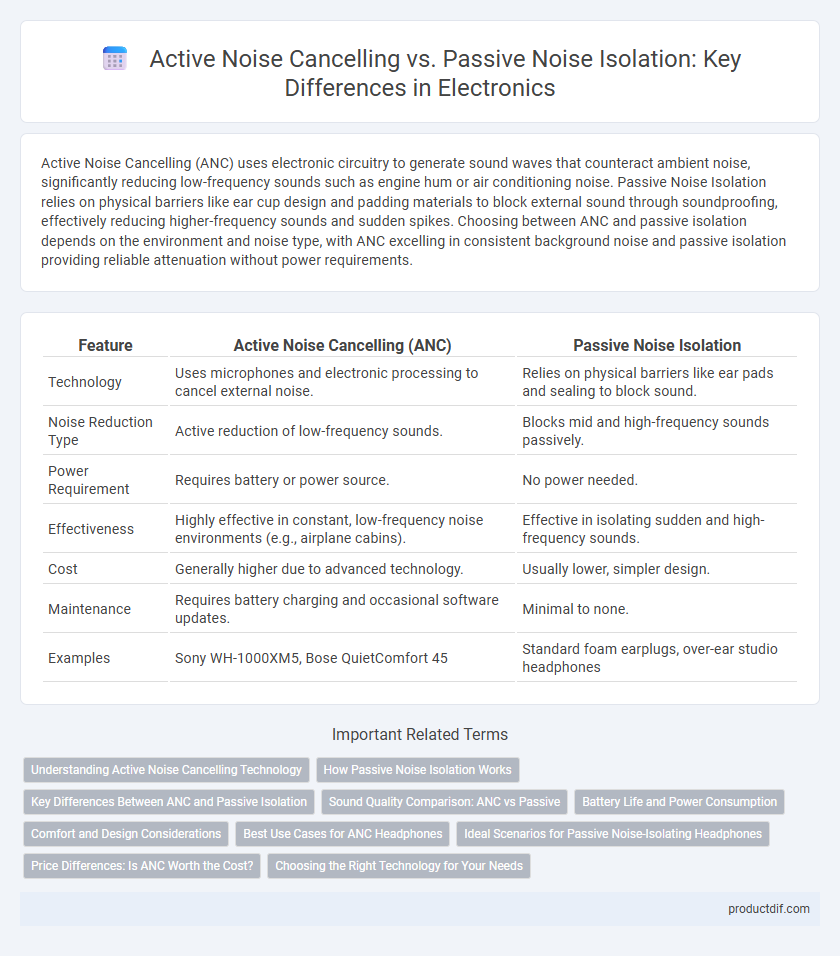
Active Noise Cancelling (ANC) uses electronic circuitry to generate sound waves that counteract ambient noise, significantly reducing low-frequency sounds such as engine hum or air conditioning noise. Passive Noise Isolation relies on physical barriers like ear cup design and padding materials to block external sound through soundproofing, effectively reducing higher-frequency sounds and sudden spikes. Choosing between ANC and passive isolation depends on the environment and noise type, with ANC excelling in consistent background noise and passive isolation providing reliable attenuation without power requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Active Noise Cancelling (ANC) | Passive Noise Isolation |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Uses microphones and electronic processing to cancel external noise. | Relies on physical barriers like ear pads and sealing to block sound. |
| Noise Reduction Type | Active reduction of low-frequency sounds. | Blocks mid and high-frequency sounds passively. |
| Power Requirement | Requires battery or power source. | No power needed. |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective in constant, low-frequency noise environments (e.g., airplane cabins). | Effective in isolating sudden and high-frequency sounds. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced technology. | Usually lower, simpler design. |
| Maintenance | Requires battery charging and occasional software updates. | Minimal to none. |
| Examples | Sony WH-1000XM5, Bose QuietComfort 45 | Standard foam earplugs, over-ear studio headphones |
Understanding Active Noise Cancelling Technology
Active Noise Cancelling (ANC) technology uses built-in microphones and advanced algorithms to detect and counteract external ambient sounds by producing anti-phase sound waves, effectively reducing unwanted noise in real time. This digital signal processing allows headphones and earbuds to offer a quieter listening experience without increasing volume, surpassing traditional Passive Noise Isolation which relies on physical barriers like ear cushions to block sound waves. Modern ANC systems often feature adaptive modes that adjust noise cancellation based on environmental factors, enhancing user comfort and audio clarity in dynamic settings.
How Passive Noise Isolation Works
Passive noise isolation works by physically blocking external sounds using materials such as dense foam, ear cushions, or sealed ear cups that create a barrier around the ear. This method relies on the acoustic attenuation properties of these materials to reduce ambient noise without electronic processing. High-quality earphones and headphones with thick padding and ergonomic design enhance passive noise isolation by fitting snugly to the ear, effectively minimizing sound leakage and external disturbances.
Key Differences Between ANC and Passive Isolation
Active Noise Cancelling (ANC) uses microphones and electronic processing to detect and counteract ambient noise, effectively reducing low-frequency sounds like engine hum or air conditioning. Passive Noise Isolation relies on physical barriers, such as earcup padding or in-ear seals, to block external noise, primarily excelling at attenuating high-frequency sounds. ANC typically requires batteries and electronics, while passive isolation operates silently without power, influencing device design and user experience.
Sound Quality Comparison: ANC vs Passive
Active Noise Cancelling (ANC) technology uses microphones and electronic processing to reduce ambient noise, providing clearer and more immersive sound quality by minimizing external distractions. Passive noise isolation relies on physical barriers such as ear cup design and materials to block sound, which can preserve the natural audio signature but may not be as effective in eliminating low-frequency noise. While ANC enhances audio clarity in noisy environments, passive isolation typically offers more accurate sound reproduction without electronic alteration, making the choice dependent on listening preferences and environment.
Battery Life and Power Consumption
Active noise cancelling (ANC) headphones rely on powered microphones and noise-cancelling circuits, which significantly increase battery consumption, typically reducing playback time to around 20-30 hours per charge. In contrast, passive noise isolation uses physical barriers like foam ear cups to block sound without requiring power, resulting in virtually unlimited battery life. Users prioritizing longer battery duration often prefer passive noise isolation, while those valuing advanced noise reduction capabilities may accept shorter usage times with ANC technology.
Comfort and Design Considerations
Active Noise Cancelling headphones use advanced microphone and speaker technology to reduce ambient sounds, offering enhanced comfort with lightweight designs and adjustable ear cups that minimize pressure during extended use. Passive Noise Isolation relies on physical materials like memory foam and tightly sealed ear cups to block external noise, often resulting in bulkier and heavier devices that may cause discomfort over long periods. Design considerations prioritize ergonomics, material breathability, and weight distribution to ensure optimal comfort for daily wear in both active noise cancelling and passive noise isolation models.
Best Use Cases for ANC Headphones
Active Noise Cancelling (ANC) headphones excel in environments with consistent, low-frequency sounds such as airplane cabins, busy offices, or public transit, effectively reducing ambient noise for an immersive audio experience. Passive noise isolation performs well in blocking higher-frequency sounds by physically sealing the ear, making it suitable for quiet settings like home or studio use where subtle noise reduction suffices. ANC technology is optimal for travelers and commuters seeking comfort and clarity without the bulk of heavy earplugs or noise-isolating earmuffs.
Ideal Scenarios for Passive Noise-Isolating Headphones
Passive noise-isolating headphones excel in environments with consistent, low-frequency background noise, such as airplane cabins and busy offices, by physically blocking external sounds using dense ear cups and snug fits. These headphones are ideal for users seeking low latency and natural sound quality without electronic interference, making them perfect for audiophiles and professional musicians during recording sessions. Their battery-free design also offers uninterrupted listening, proving advantageous during long commutes or extended use where charging opportunities are limited.
Price Differences: Is ANC Worth the Cost?
Active noise cancelling (ANC) headphones typically cost 20-50% more than passive noise isolation models due to advanced microphones and processing chips that reduce ambient noise. While ANC offers superior sound quality and comfort in noisy environments, passive isolation relies on physical barriers like ear padding and materials to block sound, often making it a more budget-friendly choice. Consumers should weigh the price premium against their usage scenarios, as ANC delivers clear benefits in high-traffic or travel settings, but may not justify the cost for casual, quiet indoor listening.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
Active noise cancelling (ANC) headphones use microphones and electronic processing to reduce ambient sounds, making them ideal for noisy environments like airplanes or busy offices. Passive noise isolation relies on physical barriers, such as snug ear cups or ear tips, to block external noise and works well in moderately loud settings or for those who prefer a simpler, battery-free solution. Selecting the right technology depends on your typical noise environment, comfort preferences, and whether you prioritize battery life or advanced sound customization.
Active Noise Cancelling vs Passive Noise Isolation Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com