Micro-USB connectors are widely used in older electronic devices but offer slower data transfer speeds and lower power delivery compared to USB-C. USB-C supports faster charging, higher data rates, and reversible plug orientation, making it the standard for modern smartphones, laptops, and other gadgets. Transitioning to USB-C enhances device compatibility and future-proofs connections due to its improved efficiency and versatility.
Table of Comparison
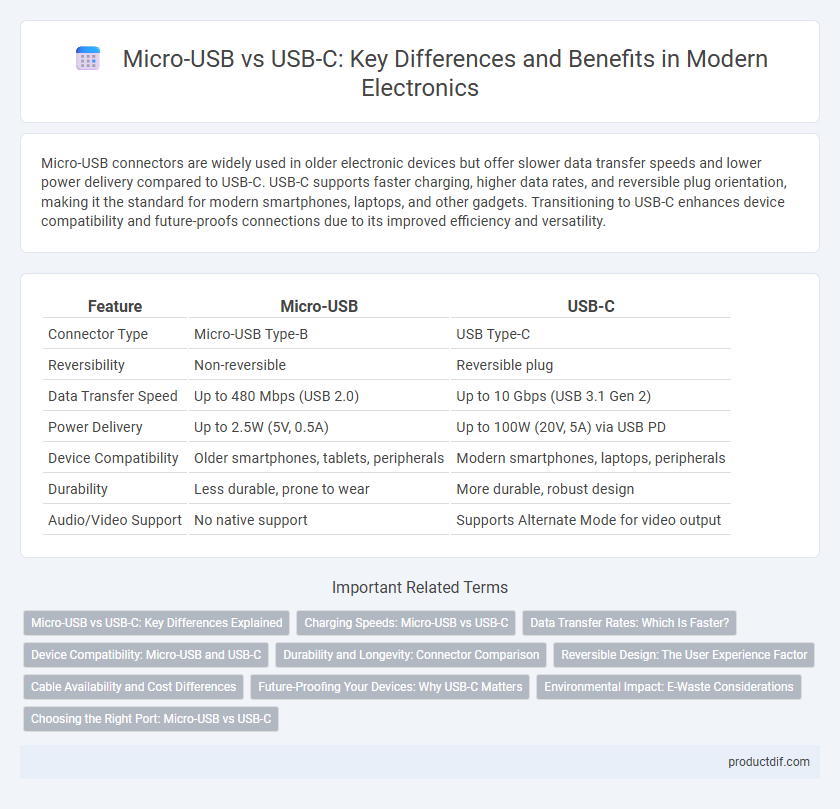
| Feature | Micro-USB | USB-C |
|---|---|---|
| Connector Type | Micro-USB Type-B | USB Type-C |
| Reversibility | Non-reversible | Reversible plug |
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 480 Mbps (USB 2.0) | Up to 10 Gbps (USB 3.1 Gen 2) |
| Power Delivery | Up to 2.5W (5V, 0.5A) | Up to 100W (20V, 5A) via USB PD |
| Device Compatibility | Older smartphones, tablets, peripherals | Modern smartphones, laptops, peripherals |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to wear | More durable, robust design |
| Audio/Video Support | No native support | Supports Alternate Mode for video output |
Micro-USB vs USB-C: Key Differences Explained
Micro-USB connectors feature a slim, tapered design with a maximum data transfer speed of 480 Mbps (USB 2.0), while USB-C supports reversible plugs and significantly faster transfer rates up to 10 Gbps (USB 3.1 and beyond). USB-C delivers higher power output up to 100W for rapid charging and supports versatile protocols, including video output via DisplayPort or HDMI, unlike Micro-USB's limited power and functionality. The adoption of USB-C benefits modern electronics with enhanced durability, universal compatibility, and future-proofing compared to the older, less robust Micro-USB standard.
Charging Speeds: Micro-USB vs USB-C
USB-C supports significantly faster charging speeds than Micro-USB due to its higher power delivery capability of up to 100W, compared to Micro-USB's maximum of 15W. USB-C utilizes advanced USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) protocols that enable dynamic voltage and current adjustments, resulting in efficient and rapid device charging. In contrast, Micro-USB is limited by older standards and lower current thresholds, making it less suitable for fast-charging modern electronics.
Data Transfer Rates: Which Is Faster?
USB-C supports significantly higher data transfer rates than Micro-USB, reaching up to 10 Gbps with USB 3.1 and beyond, compared to Micro-USB's maximum of 480 Mbps under USB 2.0 standards. This speed advantage makes USB-C ideal for transferring large files quickly and efficiently between devices. Enhanced backward compatibility and power delivery features further underscore USB-C's superiority for modern electronic applications.
Device Compatibility: Micro-USB and USB-C
Micro-USB connectors are widely compatible with older smartphones, tablets, and accessories, making them a standard for many legacy devices. USB-C offers enhanced compatibility with newer devices, including laptops, smartphones, and peripherals, supporting higher data transfer rates and power delivery. Transitioning to USB-C ensures future-proof connectivity across a broader range of modern electronics.
Durability and Longevity: Connector Comparison
USB-C connectors feature a robust design with a reinforced metal shell and symmetrical orientation, enhancing durability and reducing wear over time compared to Micro-USB. Micro-USB ports have a fragile, asymmetrical design prone to bending and damage after frequent insertions. The improved engineering of USB-C results in a longer lifespan, supporting up to 10,000 connection cycles, in contrast to Micro-USB's approximate 1,500 cycles.
Reversible Design: The User Experience Factor
Micro-USB connectors feature a non-reversible design that often leads to user frustration and increased wear due to incorrect insertion attempts. USB-C connectors offer a fully reversible design, enhancing user experience by allowing easy connection without orientation concerns. This improvement reduces port damage and streamlines device usability across smartphones, laptops, and other electronics.
Cable Availability and Cost Differences
Micro-USB cables remain widely available and generally cost less due to established manufacturing and widespread use in older devices. USB-C cables, though slightly more expensive, offer increasing availability as newer electronics adopt this versatile standard for faster data transfer and charging. Price differences are narrowing as USB-C becomes the universal choice across smartphones, tablets, and laptops, driving mass production efficiencies.
Future-Proofing Your Devices: Why USB-C Matters
USB-C supports faster data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps compared to Micro-USB's 480 Mbps, ensuring compatibility with future high-performance electronics. Its reversible connector design reduces wear and tear, enhancing durability for long-term device use. The widespread adoption of USB-C in new devices guarantees better future-proofing, making it the preferred standard over Micro-USB.
Environmental Impact: E-Waste Considerations
Micro-USB connectors contribute significantly to e-waste due to their widespread use and frequent device replacements, resulting in discarded cables and adapters. USB-C offers universal compatibility and durability, reducing the need for multiple chargers and lowering electronic waste generation. Transitioning to USB-C can promote sustainability by minimizing resource consumption and enhancing recycling efficiency in the electronics industry.
Choosing the Right Port: Micro-USB vs USB-C
Choosing the right port between Micro-USB and USB-C depends on device compatibility, charging speed, and data transfer needs. USB-C offers reversible connectors, faster charging up to 100W with USB Power Delivery, and data transfer rates reaching 10 Gbps with USB 3.1 or higher standards. Micro-USB, while widely used in older or budget devices, has slower transfer speeds and less robust durability, making USB-C the preferred choice for modern electronics.
Micro-USB vs USB-C Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com