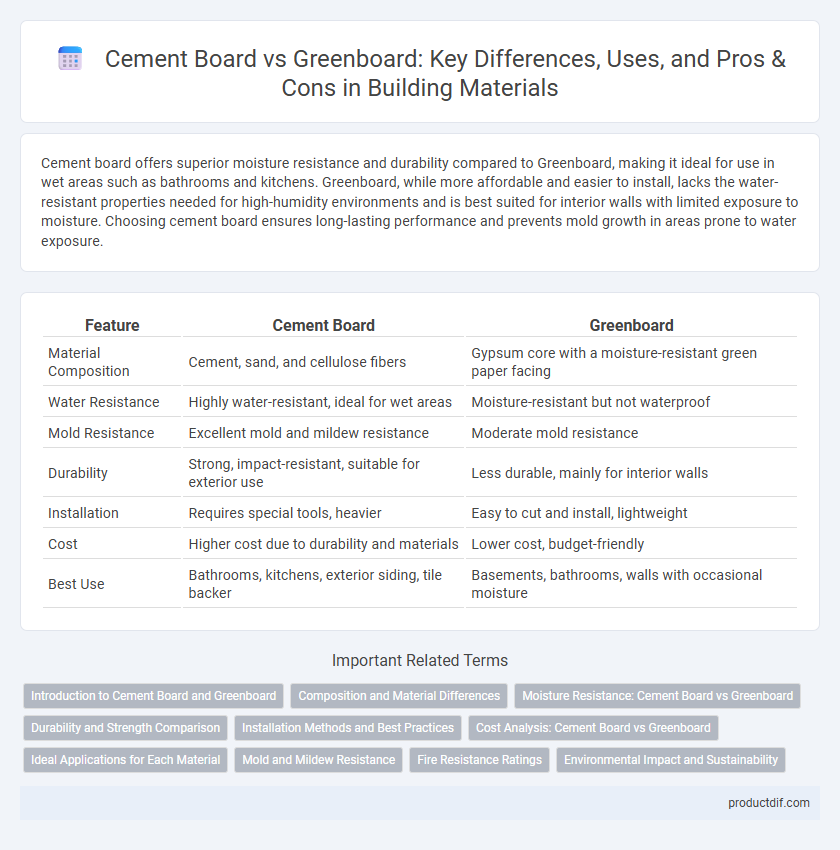
Cement board offers superior moisture resistance and durability compared to Greenboard, making it ideal for use in wet areas such as bathrooms and kitchens. Greenboard, while more affordable and easier to install, lacks the water-resistant properties needed for high-humidity environments and is best suited for interior walls with limited exposure to moisture. Choosing cement board ensures long-lasting performance and prevents mold growth in areas prone to water exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cement Board | Greenboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Cement, sand, and cellulose fibers | Gypsum core with a moisture-resistant green paper facing |
| Water Resistance | Highly water-resistant, ideal for wet areas | Moisture-resistant but not waterproof |
| Mold Resistance | Excellent mold and mildew resistance | Moderate mold resistance |
| Durability | Strong, impact-resistant, suitable for exterior use | Less durable, mainly for interior walls |
| Installation | Requires special tools, heavier | Easy to cut and install, lightweight |
| Cost | Higher cost due to durability and materials | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Best Use | Bathrooms, kitchens, exterior siding, tile backer | Basements, bathrooms, walls with occasional moisture |
Introduction to Cement Board and Greenboard
Cement board is a durable, moisture-resistant building material commonly used as a tile backer in wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens. Greenboard is a type of drywall with a moisture-resistant coating, designed primarily for areas with minimal exposure to water such as bathrooms and laundry rooms. Cement board offers superior water resistance and strength compared to greenboard, making it ideal for high-moisture applications.
Composition and Material Differences
Cement boards are composed of a mixture of cement, sand, and reinforcing fibers, providing a durable, moisture-resistant, and mold-resistant substrate ideal for wet areas. Greenboard, made primarily from gypsum plaster with a moisture-resistant green paper facing, offers moderate water resistance but lacks the structural strength and durability of cement boards. The inorganic composition of cement boards makes them suitable for exterior and high-humidity applications, while greenboard is better suited for interior walls in areas with limited moisture exposure.
Moisture Resistance: Cement Board vs Greenboard
Cement board offers superior moisture resistance compared to greenboard, making it ideal for wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens. Unlike greenboard, cement board is composed of cement and reinforcing fibers, which prevent mold growth and water damage. Greenboard contains a moisture-resistant core but lacks the durability and waterproof properties required for heavy exposure to moisture.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Cement board offers superior durability and strength compared to greenboard, making it ideal for high-moisture environments such as bathrooms and kitchens. Its composition of cement and reinforcing fibers provides resistance to mold, water damage, and impact, whereas greenboard, primarily made of gypsum, is more susceptible to moisture and deterioration over time. For construction projects requiring long-lasting, robust wall sheathing, cement board is the preferred choice due to its structural integrity and resilience.
Installation Methods and Best Practices
Cement board installation requires using corrosion-resistant screws and a waterproof membrane to prevent mold growth in wet areas, making it ideal for tile backer applications. Greenboard, a moisture-resistant drywall, should be installed with standard drywall screws and joint tape but is best suited for low-moisture environments due to its limited water resistance. Proper surface preparation and following manufacturer guidelines ensure durability and optimal performance for both materials.
Cost Analysis: Cement Board vs Greenboard
Cement board typically costs between $10 to $15 per 3x5 foot sheet, offering superior durability and moisture resistance compared to greenboard, which ranges from $8 to $12 per 4x8 foot sheet. While cement board has a higher upfront material cost, it reduces long-term maintenance and replacement expenses in wet areas such as bathrooms and kitchens. Greenboard, though cheaper initially, may incur additional costs due to susceptibility to mold and water damage, making cement board a more cost-effective solution over time for moisture-prone environments.
Ideal Applications for Each Material
Cement board excels in wet or high-moisture environments such as shower walls and exterior siding due to its water resistance and durability. Greenboard is best suited for interior areas with moderate moisture exposure like bathroom walls outside showers or kitchens, offering mold resistance without the heavy-duty properties of cement board. Selecting the appropriate material ensures optimal performance and longevity based on environmental conditions.
Mold and Mildew Resistance
Cement board offers superior mold and mildew resistance due to its inorganic composition, making it ideal for high-moisture environments like bathrooms and kitchens. Greenboard, while moisture-resistant with a paper facing treated to resist mold, is less durable against prolonged exposure to humidity and water. Choosing cement board enhances the longevity and structural integrity of walls where moisture control is critical.
Fire Resistance Ratings
Cement board offers superior fire resistance compared to greenboard, with cement boards typically rated to withstand temperatures above 1,000degF, making them ideal for fire-rated assemblies and exterior applications. Greenboard, primarily designed for moisture resistance in interior walls, generally has minimal fire resistance and lacks certification for use in fire-rated construction. Choosing cement board is critical in building designs where compliance with NFPA 285 and ASTM E119 fire rating standards is required to enhance structural safety.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cement board is highly durable, moisture-resistant, and made from environmentally inert materials, resulting in lower emissions and longer lifecycle sustainability compared to greenboard, which contains paper face layers prone to mold and degradation. Greenboard, often produced with recycled content, offers a greener profile but has a shorter lifespan and requires more frequent replacement, increasing its overall environmental impact. Choosing cement board reduces waste and maintenance needs, supporting sustainable building practices in high-moisture environments.
Cement Board vs Greenboard Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com