Laminate flooring offers a durable, scratch-resistant surface ideal for high-traffic areas, while vinyl flooring excels in water resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for bathrooms and kitchens. Laminate typically features a thicker core for added stability, whereas vinyl provides easier installation with its click-lock or peel-and-stick options. Both materials come in a variety of styles and finishes, allowing homeowners to achieve the desired aesthetic without sacrificing functionality.
Table of Comparison
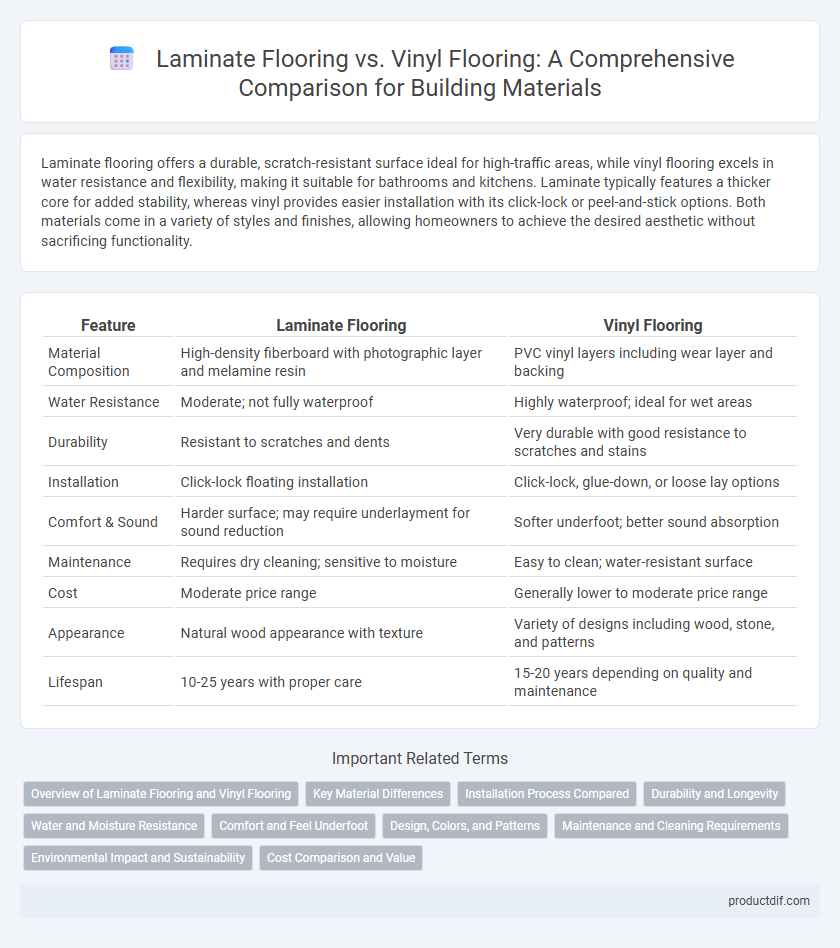
| Feature | Laminate Flooring | Vinyl Flooring |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-density fiberboard with photographic layer and melamine resin | PVC vinyl layers including wear layer and backing |
| Water Resistance | Moderate; not fully waterproof | Highly waterproof; ideal for wet areas |
| Durability | Resistant to scratches and dents | Very durable with good resistance to scratches and stains |
| Installation | Click-lock floating installation | Click-lock, glue-down, or loose lay options |
| Comfort & Sound | Harder surface; may require underlayment for sound reduction | Softer underfoot; better sound absorption |
| Maintenance | Requires dry cleaning; sensitive to moisture | Easy to clean; water-resistant surface |
| Cost | Moderate price range | Generally lower to moderate price range |
| Appearance | Natural wood appearance with texture | Variety of designs including wood, stone, and patterns |
| Lifespan | 10-25 years with proper care | 15-20 years depending on quality and maintenance |
Overview of Laminate Flooring and Vinyl Flooring
Laminate flooring consists of multiple layers fused together, typically featuring a photographic applique layer that mimics wood or stone, topped with a clear protective wear layer for durability. Vinyl flooring is made from synthetic materials--primarily polyvinyl chloride (PVC)--and is available in sheets, tiles, or planks, offering water resistance and ease of installation. Both flooring types provide affordable alternatives to hardwood, with laminate excelling in aesthetic realism and vinyl in moisture resistance.
Key Material Differences
Laminate flooring is composed of multiple layers including a high-density fiberboard core topped with a photographic applique layer and a clear protective wear layer, offering durability and scratch resistance. Vinyl flooring consists of synthetic materials such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), providing water resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for moisture-prone areas. The key difference lies in laminate's wood-based core versus vinyl's plastic composition, impacting installation methods, moisture tolerance, and maintenance requirements.
Installation Process Compared
Laminate flooring typically requires a floating installation method, where planks interlock without adhesive, allowing for quick and DIY-friendly setup over existing subfloors. Vinyl flooring offers more versatility with installation options including peel-and-stick, glue-down, or click-lock formats, accommodating a wider range of subfloor conditions and moisture levels. Vinyl's installation generally demands less precise subfloor preparation compared to laminate, making it suitable for areas with slight imperfections or higher humidity.
Durability and Longevity
Laminate flooring offers high durability with resistance to scratches, dents, and fading, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and homes with pets. Vinyl flooring provides excellent water resistance and can withstand moisture exposure without warping, extending its lifespan in kitchens and bathrooms. Both materials deliver long-lasting performance, but vinyl flooring generally has a slight edge in longevity due to its superior resistance to moisture and wear.
Water and Moisture Resistance
Laminate flooring typically features a wood-based core that is susceptible to water damage and swelling, making it less ideal for moisture-prone areas. Vinyl flooring contains a waterproof construction with PVC layers that resist water penetration, providing superior performance in bathrooms and basements. Moisture resistance in vinyl flooring reduces the risk of mold growth and enhances durability compared to laminate alternatives.
Comfort and Feel Underfoot
Laminate flooring offers a firm, smooth surface with moderate cushioning, providing a solid feel underfoot that mimics hardwood. Vinyl flooring delivers superior softness and warmth due to its resilient, pliable composition, enhancing comfort during prolonged standing or walking. Both materials vary in their thermal insulation properties, impacting overall comfort depending on installation and subfloor conditions.
Design, Colors, and Patterns
Laminate flooring offers a wide range of realistic wood, stone, and tile designs with intricate textures, providing a natural aesthetic appeal. Vinyl flooring excels in versatility with extensive color options and bold patterns, including geometric and abstract styles that can mimic almost any surface. Both materials accommodate various interior design preferences, but vinyl flooring often provides more vibrant and diverse design choices for modern, creative spaces.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Laminate flooring requires regular sweeping and occasional damp mopping with a cleaner specifically designed for laminate to avoid water damage and maintain its finish. Vinyl flooring offers superior water resistance, allowing for more flexible cleaning methods including wet mopping and even steam cleaning without risk of warping. Both materials benefit from quick spill cleanup, but vinyl flooring typically demands less specialized maintenance, making it a practical choice for high-moisture areas.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Laminate flooring is made primarily from fiberboard and resin, often utilizing recycled wood fibers, which can reduce deforestation but may release formaldehyde-based emissions during installation and disposal. Vinyl flooring, composed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), poses significant environmental concerns due to its production's reliance on fossil fuels and challenges in recyclability, leading to long-term landfill persistence and toxic chemical release. Choosing laminate flooring with low-emission certifications and recycled content improves sustainability, while innovations in phthalate-free vinyl products aim to reduce ecological harm but still lag behind in biodegradability compared to natural materials.
Cost Comparison and Value
Laminate flooring typically costs between $1 to $5 per square foot, offering a budget-friendly option with decent durability and aesthetic appeal. Vinyl flooring ranges from $2 to $7 per square foot, providing greater water resistance and longer lifespan, which can translate into better value for high-moisture areas. Considering installation and maintenance, vinyl flooring often delivers superior long-term value despite a slightly higher upfront cost.
Laminate Flooring vs Vinyl Flooring Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com