Wet-laid stone construction involves setting stones in mortar or concrete, creating a solid, durable surface with enhanced stability and resistance to shifting. Dry-laid stone uses no mortar, relying on careful stacking and gravity, which allows for natural drainage and flexibility but requires precise craftsmanship to ensure long-term structural integrity. Understanding the differences between wet-laid and dry-laid stone helps in selecting the right method for specific building projects based on durability, aesthetics, and environmental considerations.
Table of Comparison
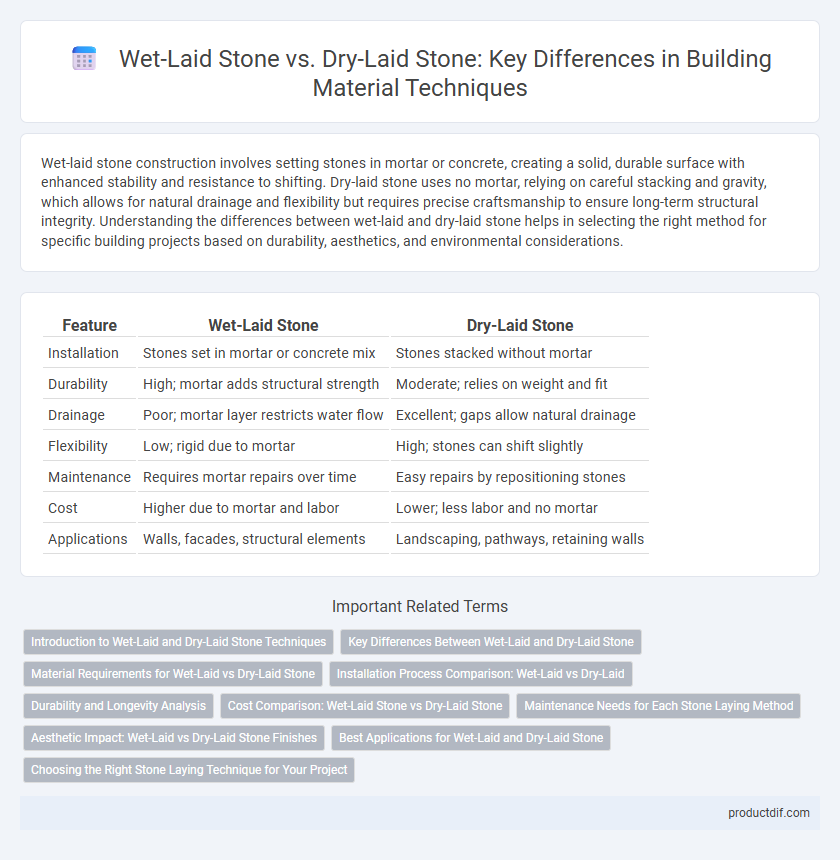
| Feature | Wet-Laid Stone | Dry-Laid Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Stones set in mortar or concrete mix | Stones stacked without mortar |
| Durability | High; mortar adds structural strength | Moderate; relies on weight and fit |
| Drainage | Poor; mortar layer restricts water flow | Excellent; gaps allow natural drainage |
| Flexibility | Low; rigid due to mortar | High; stones can shift slightly |
| Maintenance | Requires mortar repairs over time | Easy repairs by repositioning stones |
| Cost | Higher due to mortar and labor | Lower; less labor and no mortar |
| Applications | Walls, facades, structural elements | Landscaping, pathways, retaining walls |
Introduction to Wet-Laid and Dry-Laid Stone Techniques
Wet-laid stone technique involves setting stones with mortar or cement, creating a solid, weather-resistant surface ideal for structural walls and paved pathways. Dry-laid stone, stacked without mortar, relies on precise stone fitting and gravity, offering natural drainage and flexibility perfect for garden walls and rustic landscaping. Understanding these methods is crucial for selecting the appropriate stone installation based on durability, aesthetic appeal, and environmental conditions.
Key Differences Between Wet-Laid and Dry-Laid Stone
Wet-laid stone involves setting stones in a mortar or concrete base, offering enhanced structural stability and resistance to shifting, making it ideal for load-bearing applications. Dry-laid stone relies on careful stacking without mortar, allowing for natural drainage and flexibility, which is suited for landscaping and retaining walls where slight movement is expected. The choice between wet-laid and dry-laid stone depends on factors such as project stability requirements, environmental conditions, and aesthetic preferences.
Material Requirements for Wet-Laid vs Dry-Laid Stone
Wet-laid stone installation demands precise mortar composition with cement, sand, and water to ensure strong adhesion and durability, requiring consistent moisture control for optimal curing. Dry-laid stone relies on tightly fitting stones without mortar, emphasizing careful stone selection for shape and size uniformity to achieve structural stability through gravity and friction. Material requirements for wet-laid stone are stricter, including bonding agents and additives, whereas dry-laid stone prioritizes natural stone properties and mechanical interlock.
Installation Process Comparison: Wet-Laid vs Dry-Laid
Wet-laid stone installation involves setting stones in a mortar bed, creating a strong, stable bond ideal for structural applications and precise leveling, while dry-laid stone relies on gravity and friction, allowing for more natural drainage and flexibility but requiring careful placement for stability. Wet-laid methods demand longer curing times and skilled labor to ensure proper mortar application, whereas dry-laid stone can be installed faster with less technical expertise but may necessitate periodic adjustments due to settling. Choosing between wet-laid and dry-laid techniques depends on project requirements for durability, moisture management, and aesthetic preferences.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Wet-laid stone offers enhanced durability due to the mortar or concrete binding, which provides superior resistance to shifting and erosion, making it ideal for load-bearing structures and areas with frequent moisture exposure. Dry-laid stone relies on precise stone fitting and gravity, allowing for natural drainage and flexibility, which can prevent cracking but may be more susceptible to displacement over time. Long-term longevity favors wet-laid stone in high-stress environments, while dry-laid stone excels in applications requiring natural drainage and ease of maintenance.
Cost Comparison: Wet-Laid Stone vs Dry-Laid Stone
Wet-laid stone installation typically incurs higher costs due to the use of mortar, increased labor time, and material expenses compared to dry-laid stone. Dry-laid stone offers a cost-efficient alternative with reduced labor and no need for adhesive materials, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects. Maintenance costs for wet-laid stone may also be higher over time because of potential mortar degradation and necessary repairs.
Maintenance Needs for Each Stone Laying Method
Wet-laid stone requires regular inspection and prompt sealing to prevent water infiltration and mortar deterioration, ensuring long-term durability. Dry-laid stone demands routine weed removal and periodic realignment of displaced stones to maintain structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Both methods benefit from seasonal cleaning, but wet-laid stone often incurs lower ongoing maintenance due to the mortar bond stabilizing the arrangement.
Aesthetic Impact: Wet-Laid vs Dry-Laid Stone Finishes
Wet-laid stone produces a smooth, refined finish with mortar filling gaps for a uniform, polished aesthetic, ideal for formal architectural designs. Dry-laid stone emphasizes natural texture and irregularity, showcasing the organic beauty of individual stones with visible joints that enhance rustic or traditional settings. The choice between wet-laid and dry-laid stone directly influences visual harmony and the tactile character of the finished surface.
Best Applications for Wet-Laid and Dry-Laid Stone
Wet-laid stone is ideal for applications requiring enhanced stability and durability, such as retaining walls, patios, and driveways where mortar binding ensures long-lasting structure. Dry-laid stone is best suited for landscaping features like garden edging, pathways, and rustic walls that benefit from flexibility and natural drainage. Choosing between wet-laid and dry-laid stone depends on the need for structural integrity versus ease of installation and natural aesthetics.
Choosing the Right Stone Laying Technique for Your Project
Wet-laid stone involves setting stones in mortar or concrete, offering enhanced stability and weather resistance, ideal for load-bearing structures and exterior walls. Dry-laid stone relies on careful stacking without mortar, providing natural drainage, flexibility, and ease of repair, perfect for landscaping features and retaining walls. Selecting between wet-laid and dry-laid stone depends on project requirements such as structural integrity, aesthetic preference, and environmental exposure.
wet-laid stone vs dry-laid stone Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com