Thermal insulation in building materials focuses on reducing heat transfer to maintain indoor temperature, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort. Acoustic insulation primarily aims to minimize sound transmission, creating quieter living or working environments by absorbing or blocking noise. Selecting materials that balance both thermal and acoustic properties can optimize overall building performance and occupant well-being.
Table of Comparison
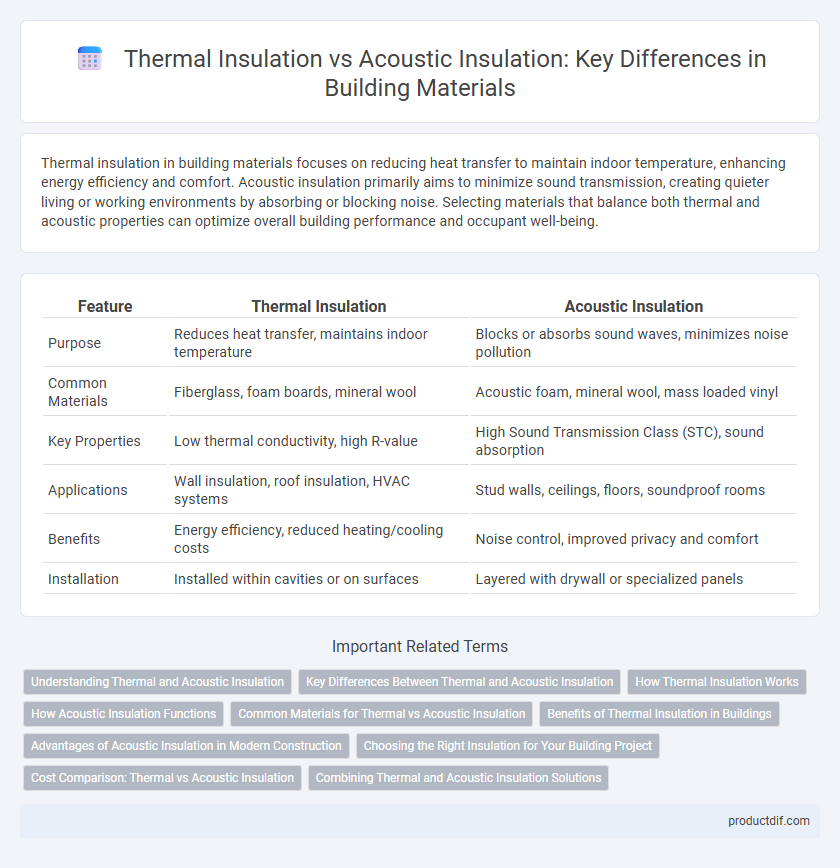
| Feature | Thermal Insulation | Acoustic Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces heat transfer, maintains indoor temperature | Blocks or absorbs sound waves, minimizes noise pollution |
| Common Materials | Fiberglass, foam boards, mineral wool | Acoustic foam, mineral wool, mass loaded vinyl |
| Key Properties | Low thermal conductivity, high R-value | High Sound Transmission Class (STC), sound absorption |
| Applications | Wall insulation, roof insulation, HVAC systems | Stud walls, ceilings, floors, soundproof rooms |
| Benefits | Energy efficiency, reduced heating/cooling costs | Noise control, improved privacy and comfort |
| Installation | Installed within cavities or on surfaces | Layered with drywall or specialized panels |
Understanding Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
Thermal insulation reduces heat transfer between objects or environments, improving energy efficiency and maintaining temperature control in buildings. Acoustic insulation blocks or absorbs sound waves to minimize noise pollution and enhance soundproofing. Effective building design incorporates both materials to ensure comfort and energy savings while managing noise levels.
Key Differences Between Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
Thermal insulation primarily reduces heat transfer by using materials like fiberglass, foam board, or cellulose to maintain temperature control and energy efficiency in buildings. Acoustic insulation focuses on soundproofing by absorbing or blocking noise through dense materials such as mineral wool, acoustic panels, or mass-loaded vinyl. The key difference lies in their functional purpose: thermal insulation targets temperature regulation, while acoustic insulation is designed to control sound transmission.
How Thermal Insulation Works
Thermal insulation works by reducing heat transfer between objects or environments through materials with low thermal conductivity, such as fiberglass, foam, or mineral wool. These materials trap air within their structure, minimizing the movement of heat via conduction, convection, and radiation. Effective thermal insulation maintains consistent indoor temperatures, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing heating and cooling costs in buildings.
How Acoustic Insulation Functions
Acoustic insulation functions by absorbing and dampening sound waves to reduce noise transmission between spaces, using materials like mineral wool, foam panels, and fiberglass that possess high sound absorption coefficients. These materials disrupt sound wave propagation through porous structures that convert sound energy into heat, minimizing echo and reverberation within rooms. Unlike thermal insulation, which primarily controls heat transfer, acoustic insulation specifically targets airborne noise and impact sounds to enhance soundproofing in building environments.
Common Materials for Thermal vs Acoustic Insulation
Common materials for thermal insulation include fiberglass, foam boards, and mineral wool, chosen for their low thermal conductivity and ability to reduce heat transfer. Acoustic insulation typically uses materials like dense fiberglass, cellulose, and specialized acoustic foam, designed to absorb and dampen sound waves effectively. Both insulation types often employ mineral wool, but variations in density and structure optimize performance for either thermal resistance or sound absorption.
Benefits of Thermal Insulation in Buildings
Thermal insulation significantly reduces heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency and lowering heating and cooling costs in buildings. It helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature, improving occupant comfort and reducing reliance on HVAC systems. Effective thermal insulation also contributes to environmental sustainability by decreasing the building's carbon footprint.
Advantages of Acoustic Insulation in Modern Construction
Acoustic insulation enhances indoor comfort by significantly reducing noise pollution, creating quieter living and working environments in modern construction. It improves privacy and productivity by minimizing sound transmission between rooms and from external sources. High-performance acoustic materials also contribute to energy efficiency by complementing thermal insulation, resulting in comprehensive building performance.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Building Project
Thermal insulation materials, such as fiberglass and foam boards, primarily reduce heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency and indoor comfort, while acoustic insulation focuses on minimizing sound transmission using products like mineral wool or acoustic panels. Choosing the right insulation depends on the building's location, climate, and specific needs for temperature control or noise reduction. Proper assessment of project requirements ensures optimal material selection, balancing insulation performance, cost, and sustainability.
Cost Comparison: Thermal vs Acoustic Insulation
Thermal insulation materials such as fiberglass and foam boards typically have lower initial costs compared to acoustic insulation products like mineral wool and specialized soundproof panels, which require denser and more expensive components to effectively reduce noise. While thermal insulation focuses on minimizing heat transfer, acoustic insulation demands higher density and thickness, contributing to increased material and installation expenses. Long-term energy savings from thermal insulation often offset upfront costs, whereas acoustic insulation's investment primarily enhances comfort and noise control without direct energy savings.
Combining Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Solutions
Combining thermal and acoustic insulation solutions enhances building performance by simultaneously reducing heat transfer and minimizing sound transmission. High-performance materials like mineral wool and spray foam provide dual benefits, improving energy efficiency and indoor comfort. Integrating these insulation types supports sustainable construction practices and contributes to quieter, more temperature-stable environments.
Thermal Insulation vs Acoustic Insulation Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com