Optical zoom uses the camera's lens to magnify the subject, preserving image quality by capturing details through physical adjustments. Digital zoom enlarges the image by cropping and interpolating pixels, often resulting in reduced sharpness and clarity. For high-resolution and detailed images, optical zoom is the preferred choice over digital zoom.
Table of Comparison
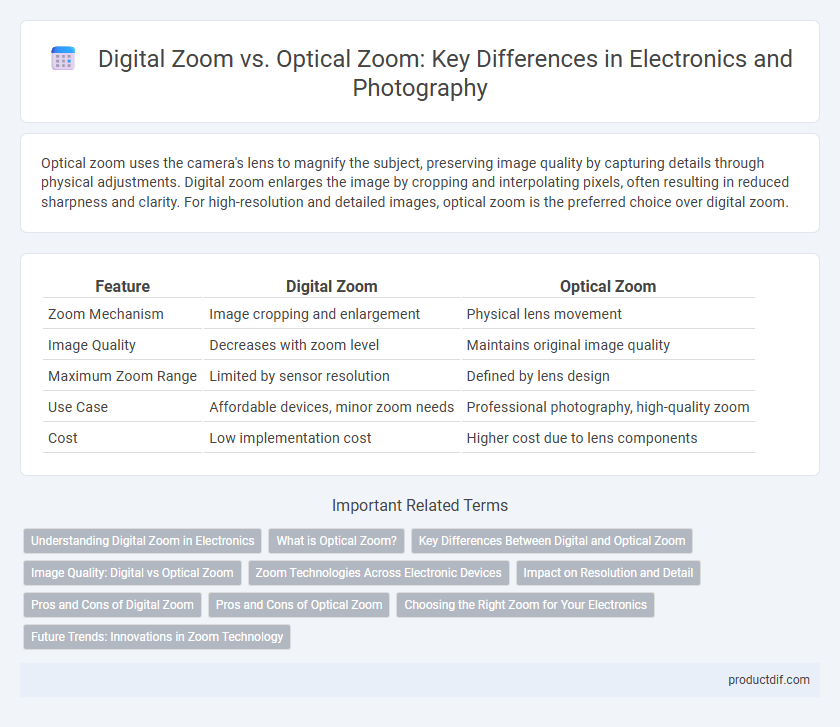
| Feature | Digital Zoom | Optical Zoom |
|---|---|---|
| Zoom Mechanism | Image cropping and enlargement | Physical lens movement |
| Image Quality | Decreases with zoom level | Maintains original image quality |
| Maximum Zoom Range | Limited by sensor resolution | Defined by lens design |
| Use Case | Affordable devices, minor zoom needs | Professional photography, high-quality zoom |
| Cost | Low implementation cost | Higher cost due to lens components |
Understanding Digital Zoom in Electronics
Digital zoom in electronics uses software algorithms to enlarge an image by cropping and interpolating pixels, resulting in lower image quality compared to optical zoom. Unlike optical zoom, which physically adjusts the lens to magnify the subject without loss of resolution, digital zoom can introduce noise and reduce sharpness. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting cameras or devices where image clarity and detail retention are important.
What is Optical Zoom?
Optical zoom is a camera feature that uses the lens's physical movement to magnify the subject without losing image quality. It relies on adjustable focal length to bring distant objects closer, preserving sharpness and detail. Unlike digital zoom, optical zoom captures images with true optical resolution, ensuring clearer and more accurate photos.
Key Differences Between Digital and Optical Zoom
Optical zoom uses the camera's lens to magnify the subject by adjusting the focal length, preserving image quality and detail without pixelation. Digital zoom enlarges the image by cropping and interpolating pixels, often resulting in reduced resolution and a loss of sharpness. Key differences include optical zoom's use of physical lens movement versus digital zoom's reliance on software processing, impacting image clarity and overall photographic quality.
Image Quality: Digital vs Optical Zoom
Optical zoom maintains image quality by physically adjusting the lens to magnify the subject, preserving detail and sharpness without pixelation. Digital zoom enlarges the image digitally by cropping and interpolating pixels, often resulting in reduced resolution and blurred details. For superior image quality, optical zoom is preferred as it delivers true optical magnification without degrading the original image data.
Zoom Technologies Across Electronic Devices
Digital zoom enlarges images by cropping and digitally interpolating pixels, often resulting in reduced image quality, while optical zoom uses the physical movement of lens elements to magnify the subject, maintaining clarity and detail. Optical zoom is preferred in cameras and smartphones for high-quality image capture, especially in varying lighting conditions, whereas digital zoom serves as a convenient but less precise enhancement when optical zoom reaches its limit. Advances in hybrid zoom technologies combine optical and digital methods to optimize zoom performance across devices like smartphones, action cameras, and drones.
Impact on Resolution and Detail
Optical zoom uses the camera lens to magnify an image, preserving original resolution and detail by physically adjusting the focal length. Digital zoom enlarges a cropped portion of the image digitally, which reduces resolution and results in loss of fine detail. High-quality optical zoom lenses deliver sharper images and clearer detail compared to digital zoom, which often produces pixelation and blur.
Pros and Cons of Digital Zoom
Digital zoom enlarges the image by cropping and interpolating pixels, which often results in reduced image quality and loss of detail compared to optical zoom, which uses lens movement for true magnification. Digital zoom is advantageous for its cost-effectiveness and ease of implementation in compact devices without moving parts. However, the primary drawback is the degradation of image sharpness and increased pixelation, making it less suitable for professional photography or high-quality imaging applications.
Pros and Cons of Optical Zoom
Optical zoom leverages the camera lens' physical movement to magnify images, delivering high-resolution and clear pictures without quality loss compared to digital zoom. Its main advantage is preserving image detail, making it ideal for professional photography and long-distance shots, though optical zoom lenses tend to be bulkier and more expensive. The drawback includes limited zoom range and mechanical complexity, which can result in slower focus speeds and increased camera size.
Choosing the Right Zoom for Your Electronics
Optical zoom uses lens movement to magnify images without quality loss, ideal for cameras and smartphones needing sharp, high-resolution photos. Digital zoom enlarges images by cropping and interpolating pixels, which can degrade clarity but offers a budget-friendly option for devices with fixed lenses. Selecting the right zoom depends on your device's hardware capabilities and your priority for image quality versus convenience and cost.
Future Trends: Innovations in Zoom Technology
Emerging innovations in zoom technology emphasize the fusion of digital zoom algorithms with advanced optical components to enhance image clarity without pixel loss. Computational photography leverages AI-driven super-resolution and real-time image stabilization to push the boundaries of digital zoom capabilities. Future trends also highlight the integration of periscope lenses and liquid lens technology, enabling compact designs alongside superior zoom ranges.
Digital Zoom vs Optical Zoom Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com