Hot rolled steel is produced by rolling the steel at high temperatures, making it easier to shape and more malleable, ideal for structural applications where strength is crucial. Cold rolled steel undergoes further processing at room temperature, resulting in a smoother surface finish and tighter dimensional tolerances, perfect for precise building components and aesthetic applications. Choosing between hot rolled and cold rolled steel depends on the balance needed between structural strength, surface quality, and manufacturing precision in construction projects.
Table of Comparison
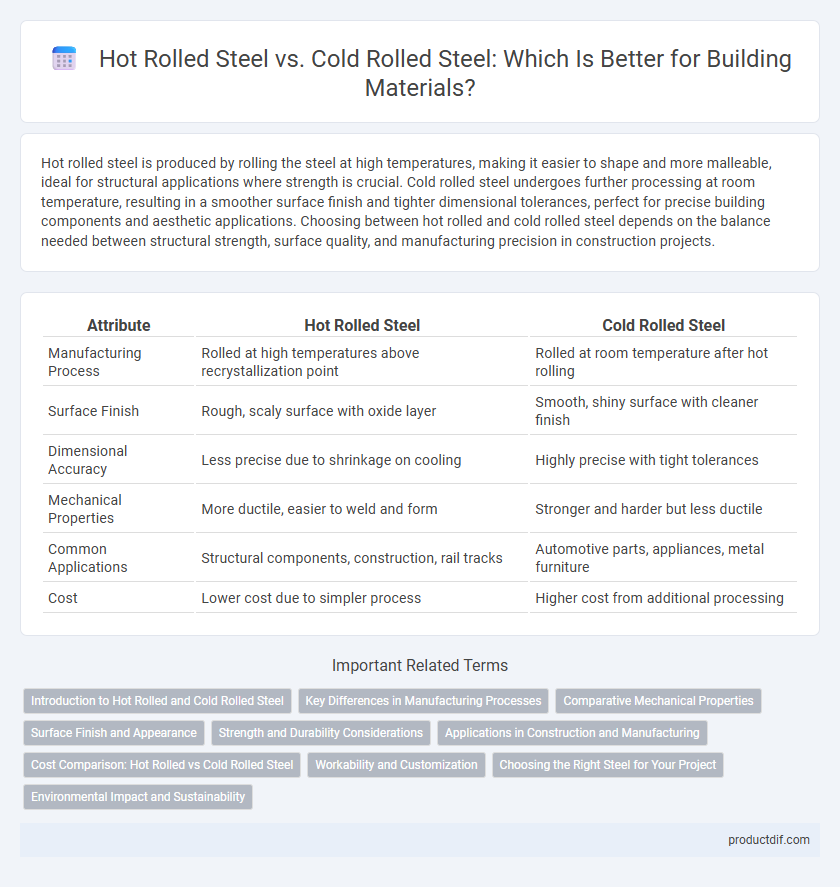
| Attribute | Hot Rolled Steel | Cold Rolled Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Rolled at high temperatures above recrystallization point | Rolled at room temperature after hot rolling |
| Surface Finish | Rough, scaly surface with oxide layer | Smooth, shiny surface with cleaner finish |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Less precise due to shrinkage on cooling | Highly precise with tight tolerances |
| Mechanical Properties | More ductile, easier to weld and form | Stronger and harder but less ductile |
| Common Applications | Structural components, construction, rail tracks | Automotive parts, appliances, metal furniture |
| Cost | Lower cost due to simpler process | Higher cost from additional processing |
Introduction to Hot Rolled and Cold Rolled Steel
Hot rolled steel is produced by rolling the steel at high temperatures above its recrystallization point, resulting in a rougher surface and increased ductility. Cold rolled steel undergoes further processing at room temperature, enhancing its surface finish, strength, and dimensional accuracy. Both types serve distinct applications in construction and manufacturing, with hot rolled steel favored for structural components and cold rolled steel preferred for precision parts.
Key Differences in Manufacturing Processes
Hot rolled steel is manufactured by heating steel above its recrystallization temperature and then rolling it into shape, resulting in a rougher surface and less precise dimensions. Cold rolled steel is processed at room temperature after hot rolling, involving additional steps like annealing and temper rolling, which enhance surface finish, strength, and dimensional accuracy. The key manufacturing difference lies in temperature control and mechanical working, directly impacting material properties and applications.
Comparative Mechanical Properties
Hot rolled steel exhibits greater ductility and impact resistance due to its higher carbon content and grain size, making it ideal for structural applications requiring toughness. Cold rolled steel offers superior tensile strength, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy as a result of work hardening during processing, which enhances its suitability for precision components and automotive parts. The choice between hot rolled and cold rolled steel depends on the mechanical property priorities, such as flexibility versus strength and surface quality.
Surface Finish and Appearance
Hot rolled steel exhibits a rough, scaled surface finish due to the high-temperature manufacturing process, resulting in a matte, less aesthetically refined appearance. Cold rolled steel undergoes further processing at room temperature, producing a smoother, shinier surface with improved dimensional accuracy and better suitability for applications requiring a clean, polished look. The enhanced surface quality of cold rolled steel makes it ideal for finished products such as automotive panels, appliances, and furniture components.
Strength and Durability Considerations
Hot rolled steel exhibits superior strength and durability due to its manufacturing process, which involves rolling the steel at high temperatures, allowing for improved toughness and resistance to wear and tear. Cold rolled steel, processed at room temperature, offers enhanced surface finish and dimensional precision but generally has slightly reduced strength compared to hot rolled steel. When selecting materials for construction projects requiring high load-bearing capacity and impact resistance, hot rolled steel is often preferred for its robustness and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Applications in Construction and Manufacturing
Hot rolled steel is favored in construction for structural components such as beams, columns, and railroad tracks due to its strength and ability to withstand heavy loads. Cold rolled steel is commonly used in manufacturing applications requiring precise dimensions and a smooth finish, including automotive parts, appliances, and metal furniture. Both types offer distinct advantages, with hot rolled steel excelling in rough applications and cold rolled steel preferred for detailed, high-quality products.
Cost Comparison: Hot Rolled vs Cold Rolled Steel
Hot rolled steel typically costs less than cold rolled steel due to its simpler manufacturing process involving heating and rolling at high temperatures. Cold rolled steel undergoes additional processing steps such as annealing and rolling at room temperature, which increases production costs and results in higher prices. The price difference can vary from 10% to 30%, depending on thickness, grade, and supplier, making hot rolled steel more cost-effective for large structural applications.
Workability and Customization
Hot rolled steel offers superior workability due to its ability to be shaped and formed at high temperatures, allowing for easier bending and welding. Cold rolled steel provides enhanced customization options with tighter tolerances, smoother surface finishes, and increased strength from the cold working process. Choosing between hot rolled and cold rolled steel depends on the specific requirements for precision, surface quality, and fabrication complexity in building applications.
Choosing the Right Steel for Your Project
Hot rolled steel offers enhanced malleability and is ideal for large structural components, while cold rolled steel provides superior surface finish and tighter tolerances suited for precise applications. Project requirements such as durability, appearance, and machining quality dictate the choice between hot rolled steel and cold rolled steel. Understanding factors like load capacity, environmental exposure, and fabrication needs ensures optimal material selection for construction projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hot rolled steel typically consumes less energy during production compared to cold rolled steel, reducing its overall carbon footprint. Cold rolled steel, however, offers higher material efficiency with less waste due to its precise finishing, which can contribute to sustainability by minimizing resource use. Recycling rates for both hot and cold rolled steel are high, making them environmentally favorable building materials when incorporated into sustainable construction practices.
Hot Rolled Steel vs Cold Rolled Steel Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com