Analog tuning offers a tactile and continuous frequency adjustment, favored for its smooth control and simplicity in radio receivers. Digital tuning provides precise frequency selection with enhanced stability and the capability to store presets, improving user convenience and accuracy. While analog tuning delivers a traditional experience, digital tuning leverages modern technology for efficiency and repeatability in electronic devices.
Table of Comparison
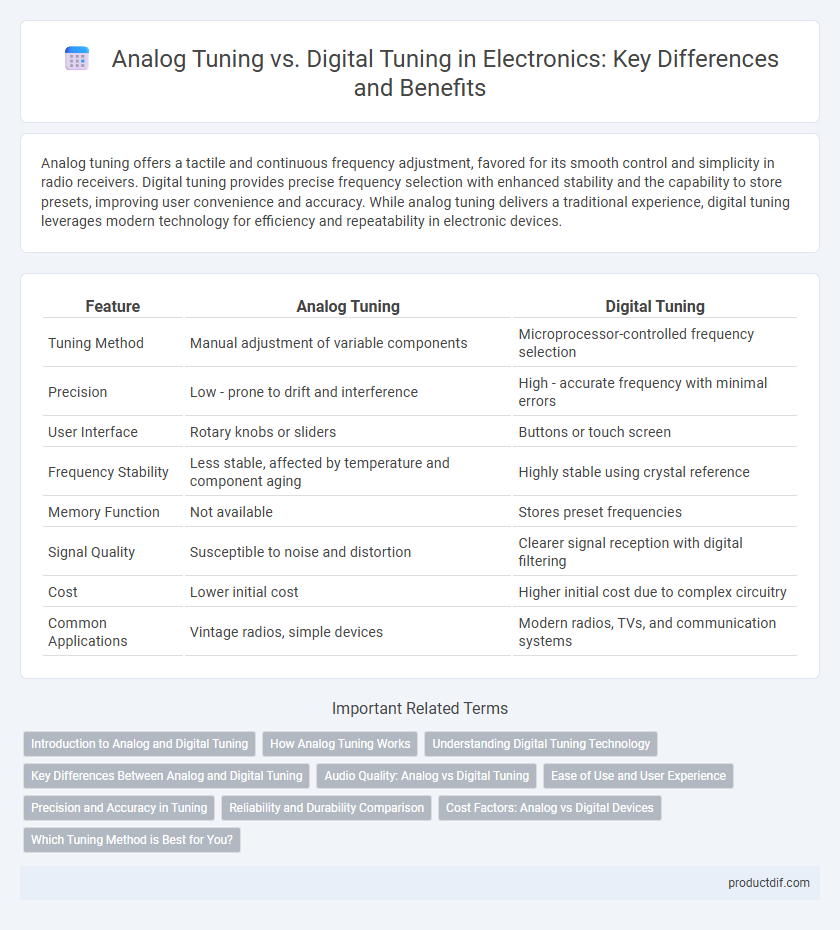
| Feature | Analog Tuning | Digital Tuning |
|---|---|---|
| Tuning Method | Manual adjustment of variable components | Microprocessor-controlled frequency selection |
| Precision | Low - prone to drift and interference | High - accurate frequency with minimal errors |
| User Interface | Rotary knobs or sliders | Buttons or touch screen |
| Frequency Stability | Less stable, affected by temperature and component aging | Highly stable using crystal reference |
| Memory Function | Not available | Stores preset frequencies |
| Signal Quality | Susceptible to noise and distortion | Clearer signal reception with digital filtering |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost due to complex circuitry |
| Common Applications | Vintage radios, simple devices | Modern radios, TVs, and communication systems |
Introduction to Analog and Digital Tuning
Analog tuning relies on continuous variable signals to adjust frequencies, offering smooth, intuitive control commonly used in traditional radios and older television sets. Digital tuning employs microprocessors and digital signal processing to precisely select frequencies, enabling features like preset stations and enhanced signal stability. The transition from analog to digital tuning reflects advancements in electronics, improving accuracy and user experience in modern devices.
How Analog Tuning Works
Analog tuning operates through a variable capacitor or inductor that adjusts the resonant frequency of the radio circuit, allowing precise selection of specific frequencies. This mechanical method relies on continuous voltage control, providing smooth and gradual frequency changes without discrete steps. The tactile feedback from the tuning knob offers intuitive operation, favored in vintage radios and simpler electronic devices.
Understanding Digital Tuning Technology
Digital tuning technology utilizes microprocessors and digital signal processing to precisely select frequencies, offering improved accuracy and stability over analog tuning methods. It converts analog signals into digital data, allowing for seamless channel selection, noise reduction, and enhanced signal clarity. This technology supports features like automatic frequency control and memory presets, significantly enhancing user experience and device performance in modern electronic systems.
Key Differences Between Analog and Digital Tuning
Analog tuning relies on continuous signal adjustment through variable capacitors or inductors, offering a smooth frequency change but often lacks precision. Digital tuning uses microcontrollers and digital signal processing (DSP) techniques, enabling exact frequency selection and improved stability. Key differences include analog's susceptibility to drift and noise versus digital's enhanced accuracy and programmability in devices like radios and televisions.
Audio Quality: Analog vs Digital Tuning
Analog tuning offers continuous signal variation, preserving the natural warmth and subtle nuances of audio, which audiophiles often prefer for its rich, authentic sound quality. Digital tuning converts audio signals into discrete digital data, enabling precise frequency control and noise reduction, resulting in clearer sound but sometimes perceived as less "organic." The choice between analog and digital tuning significantly impacts audio fidelity, with analog favored for warmth and digital for clarity and consistency.
Ease of Use and User Experience
Analog tuning offers a tactile and intuitive experience with a physical dial that provides immediate feedback, appealing to users who prefer manual control and simplicity. Digital tuning enhances precision and speed, allowing users to quickly access exact frequencies with minimal effort through buttons or touch interfaces. User experience is often improved in digital systems by features like presets and automatic station scanning, reducing the need for constant adjustment.
Precision and Accuracy in Tuning
Analog tuning relies on variable resistors or capacitors to adjust frequency, offering smooth but often less precise control prone to drift and component tolerance issues. Digital tuning employs microcontrollers and digital signal processors, providing highly accurate frequency settings with repeatability and minimal deviation. Enhanced precision and stability in digital tuning improve overall performance in modern electronic devices requiring exact frequency alignment.
Reliability and Durability Comparison
Analog tuning systems offer simplicity and robustness with fewer electronic components, enhancing long-term reliability and resistance to power fluctuations. Digital tuning provides precise frequency control and stability but relies on microcontrollers and digital circuits that may be more susceptible to environmental factors and component wear over time. In terms of durability, analog mechanisms often withstand harsh conditions better, while digital systems excel in repeatability but may require periodic firmware updates or recalibration.
Cost Factors: Analog vs Digital Devices
Analog tuning devices typically incur lower initial costs due to simpler circuitry and fewer components, making them more economical for basic applications. Digital tuning systems, while often more expensive upfront due to advanced microprocessors and software integration, offer greater precision and flexibility that can reduce long-term maintenance and upgrade expenses. Cost factors also include the scalability and production volume, where digital devices benefit from economies of scale, potentially narrowing the price gap over time.
Which Tuning Method is Best for You?
Analog tuning offers precise manual control with a tactile dial experience, ideal for users who prefer hands-on adjustment and simplicity without relying on software. Digital tuning provides enhanced accuracy, preset memory channels, and ease of use, making it suitable for those seeking convenience and modern features. Choosing the best tuning method depends on your preference for manual interaction versus automated precision and functionality in electronic devices.
Analog Tuning vs Digital Tuning Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com