Low-E glass features a microscopically thin coating that reflects infrared energy while allowing visible light to pass through, improving energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer. Double glazing consists of two glass panes separated by a gas-filled space that acts as an insulator, significantly reducing heat loss and sound transmission. Comparing both, Low-E glass enhances thermal performance mainly through its reflective coating, whereas double glazing relies on the insulating air or gas gap, with many modern windows combining both technologies for optimal energy savings.
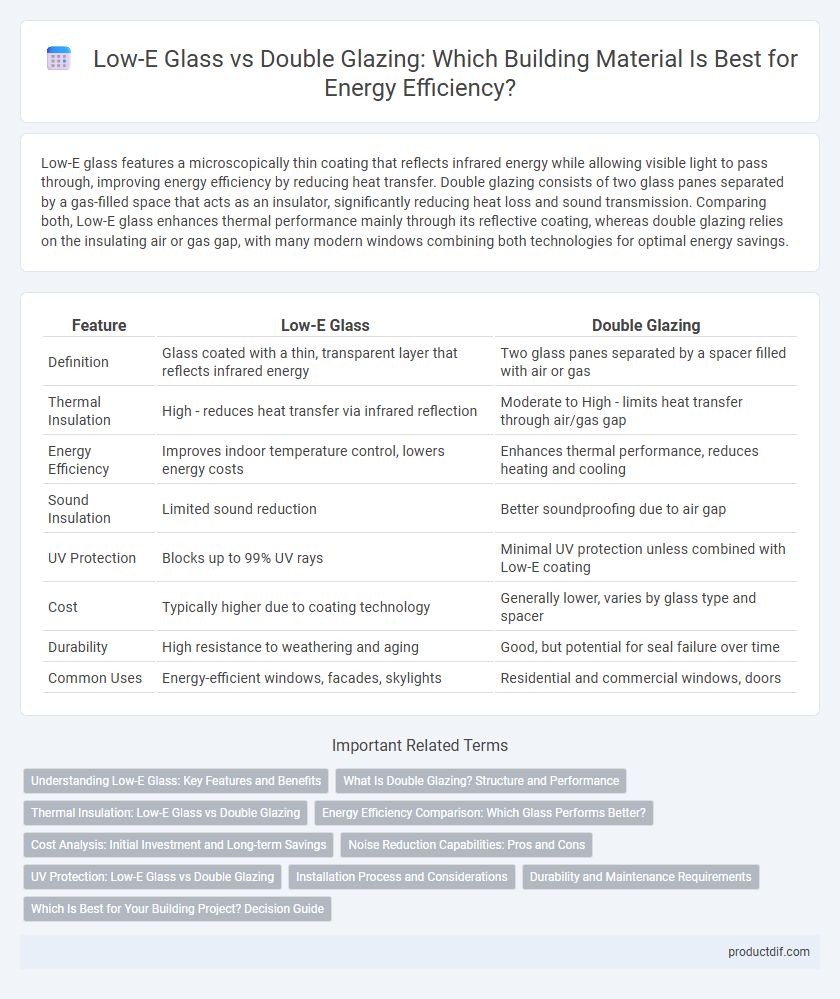
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Low-E Glass | Double Glazing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass coated with a thin, transparent layer that reflects infrared energy | Two glass panes separated by a spacer filled with air or gas |
| Thermal Insulation | High - reduces heat transfer via infrared reflection | Moderate to High - limits heat transfer through air/gas gap |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves indoor temperature control, lowers energy costs | Enhances thermal performance, reduces heating and cooling |
| Sound Insulation | Limited sound reduction | Better soundproofing due to air gap |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% UV rays | Minimal UV protection unless combined with Low-E coating |
| Cost | Typically higher due to coating technology | Generally lower, varies by glass type and spacer |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering and aging | Good, but potential for seal failure over time |
| Common Uses | Energy-efficient windows, facades, skylights | Residential and commercial windows, doors |
Understanding Low-E Glass: Key Features and Benefits
Low-E glass features a microscopically thin, transparent coating that reflects infrared energy while allowing visible light to pass through, enhancing energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer. It helps maintain indoor temperature stability, lowers heating and cooling costs, and minimizes UV damage to interiors. Compared to standard double glazing, Low-E glass offers superior thermal insulation and improved comfort without compromising natural light.
What Is Double Glazing? Structure and Performance
Double glazing consists of two glass panes separated by a spacer and sealed to create an insulating air or gas-filled cavity, enhancing thermal insulation and reducing heat transfer. This structure improves energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss and condensation compared to single-pane windows. The performance of double glazing is characterized by its ability to provide sound insulation, increased security, and better climate control in residential and commercial buildings.
Thermal Insulation: Low-E Glass vs Double Glazing
Low-E glass significantly enhances thermal insulation by reflecting infrared heat while allowing visible light to pass through, reducing energy loss compared to standard double glazing. Double glazing provides an insulating air or gas layer between two glass panes, which minimizes heat transfer but may not block radiant heat as effectively as Low-E coatings. Combining Low-E coatings with double glazing optimizes thermal performance, improving energy efficiency in building materials.
Energy Efficiency Comparison: Which Glass Performs Better?
Low-E glass features a microscopically thin coating that significantly reduces infrared and ultraviolet light transmission, enhancing thermal insulation and reducing energy consumption compared to standard double glazing. Double glazing consists of two glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled space, providing improved insulation but typically less effective in blocking radiant heat than Low-E coatings. Studies show Low-E glass can improve energy efficiency by up to 30% more than traditional double glazing, making it the superior choice for reducing heating and cooling costs in buildings.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-term Savings
Low-E glass typically involves a higher initial investment compared to standard double glazing due to its advanced coatings that improve energy efficiency by reflecting infrared heat while allowing visible light. Though the upfront cost is greater, Low-E glass offers significant long-term savings through reduced heating and cooling expenses, lowering overall energy bills. Double glazing provides moderate cost savings by reducing heat transfer, but lacks the enhanced thermal performance of Low-E coatings, making it less effective in maximizing energy efficiency over time.
Noise Reduction Capabilities: Pros and Cons
Low-E glass features a thin metallic coating that reduces heat transfer while offering moderate noise reduction by dampening sound vibrations. Double glazing consists of two glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled gap, providing superior noise insulation by creating a thicker barrier against sound transmission. While double glazing excels in blocking external noise, Low-E glass primarily enhances thermal performance but can complement noise reduction when combined in double-glazed units.
UV Protection: Low-E Glass vs Double Glazing
Low-E glass provides superior UV protection by reflecting up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays, significantly reducing interior fading and damage compared to standard double glazing. Double glazing primarily offers thermal insulation but allows more UV transmission, which can lead to faster deterioration of furnishings and materials. Choosing Low-E glass enhances energy efficiency while safeguarding interiors against long-term UV exposure.
Installation Process and Considerations
Low-E glass installation requires precise handling to maintain its thin metallic coating and optimize energy efficiency, often involving professional glazing services to ensure proper sealing and positioning. Double glazing installation involves fitting two glass panes separated by a spacer and sealed to create an insulating air gap, demanding careful alignment to prevent condensation and maximize thermal insulation. Both require consideration of frame compatibility, weatherproofing, and local building codes to ensure durability and performance.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Low-E glass offers enhanced durability due to its thin metallic coating that resists scratches and weathering better than standard glass layers found in double glazing. Double glazing requires occasional seal checks to prevent moisture buildup and fogging between panes, which can diminish insulation efficiency over time. Maintenance for Low-E glass is minimal, mainly limited to gentle cleaning, while double-glazed units may need more frequent attention or replacement if seals fail.
Which Is Best for Your Building Project? Decision Guide
Low-E glass enhances energy efficiency by reflecting infrared heat while allowing visible light, reducing heating and cooling costs compared to standard double glazing. Double glazing consists of two glass panes separated by a spacer filled with air or inert gas, providing superior insulation and noise reduction. Choosing between Low-E glass and double glazing depends on your building's climate, budget, and specific thermal performance requirements for optimal comfort and energy savings.
Low-E Glass vs Double Glazing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com