and Office Use
Wi-Fi 6E extends the capabilities of Wi-Fi 6 by utilizing the newly available 6 GHz band, offering increased bandwidth, lower latency, and reduced interference for home and office environments. Devices supporting Wi-Fi 6E experience faster data transfer speeds and more reliable connections, especially in crowded networks with multiple users and smart devices. Enhanced spectrum availability in Wi-Fi 6E enables smoother streaming, gaming, and video conferencing, making it ideal for modern wireless demands.
Backward Compatibility and Future-Proofing
Wi-Fi 6E extends Wi-Fi 6 capabilities by operating in the 6 GHz band, offering less interference and faster speeds while maintaining backward compatibility with Wi-Fi 6 and earlier standards. Devices supporting Wi-Fi 6E ensure future-proofing by leveraging the newly available spectrum, which accommodates increasing device density and bandwidth demands. This enhanced spectrum availability reduces network congestion, making Wi-Fi 6E a strategic choice for next-generation wireless environments.
Security Enhancements in Wi-Fi 6 and 6E
Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E both incorporate WPA3 encryption, providing robust protection against brute-force attacks and improving overall network security. Wi-Fi 6E extends these enhancements by leveraging the 6 GHz band, reducing network congestion and minimizing interference, which enhances the reliability and integrity of secure connections. The increased spectrum availability in Wi-Fi 6E also supports more secure simultaneous connections, benefiting environments requiring stringent data protection.
Choosing the Right Router: Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E?
Wi-Fi 6E extends Wi-Fi 6 by operating in the 6 GHz band, offering increased capacity, lower latency, and less interference for compatible devices. When choosing between Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E routers, consider the number of 6 GHz-capable devices in your environment and the need for ultra-fast, congestion-free connections in high-density areas. Budget and device compatibility are key factors since Wi-Fi 6 routers provide strong performance for most households, while Wi-Fi 6E is optimal for future-proofing and advanced networking scenarios.
Summary: Which Wi-Fi Standard is Right for You?
Wi-Fi 6E extends Wi-Fi 6 by operating in the 6 GHz band, offering lower latency, higher throughput, and reduced congestion compared to Wi-Fi 6's 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. For environments with many connected devices or high-density usage, Wi-Fi 6E provides superior performance and future-proofing. Wi-Fi 6 remains a cost-effective choice for typical home or office use where 6 GHz support is not crucial.
Wi-Fi 6 vs Wi-Fi 6E Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com