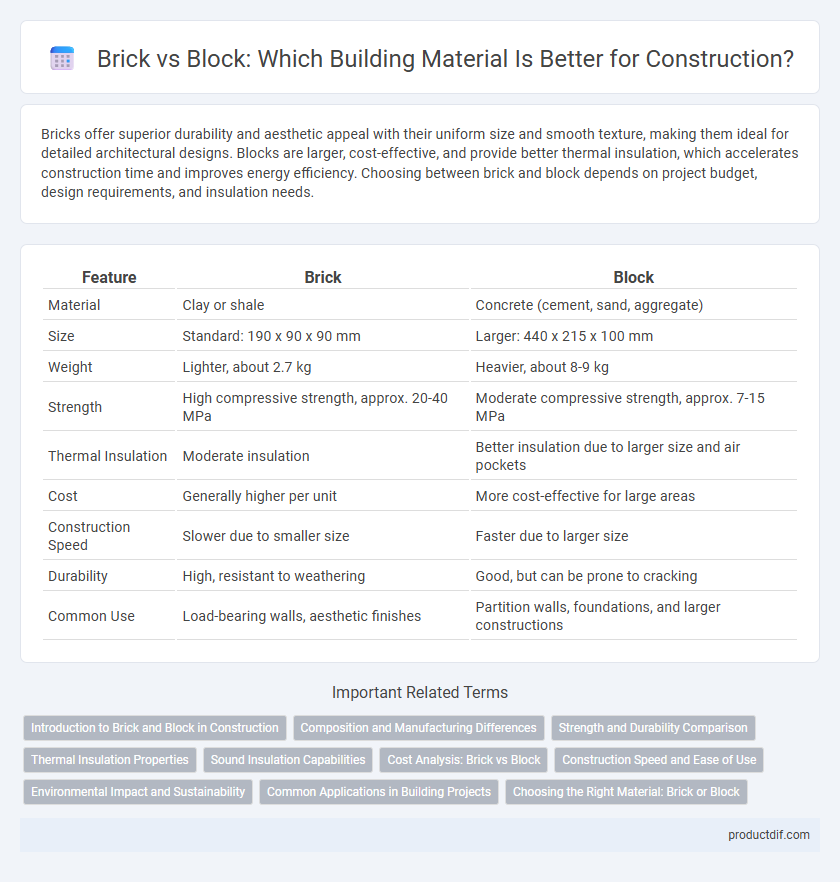
Bricks offer superior durability and aesthetic appeal with their uniform size and smooth texture, making them ideal for detailed architectural designs. Blocks are larger, cost-effective, and provide better thermal insulation, which accelerates construction time and improves energy efficiency. Choosing between brick and block depends on project budget, design requirements, and insulation needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Brick | Block |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Clay or shale | Concrete (cement, sand, aggregate) |
| Size | Standard: 190 x 90 x 90 mm | Larger: 440 x 215 x 100 mm |
| Weight | Lighter, about 2.7 kg | Heavier, about 8-9 kg |
| Strength | High compressive strength, approx. 20-40 MPa | Moderate compressive strength, approx. 7-15 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation | Better insulation due to larger size and air pockets |
| Cost | Generally higher per unit | More cost-effective for large areas |
| Construction Speed | Slower due to smaller size | Faster due to larger size |
| Durability | High, resistant to weathering | Good, but can be prone to cracking |
| Common Use | Load-bearing walls, aesthetic finishes | Partition walls, foundations, and larger constructions |
Introduction to Brick and Block in Construction
Bricks and blocks serve as fundamental building materials in construction, each offering distinct structural properties and applications. Bricks, typically made from clay or concrete, provide high durability and aesthetic appeal, making them ideal for walls and facades. Concrete blocks, larger and hollow, offer superior insulation and faster construction times, often used for load-bearing walls and foundational structures.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Bricks are typically made from clay or shale, molded and fired at high temperatures to achieve hardness and durability; blocks are generally composed of concrete, consisting of cement, sand, and aggregate, and are cured rather than fired. Brick manufacturing involves a kiln-based process that enhances compressive strength and color uniformity, while block production uses molds and steam curing to optimize size precision and thermal insulation properties. The distinct composition and production methods result in varying physical characteristics, cost implications, and application suitability for bricks and blocks in construction.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Bricks typically offer higher compressive strength ranging from 7 to 100 MPa, making them suitable for load-bearing structures, whereas concrete blocks generally exhibit strengths between 3.5 to 17 MPa. The dense composition of bricks contributes to better durability against weathering and erosion, while blocks, with their larger size and hollow cores, provide enhanced thermal insulation but may require reinforcement for long-term structural integrity. Both materials demonstrate distinct performance characteristics, with bricks excelling in strength and longevity, while blocks offer advantages in construction efficiency and insulation.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Bricks and blocks differ significantly in thermal insulation properties, with blocks generally offering superior insulation due to their larger size and porous composition. Concrete blocks often incorporate air pockets, which reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency in buildings. In contrast, traditional clay bricks have higher thermal conductivity, resulting in less effective insulation performance.
Sound Insulation Capabilities
Bricks provide superior sound insulation compared to concrete blocks due to their dense and compact structure, which effectively absorbs and reduces noise transmission. The mass and material composition of bricks contribute to higher soundproofing performance, making them ideal for residential and commercial buildings requiring quieter interiors. Concrete blocks often require additional soundproofing treatments to match the acoustic benefits naturally offered by bricks.
Cost Analysis: Brick vs Block
Block construction generally offers lower material and labor costs compared to bricks due to larger sizes and faster installation times. Bricks tend to have higher durability and aesthetic appeal but come at an increased price per unit and longer build duration. Evaluating total expenses requires considering regional pricing variations, project scale, and long-term maintenance implications for both bricks and blocks.
Construction Speed and Ease of Use
Bricks offer faster construction speed due to their smaller size, allowing for quicker alignment and easier handling by masons. Blocks, being larger and lighter, reduce the number of joints and overall laying time, streamlining large-scale projects and minimizing labor effort. The ease of use of blocks contributes to accelerated wall erection, while bricks provide finer detail work for complex architectural designs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bricks, made from natural clay, require high-temperature kilns that emit significant CO2, but they offer durability and can be recycled or reused in construction. Blocks, particularly aerated autoclaved concrete (AAC) blocks, consume less energy during production and provide better thermal insulation, reducing building energy consumption and overall carbon footprint. Sustainable building projects increasingly favor blocks for their lower environmental impact and resource efficiency, contributing to greener construction practices.
Common Applications in Building Projects
Bricks are commonly used in residential construction for walls, facades, and decorative features due to their durability and aesthetic appeal. Blocks, particularly concrete blocks, are favored in commercial and industrial projects for load-bearing walls, foundations, and retaining structures because of their size and structural strength. Both materials offer specific advantages depending on project requirements such as insulation, cost-efficiency, and construction speed.
Choosing the Right Material: Brick or Block
Selecting the right material between brick and block depends on factors such as structural strength, thermal insulation, and cost-efficiency. Bricks offer superior aesthetic appeal and better fire resistance, while blocks provide enhanced load-bearing capacity and faster construction due to their larger size. Evaluating project requirements and budget constraints ensures optimal choice for durability and performance in building construction.
Brick vs Block Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com