Stick-built construction offers greater design flexibility and customization by assembling materials piece-by-piece on-site, allowing for adjustments during the building process. Modular construction involves fabricating building sections in a controlled factory environment, resulting in faster construction times and reduced on-site labor. Both methods use durable building materials, but choosing between stick-built and modular construction depends on project timelines, budget, and design complexity.
Table of Comparison
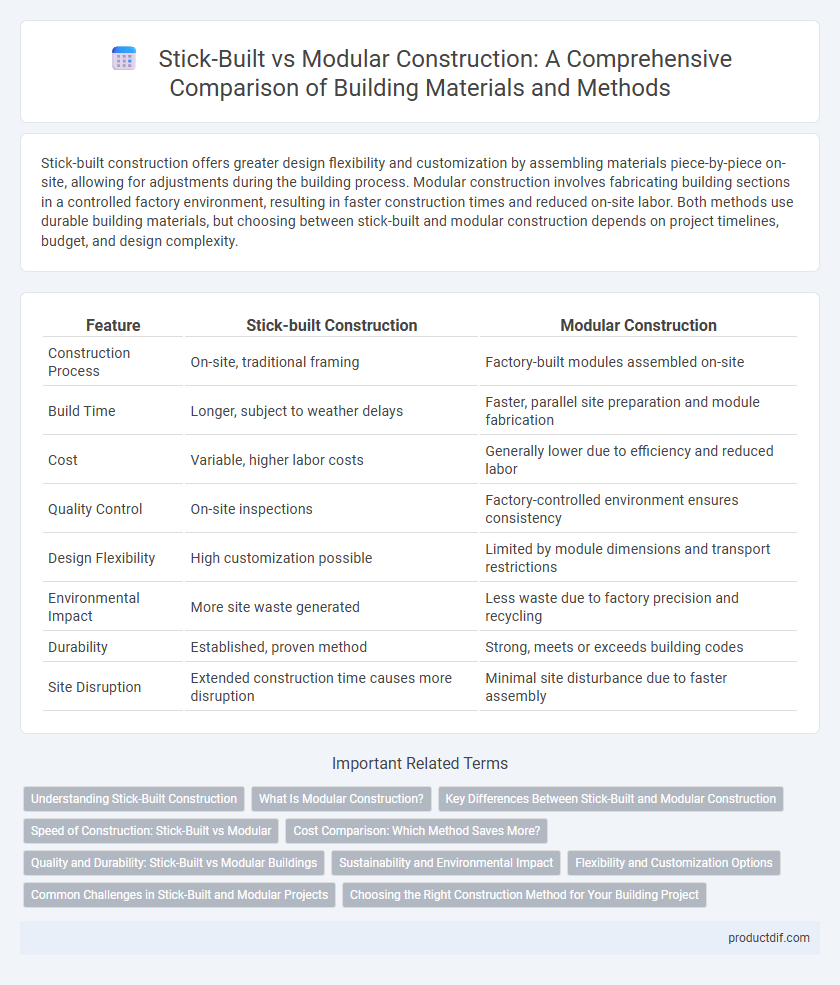
| Feature | Stick-built Construction | Modular Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Process | On-site, traditional framing | Factory-built modules assembled on-site |
| Build Time | Longer, subject to weather delays | Faster, parallel site preparation and module fabrication |
| Cost | Variable, higher labor costs | Generally lower due to efficiency and reduced labor |
| Quality Control | On-site inspections | Factory-controlled environment ensures consistency |
| Design Flexibility | High customization possible | Limited by module dimensions and transport restrictions |
| Environmental Impact | More site waste generated | Less waste due to factory precision and recycling |
| Durability | Established, proven method | Strong, meets or exceeds building codes |
| Site Disruption | Extended construction time causes more disruption | Minimal site disturbance due to faster assembly |
Understanding Stick-Built Construction
Stick-built construction involves assembling the building frame piece by piece on site using traditional lumber, offering flexibility in design and customization. This method allows for precise adjustments during the construction process and is well-suited for complex architectural styles. Stick-built homes often require longer construction times but provide opportunities for unique detailing and material choices.
What Is Modular Construction?
Modular construction involves manufacturing building sections in a controlled factory environment before transporting and assembling them on-site, significantly reducing construction time and waste. This method ensures consistent quality through standardized processes and enhances energy efficiency by utilizing precise material handling. Compared to stick-built construction, modular techniques minimize disruptions at the building site and often result in cost savings through streamlined logistics and labor.
Key Differences Between Stick-Built and Modular Construction
Stick-built construction involves building a structure piece-by-piece on site, allowing for extensive customization and flexibility in design. Modular construction assembles prefabricated sections in a factory setting, significantly reducing construction time and minimizing site disruption. Key differences include project timelines, cost efficiency, material waste, and quality control, with modular methods offering faster completion and consistent precision, while stick-built allows for on-site adjustments and customization.
Speed of Construction: Stick-Built vs Modular
Modular construction significantly reduces overall build time by up to 50% compared to traditional stick-built methods, as modules are fabricated off-site simultaneously with site preparation. Stick-built construction requires sequential, on-site assembly, often extending project timelines due to weather delays and labor availability. The accelerated schedule of modular construction facilitates faster occupancy and cost savings in labor and financing.
Cost Comparison: Which Method Saves More?
Stick-built construction typically incurs higher labor costs due to on-site assembly and longer project timelines, whereas modular construction benefits from factory-controlled processes that reduce labor expenses and material waste. Modular homes often achieve cost savings of 10-20% compared to traditional stick-built methods through streamlined production and minimized weather delays. Evaluating total project expenses, modular construction generally offers greater affordability by accelerating completion time and lowering overhead costs.
Quality and Durability: Stick-Built vs Modular Buildings
Stick-built construction offers customizable craftsmanship with materials selected on-site, often allowing for higher-grade finishes and tailored durability standards. Modular construction uses factory-controlled processes yielding consistent quality and reduced material waste, enhancing overall structural integrity. Both methods meet rigorous building codes, but modular buildings benefit from precise quality control, while stick-built structures provide flexibility for specialized durability requirements.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Stick-built construction often results in higher material waste and longer on-site construction times, leading to greater environmental disruption and carbon emissions. Modular construction enhances sustainability by using precise factory fabrication, which minimizes waste, improves energy efficiency, and reduces transportation emissions through consolidated deliveries. Studies show modular buildings typically have a lower carbon footprint and can achieve higher green building certifications such as LEED or BREEAM compared to traditional stick-built methods.
Flexibility and Customization Options
Stick-built construction offers superior flexibility and extensive customization options, allowing for intricate architectural designs and personalized features tailored to specific site conditions. Modular construction provides standardized components that speed up the building process but often limits design variations and intricate customization due to factory production constraints. Choosing between these methods depends on balancing the need for customized detailing against project timelines and budget considerations.
Common Challenges in Stick-Built and Modular Projects
Stick-built construction often faces challenges such as extended timelines, weather delays, and higher labor costs due to on-site building processes. Modular construction struggles with transportation logistics, limited customization options, and the need for precise on-site assembly to ensure structural integrity. Both methods require careful coordination and quality control to address these issues effectively.
Choosing the Right Construction Method for Your Building Project
Stick-built construction offers superior customization and adaptability on-site, making it ideal for projects requiring unique designs or frequent modifications. Modular construction provides enhanced speed, cost-efficiency, and reduced waste by assembling pre-fabricated sections in a controlled factory environment. Evaluating project timelines, budget constraints, site accessibility, and design complexity helps determine the optimal construction method for your building project.
Stick-built vs Modular Construction Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com