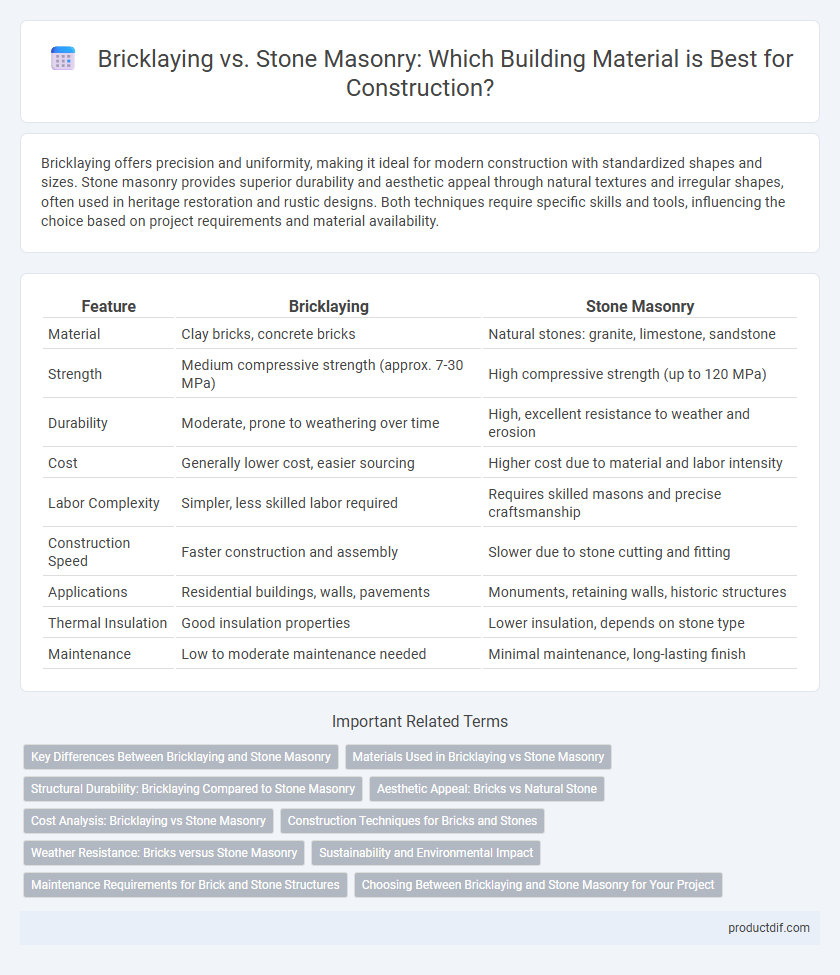
Bricklaying offers precision and uniformity, making it ideal for modern construction with standardized shapes and sizes. Stone masonry provides superior durability and aesthetic appeal through natural textures and irregular shapes, often used in heritage restoration and rustic designs. Both techniques require specific skills and tools, influencing the choice based on project requirements and material availability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bricklaying | Stone Masonry |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Clay bricks, concrete bricks | Natural stones: granite, limestone, sandstone |
| Strength | Medium compressive strength (approx. 7-30 MPa) | High compressive strength (up to 120 MPa) |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to weathering over time | High, excellent resistance to weather and erosion |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, easier sourcing | Higher cost due to material and labor intensity |
| Labor Complexity | Simpler, less skilled labor required | Requires skilled masons and precise craftsmanship |
| Construction Speed | Faster construction and assembly | Slower due to stone cutting and fitting |
| Applications | Residential buildings, walls, pavements | Monuments, retaining walls, historic structures |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulation properties | Lower insulation, depends on stone type |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate maintenance needed | Minimal maintenance, long-lasting finish |
Key Differences Between Bricklaying and Stone Masonry
Bricklaying involves the precise arrangement of uniform, rectangular bricks typically made from clay or concrete, ensuring consistent size and shape for faster construction and ease of alignment. Stone masonry requires the careful selection and placement of irregularly shaped natural stones, demanding more skilled craftsmanship to fit pieces together securely and achieve structural stability. The key differences lie in material uniformity, construction techniques, and the level of skill required, with bricklaying favoring speed and uniformity while stone masonry emphasizes durability and aesthetic variation.
Materials Used in Bricklaying vs Stone Masonry
Bricklaying primarily uses clay bricks, which are kiln-fired for durability, while stone masonry involves natural stones such as granite, limestone, and marble, chosen for their strength and aesthetic appeal. Bricks offer uniformity and ease of handling, making them ideal for precise construction, whereas stone requires skilled cutting and shaping to fit architectural designs. Mortar binds both materials, but the composition may vary to accommodate the differing porosity and weight of bricks versus stone.
Structural Durability: Bricklaying Compared to Stone Masonry
Bricklaying offers consistent structural integrity due to uniform brick sizes and controlled manufacturing processes, ensuring predictable load distribution in construction. Stone masonry, while often more durable under extreme weather conditions, can exhibit variability in strength depending on stone type and craftsmanship quality. Advances in brick bonding techniques contribute to improved long-term durability, making bricklaying a reliable choice for resilient building structures.
Aesthetic Appeal: Bricks vs Natural Stone
Bricks offer a uniform, clean aesthetic with consistent color and size, making them ideal for modern and traditional architectural styles requiring symmetry and pattern repetition. Natural stone provides unique textures, varied hues, and organic shapes, lending a rustic, timeless beauty that enhances the building's connection to nature. The choice between bricklaying and stone masonry significantly influences the visual character and overall ambiance of the constructed space.
Cost Analysis: Bricklaying vs Stone Masonry
Bricklaying typically offers a lower cost per square foot compared to stone masonry due to the widespread availability of bricks and faster installation times. Stone masonry involves higher expenses from labor-intensive processes and the premium price of natural stone materials. Budget considerations often favor bricklaying for large-scale projects, while stone masonry, despite its higher cost, provides superior durability and aesthetic appeal in premium construction.
Construction Techniques for Bricks and Stones
Bricklaying involves using uniformly shaped bricks bonded with mortar to create consistent, scalable structures, while stone masonry employs irregular or shaped stones fitted together to form durable, load-bearing walls. Brick construction techniques prioritize precise joint spacing and mortar composition for strength and weather resistance, whereas stone masonry requires skillful cutting, dressing, and placement to ensure stability and aesthetic appeal. Both methods demand meticulous craftsmanship, but bricklaying benefits from modularity and faster assembly, whereas stone masonry offers enhanced natural texture and increased structural mass.
Weather Resistance: Bricks versus Stone Masonry
Bricks exhibit strong weather resistance due to their uniform size and dense composition, which reduces water absorption and enhances durability against freeze-thaw cycles. Stone masonry offers superior natural resistance to extreme weather conditions because of stone's inherent hardness and low porosity, making it more suitable for harsh climates. Choosing between bricks and stone masonry depends on specific environmental factors, as stone tends to perform better in moisture-prone areas while bricks provide consistent protection in moderate weather.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Bricklaying often utilizes fired clay bricks, which involve high energy consumption and carbon emissions during production, whereas stone masonry typically uses natural stone that requires less processing but may involve significant quarrying impacts. Stone's durability and longevity contribute to reduced environmental impact over time, while bricks can offer better thermal insulation, lowering energy use in buildings. Selecting sustainably sourced materials and incorporating recycled content in both bricklaying and stone masonry enhances environmental performance in construction projects.
Maintenance Requirements for Brick and Stone Structures
Brick structures typically require regular inspection for mortar joint deterioration and periodic repointing to prevent water infiltration, ensuring long-term durability. Stone masonry demands occasional cleaning to remove biological growth and careful monitoring of stone erosion or cracking caused by environmental exposure. Both materials benefit from protective sealants, but stone often requires more specialized maintenance due to its natural variability and susceptibility to weathering.
Choosing Between Bricklaying and Stone Masonry for Your Project
Choosing between bricklaying and stone masonry depends on project requirements such as durability, aesthetic preference, and budget constraints. Bricklaying offers uniformity and cost-effectiveness with easier installation, while stone masonry provides superior strength and natural beauty suitable for structural or decorative purposes. Consider project location, intended use, and maintenance needs to determine the best building material that balances performance and design.
Bricklaying vs Stone Masonry Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com