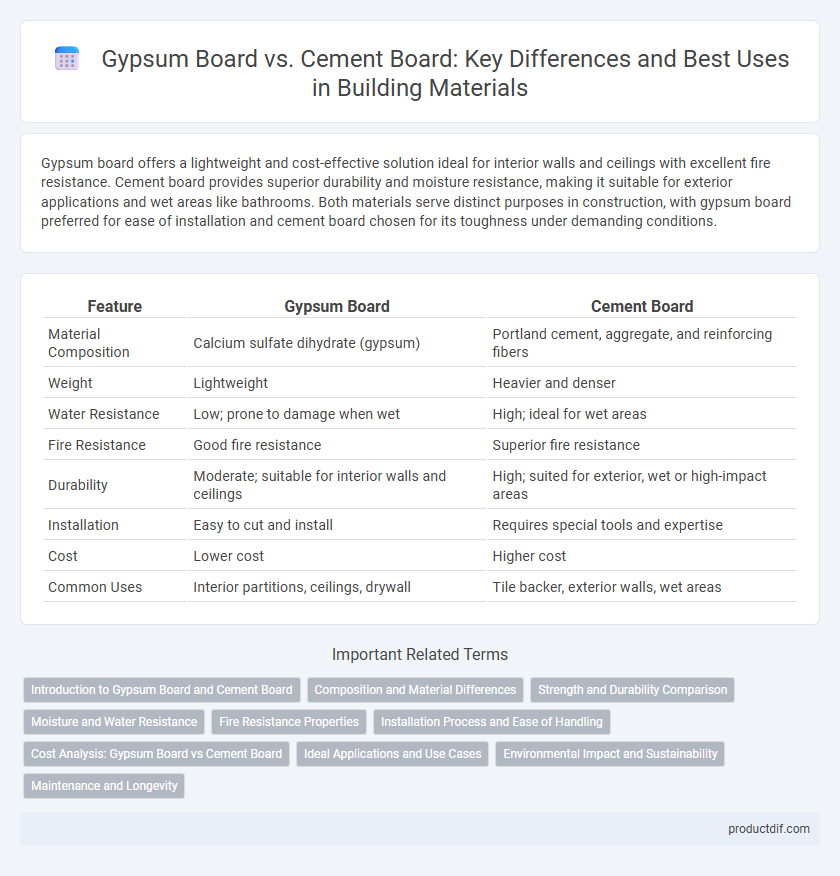
Gypsum board offers a lightweight and cost-effective solution ideal for interior walls and ceilings with excellent fire resistance. Cement board provides superior durability and moisture resistance, making it suitable for exterior applications and wet areas like bathrooms. Both materials serve distinct purposes in construction, with gypsum board preferred for ease of installation and cement board chosen for its toughness under demanding conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gypsum Board | Cement Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum) | Portland cement, aggregate, and reinforcing fibers |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier and denser |
| Water Resistance | Low; prone to damage when wet | High; ideal for wet areas |
| Fire Resistance | Good fire resistance | Superior fire resistance |
| Durability | Moderate; suitable for interior walls and ceilings | High; suited for exterior, wet or high-impact areas |
| Installation | Easy to cut and install | Requires special tools and expertise |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Uses | Interior partitions, ceilings, drywall | Tile backer, exterior walls, wet areas |
Introduction to Gypsum Board and Cement Board
Gypsum board, composed mainly of calcium sulfate dihydrate, provides a smooth, fire-resistant surface ideal for interior walls and ceilings, featuring easy installation and excellent sound insulation properties. Cement board consists of a mixture of cement and reinforcing fibers, offering superior moisture and mold resistance, making it suitable for wet areas like bathrooms and exterior applications. Both materials serve distinct purposes in construction, with gypsum board preferred for dry environments and cement board for high-moisture or outdoor settings.
Composition and Material Differences
Gypsum board consists primarily of a gypsum core wrapped in paper facing, making it lightweight and easy to install but prone to moisture damage. Cement board features a core of cement reinforced with fiberglass mesh, enhancing its durability, moisture resistance, and suitability for wet areas. These composition differences directly impact their application, with gypsum board preferred for interior walls and ceilings, while cement board is ideal for tile backer in bathrooms and exterior environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Gypsum board offers moderate strength suitable for interior walls with good fire resistance but limited impact and water durability. Cement board provides superior strength and durability, excelling in moisture resistance and structural support, making it ideal for areas exposed to water and heavy wear. The denser composition of cement board enhances its ability to withstand impact and prolonged exposure to harsh conditions compared to gypsum board.
Moisture and Water Resistance
Gypsum board offers moderate moisture resistance, making it suitable for interior walls in low-humidity areas, but it deteriorates quickly when exposed to water. Cement board provides superior water resistance and durability, making it ideal for wet areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, and exterior applications. Its composition of cement and reinforcing fibers prevents mold and mildew growth, ensuring long-lasting performance in moisture-prone environments.
Fire Resistance Properties
Gypsum board offers excellent fire resistance due to its core of chemically combined water, which releases steam and slows heat transfer during exposure to fire. Cement board is highly fire-resistant as well, composed of cement and reinforcing fibers that can withstand higher temperatures without deteriorating or emitting toxic fumes. When comparing fire resistance, cement board generally provides superior durability and structural integrity under prolonged heat, making it ideal for fire-rated walls and areas prone to moisture exposure.
Installation Process and Ease of Handling
Gypsum board is lightweight and easy to cut with standard tools, allowing for quick installation and minimal labor costs, making it ideal for interior walls and ceilings. Cement board is denser and requires specialized tools for cutting and handling, increasing installation time and effort but providing superior moisture resistance for wet areas. The ease of handling gypsum board reduces fatigue and speeds up framing and finishing tasks compared to the more cumbersome cement board.
Cost Analysis: Gypsum Board vs Cement Board
Gypsum board typically costs between $0.30 to $0.60 per square foot, making it a more budget-friendly option for interior walls and ceilings. Cement board prices range from $1.00 to $2.00 per square foot, reflecting its durability and moisture resistance, which justify higher initial expenses. Cost efficiency depends on project requirements, with gypsum board preferred for dry areas and cement board favored in wet or high-impact environments.
Ideal Applications and Use Cases
Gypsum board excels in interior applications such as residential walls and ceilings due to its lightweight nature, ease of installation, and excellent fire resistance. Cement board is ideal for wet or high-moisture areas, including tile backer boards in bathrooms, kitchens, and exterior siding, offering superior durability, moisture resistance, and mold prevention. Choosing between gypsum board and cement board depends on the project's environmental conditions and structural requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum board offers advantages with its recyclable content and low embodied energy, making it a more sustainable choice in indoor environments. Cement board, while more durable and moisture-resistant, has a higher carbon footprint due to the energy-intensive cement production process. Choosing gypsum board reduces environmental impact through lower greenhouse gas emissions and enhanced recyclability compared to cement-based alternatives.
Maintenance and Longevity
Gypsum board requires regular maintenance to prevent moisture damage and is susceptible to mold growth, making it less durable in high-humidity environments. Cement board offers superior longevity due to its water resistance, strength, and ability to withstand harsh conditions without deteriorating. Choosing cement board significantly reduces long-term repair costs and ensures a more robust, low-maintenance building material solution.
Gypsum board vs Cement board Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com