Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer cycle life compared to NiMH batteries, making them ideal for compact electronics and high-drain devices. NiMH batteries are more environmentally friendly and perform better in low-temperature conditions, but they generally have a lower capacity and higher self-discharge rate. Choosing between Li-ion and NiMH depends on specific device requirements, balancing energy needs, longevity, and environmental considerations.
Table of Comparison
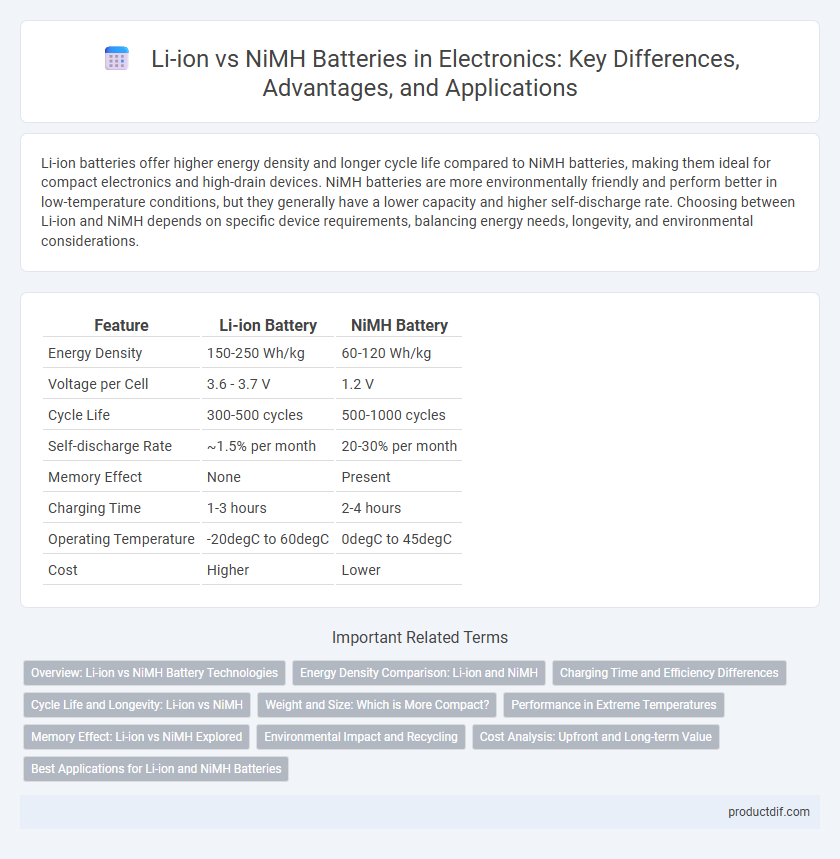
| Feature | Li-ion Battery | NiMH Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 150-250 Wh/kg | 60-120 Wh/kg |
| Voltage per Cell | 3.6 - 3.7 V | 1.2 V |
| Cycle Life | 300-500 cycles | 500-1000 cycles |
| Self-discharge Rate | ~1.5% per month | 20-30% per month |
| Memory Effect | None | Present |
| Charging Time | 1-3 hours | 2-4 hours |
| Operating Temperature | -20degC to 60degC | 0degC to 45degC |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Overview: Li-ion vs NiMH Battery Technologies
Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer cycle life compared to NiMH batteries, making them ideal for portable electronics requiring lightweight and compact power sources. NiMH batteries provide better performance in high-drain applications and exhibit less memory effect, but have lower energy capacity and a shorter lifespan. Both technologies involve electrochemical reactions with different electrode materials: Li-ion uses lithium compounds, while NiMH uses nickel and metal hydride alloys.
Energy Density Comparison: Li-ion and NiMH
Li-ion batteries offer a significantly higher energy density, typically ranging from 150 to 250 Wh/kg, compared to NiMH batteries, which usually provide around 60 to 120 Wh/kg. This higher energy density enables Li-ion batteries to store more energy in a smaller and lighter package, making them ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles. Furthermore, Li-ion cells maintain better voltage stability throughout discharge, enhancing overall device performance relative to NiMH technology.
Charging Time and Efficiency Differences
Li-ion batteries typically offer faster charging times, often reaching full charge within 1 to 3 hours, compared to NiMH batteries which may require 4 to 6 hours. Li-ion cells exhibit higher energy efficiency, retaining up to 90-95% of charge capacity, while NiMH batteries usually maintain around 70-80%. These efficiency differences lead to longer runtimes and lower energy loss for Li-ion batteries in electronic devices.
Cycle Life and Longevity: Li-ion vs NiMH
Li-ion batteries typically offer a cycle life of 300 to 500 full charge-discharge cycles, while NiMH batteries generally provide around 500 to 1000 cycles depending on usage and quality. Despite a lower cycle life, Li-ion batteries maintain higher capacity retention and efficiency throughout their lifespan, contributing to superior longevity in most electronic applications. NiMH batteries tend to suffer from higher self-discharge rates and gradual capacity loss, which can reduce effective operational life despite their higher nominal cycle count.
Weight and Size: Which is More Compact?
Li-ion batteries are significantly more compact and lightweight compared to NiMH batteries, making them ideal for portable electronic devices where space and weight are critical. Li-ion cells offer higher energy density, allowing smaller battery packs without sacrificing capacity. In contrast, NiMH batteries tend to be bulkier and heavier, reducing their suitability for slim and lightweight gadgets.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Li-ion batteries maintain higher capacity and discharge rates in extreme temperatures, performing efficiently between -20degC and 60degC, making them suitable for harsh environmental conditions. NiMH batteries suffer significant capacity loss below 0degC and degrade rapidly above 40degC, resulting in reduced overall performance and shorter lifespan. For applications requiring reliable power delivery in extreme climates, Li-ion batteries offer superior thermal stability and efficiency compared to NiMH alternatives.
Memory Effect: Li-ion vs NiMH Explored
Li-ion batteries exhibit minimal memory effect, allowing users to recharge at any time without significant capacity loss, unlike NiMH batteries which suffer notable memory effect if repeatedly recharged before full discharge. NiMH cells require periodic full discharge cycles to maintain optimal performance and prevent capacity degradation caused by the accumulation of partial charge cycles. Choosing Li-ion over NiMH is advantageous for devices demanding frequent, irregular charging due to its superior charge retention and reduced maintenance needs.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Li-ion batteries have a higher energy density and longer lifecycle but pose greater environmental risks due to the extraction of lithium and cobalt, which can cause habitat damage and pollution. NiMH batteries use less toxic materials and are easier to recycle, reducing their ecological footprint compared to Li-ion cells. Efficient recycling programs for both battery types are crucial to minimize landfill waste and recover valuable metals like nickel, cobalt, and rare earth elements.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-term Value
Li-ion batteries typically have a higher upfront cost compared to NiMH batteries but offer greater energy density and longer lifespan, resulting in lower replacement frequency and overall cost savings. NiMH batteries are more affordable initially but tend to suffer from higher self-discharge rates and shorter cycle life, increasing long-term expenses due to frequent replacements. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors Li-ion technology for applications requiring high efficiency and durability despite the initial investment.
Best Applications for Li-ion and NiMH Batteries
Li-ion batteries excel in high-energy-density applications such as smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles due to their lightweight and long cycle life. NiMH batteries are preferred in devices requiring moderate energy density and robust performance at lower costs, like cordless power tools and hybrid vehicles. Their tolerance for high discharge rates and better environmental profile makes NiMH suitable for rugged and budget-conscious electronics.
Li-ion vs NiMH Battery Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com