Wood joists offer natural insulation and ease of handling, making them ideal for residential construction and small-scale projects. Steel joists provide superior strength and durability, supporting longer spans and heavier loads in commercial and industrial buildings. Choosing between wood joist vs steel joist depends on factors such as budget, structural requirements, and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
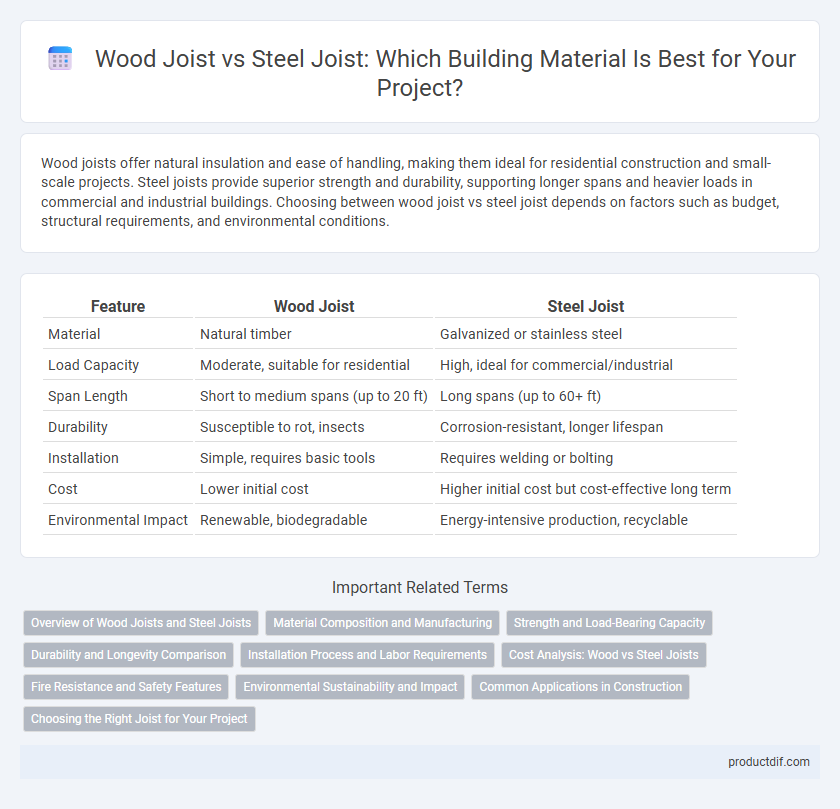
| Feature | Wood Joist | Steel Joist |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural timber | Galvanized or stainless steel |
| Load Capacity | Moderate, suitable for residential | High, ideal for commercial/industrial |
| Span Length | Short to medium spans (up to 20 ft) | Long spans (up to 60+ ft) |
| Durability | Susceptible to rot, insects | Corrosion-resistant, longer lifespan |
| Installation | Simple, requires basic tools | Requires welding or bolting |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but cost-effective long term |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable | Energy-intensive production, recyclable |
Overview of Wood Joists and Steel Joists
Wood joists, commonly crafted from dimensional lumber or engineered wood like LVL, offer natural insulation properties and ease of customization, making them favorable for residential construction. Steel joists, fabricated from cold-formed or hot-rolled steel, provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, enhanced load-bearing capacity, and resistance to warping or insect damage, ideal for commercial or industrial applications. Both types serve as structural supports in flooring and roofing systems, with material choice often dictated by building codes, budget constraints, and environmental considerations.
Material Composition and Manufacturing
Wood joists are typically made from softwood species such as pine, fir, or spruce, using kiln drying and gluing techniques to enhance strength and durability. Steel joists consist of cold-formed steel or hot-rolled sections, fabricated through cutting, welding, and galvanization processes to ensure corrosion resistance and load-bearing capacity. The choice between wood and steel joists depends on factors like structural requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Wood joists offer reliable load-bearing capacity suitable for residential construction, supporting moderate weights with natural flexibility that helps absorb vibrations. Steel joists provide superior strength, allowing for longer spans and higher load capacity, making them ideal for commercial buildings and heavy-duty applications. The choice between wood and steel joists depends on specific structural demands, budget, and environmental factors influencing durability and performance.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Steel joists offer superior durability compared to wood joists due to their resistance to rot, insects, and warping, ensuring a longer structural lifespan. Wood joists, while naturally strong and flexible, are more susceptible to moisture damage and termite infestation, which can compromise longevity. For projects prioritizing extended lifespan and minimal maintenance, steel joists provide a more reliable solution in diverse environmental conditions.
Installation Process and Labor Requirements
Wood joists offer simpler installation with basic woodworking tools, making them suitable for residential projects and reducing labor costs due to ease of handling. Steel joists require specialized equipment, including welding tools and cranes, demanding skilled labor to ensure precise alignment and secure connections. The installation process of steel joists often takes longer and involves strict safety protocols, increasing overall labor intensity compared to wood joists.
Cost Analysis: Wood vs Steel Joists
Wood joists typically offer a lower initial cost compared to steel joists, making them a cost-effective option for residential and small-scale construction projects. Steel joists provide greater durability and require less maintenance, potentially reducing long-term expenses despite higher upfront costs. Evaluating total project budget should include initial material costs, installation complexity, and lifecycle maintenance to determine overall cost efficiency between wood and steel joists.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Steel joists offer superior fire resistance compared to wood joists due to their non-combustible nature and ability to withstand high temperatures without loss of structural integrity. Wood joists require additional fireproofing treatments or fire-resistant coatings to meet safety standards, increasing maintenance and costs. Building designs prioritizing fire safety often favor steel joists to reduce fire risk and enhance occupant protection.
Environmental Sustainability and Impact
Wood joists offer a renewable resource advantage with lower embodied energy and carbon footprint compared to steel joists, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions in construction. Steel joists, while durable and recyclable, often require energy-intensive production processes involving mining and smelting that increase environmental impact. Choosing wood joists supports sustainable forestry and carbon sequestration, whereas steel joists emphasize longevity and potential for material reuse in circular economy strategies.
Common Applications in Construction
Wood joists are commonly used in residential buildings, light commercial structures, and interior floors due to their cost-efficiency, ease of installation, and natural insulation properties. Steel joists are preferred in commercial and industrial constructions where greater load capacity, longer spans, and resistance to fire and pests are critical factors. Both materials are selected based on structural requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Joist for Your Project
Wood joists offer natural insulation, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness for residential projects, making them ideal for smaller spans and lighter loads. Steel joists provide superior strength, durability, and resistance to fire and pests, suitable for commercial buildings and larger spans requiring higher load capacity. Evaluate factors such as load requirements, environmental conditions, budget, and project scale to determine whether wood or steel joists best meet structural and performance needs.
Wood Joist vs Steel Joist Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com