AUX and Optical Audio serve as common methods for transmitting sound signals, with AUX utilizing analog connections through a 3.5mm jack that allows compatibility with most devices but is prone to interference and signal degradation. Optical Audio uses fiber optic cables to deliver high-quality digital audio with minimal noise, supporting surround sound formats and providing better clarity for home theater systems. Choosing between AUX and Optical Audio depends on your equipment's compatibility and the desired audio fidelity, with Optical Audio being superior for immersive and noise-free listening experiences.
Table of Comparison
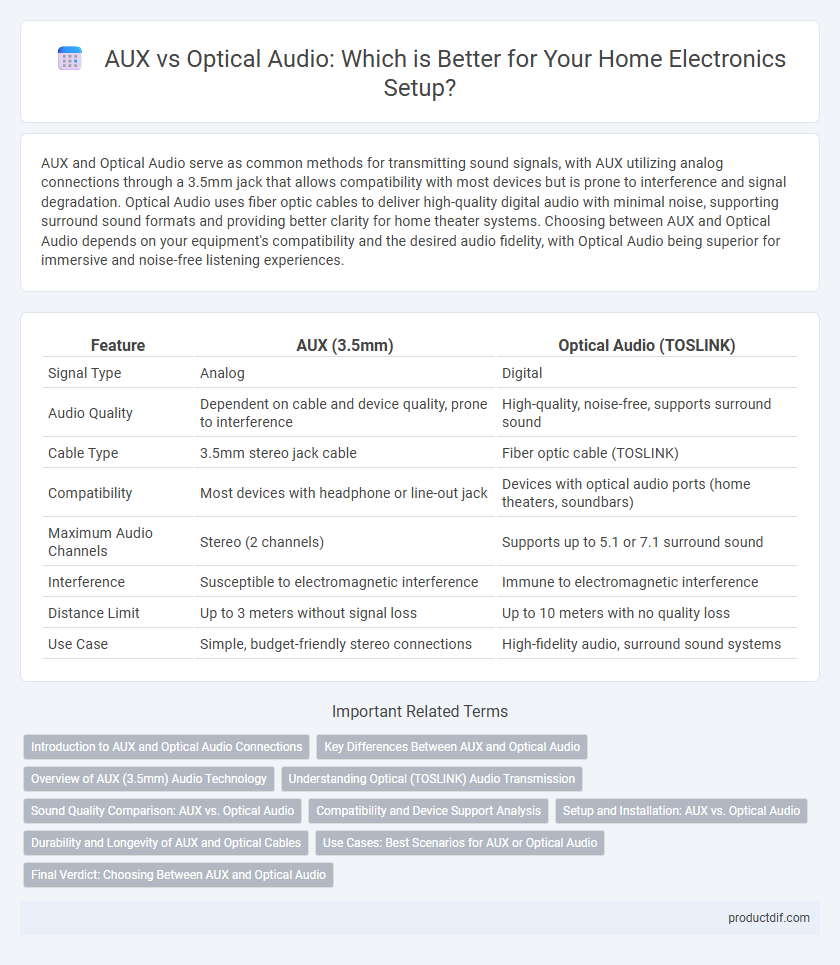
| Feature | AUX (3.5mm) | Optical Audio (TOSLINK) |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Analog | Digital |
| Audio Quality | Dependent on cable and device quality, prone to interference | High-quality, noise-free, supports surround sound |
| Cable Type | 3.5mm stereo jack cable | Fiber optic cable (TOSLINK) |
| Compatibility | Most devices with headphone or line-out jack | Devices with optical audio ports (home theaters, soundbars) |
| Maximum Audio Channels | Stereo (2 channels) | Supports up to 5.1 or 7.1 surround sound |
| Interference | Susceptible to electromagnetic interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference |
| Distance Limit | Up to 3 meters without signal loss | Up to 10 meters with no quality loss |
| Use Case | Simple, budget-friendly stereo connections | High-fidelity audio, surround sound systems |
Introduction to AUX and Optical Audio Connections
AUX (auxiliary) audio connections utilize a 3.5mm jack to transmit analog sound signals, making them compatible with most headphones, smartphones, and portable speakers. Optical audio connections, also known as TOSLINK, transmit digital audio signals through fiber optic cables, providing higher sound quality and resistance to electromagnetic interference. While AUX is widely used for convenience and compatibility, optical audio is preferred for home theater systems and professional audio equipment due to its superior audio fidelity.
Key Differences Between AUX and Optical Audio
AUX audio transmits analog signals through a 3.5mm jack, while Optical audio uses fiber optic cables to deliver digital sound via light pulses, ensuring higher audio fidelity and reduced interference. AUX cables support stereo sound and are commonly compatible with most portable devices, whereas Optical audio enables multi-channel surround sound, ideal for home theater systems. The key difference lies in signal type and quality, with Optical providing clearer, noise-free audio compared to the susceptible-to-interference analog AUX connection.
Overview of AUX (3.5mm) Audio Technology
AUX (3.5mm) audio technology serves as a versatile analog connection widely used for transmitting stereo sound between devices like smartphones, headphones, and car audio systems. This standard 3.5mm jack supports uncompressed audio signals, offering compatibility with a broad range of consumer electronics without the need for digital-to-analog conversion. Despite limitations in noise immunity compared to digital formats, AUX cables provide reliable, low-latency audio transmission ideal for everyday use.
Understanding Optical (TOSLINK) Audio Transmission
Optical (TOSLINK) audio transmission uses fiber optic cables to transmit digital audio signals as pulses of light, ensuring minimal interference and superior sound quality compared to analog AUX cables. This method supports multi-channel audio formats such as Dolby Digital and DTS, making it ideal for home theater systems and high-fidelity audio setups. The TOSLINK connector's immunity to electromagnetic interference makes it a reliable choice for clear, distortion-free audio transmission over moderate distances.
Sound Quality Comparison: AUX vs. Optical Audio
Optical audio delivers superior sound quality compared to AUX by transmitting digital signals with minimal interference, preserving audio fidelity. AUX cables rely on analog transmission, which can introduce noise and signal degradation, especially over longer distances. Optical connections support higher bandwidth and surround sound formats, making them ideal for high-definition audio experiences.
Compatibility and Device Support Analysis
AUX audio output supports a wide range of devices including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and older audio systems due to its analog nature and 3.5mm jack compatibility. Optical audio, using TOSLINK connections, offers superior digital sound quality but requires devices equipped with compatible optical ports, commonly found in modern TVs, gaming consoles, and higher-end audio receivers. Compatibility analysis reveals AUX is more universally supported across legacy and contemporary electronics, while optical audio demands specific hardware, limiting its device support but enhancing audio fidelity.
Setup and Installation: AUX vs. Optical Audio
AUX setup requires a 3.5mm analog cable, making installation straightforward and compatible with most devices, but it is prone to signal degradation over long distances. Optical audio setup involves TOSLINK cables, which transmit digital signals, eliminating interference and delivering higher sound quality, yet require devices with optical ports and more careful cable alignment. Choosing between AUX and optical audio depends on device compatibility, desired audio fidelity, and installation complexity.
Durability and Longevity of AUX and Optical Cables
AUX cables, typically made with copper wiring and plastic insulation, offer moderate durability but are prone to wear and signal degradation over time due to frequent bending and connector stress. Optical cables, using fiber optic strands encased in protective sheathing, provide superior longevity and resistance to electromagnetic interference, maintaining high-quality audio signals with less risk of damage. The inherent durability of optical cables makes them a preferred choice for long-term use in high-fidelity audio setups, while AUX cables often require more frequent replacement.
Use Cases: Best Scenarios for AUX or Optical Audio
AUX cables excel in scenarios requiring simple, low-cost connections for portable devices like smartphones and laptops, offering compatibility with most audio sources despite potential signal degradation over long distances. Optical audio is ideal for high-fidelity sound systems such as home theaters and gaming consoles, providing superior digital audio quality and eliminating electrical interference. Selecting between AUX and optical depends largely on the priority of audio quality versus device compatibility and cable length.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between AUX and Optical Audio
For optimal audio quality, Optical Audio delivers superior digital sound with minimal interference, making it ideal for high-fidelity setups and home theaters. AUX cables provide versatile analog connectivity compatible with a wide range of devices but may introduce signal degradation and noise. Selecting between AUX and Optical Audio depends on the user's priority for sound clarity, device compatibility, and cable convenience.
AUX vs Optical Audio Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com