Fiber cement siding offers superior durability, resistance to moisture, and minimal maintenance compared to wood siding, making it ideal for harsh weather conditions. Wood siding provides natural insulation and aesthetic warmth but requires regular upkeep to prevent rot and insect damage. Choosing between fiber cement and wood siding depends on balancing long-term performance with the desire for traditional appearance and texture.
Table of Comparison
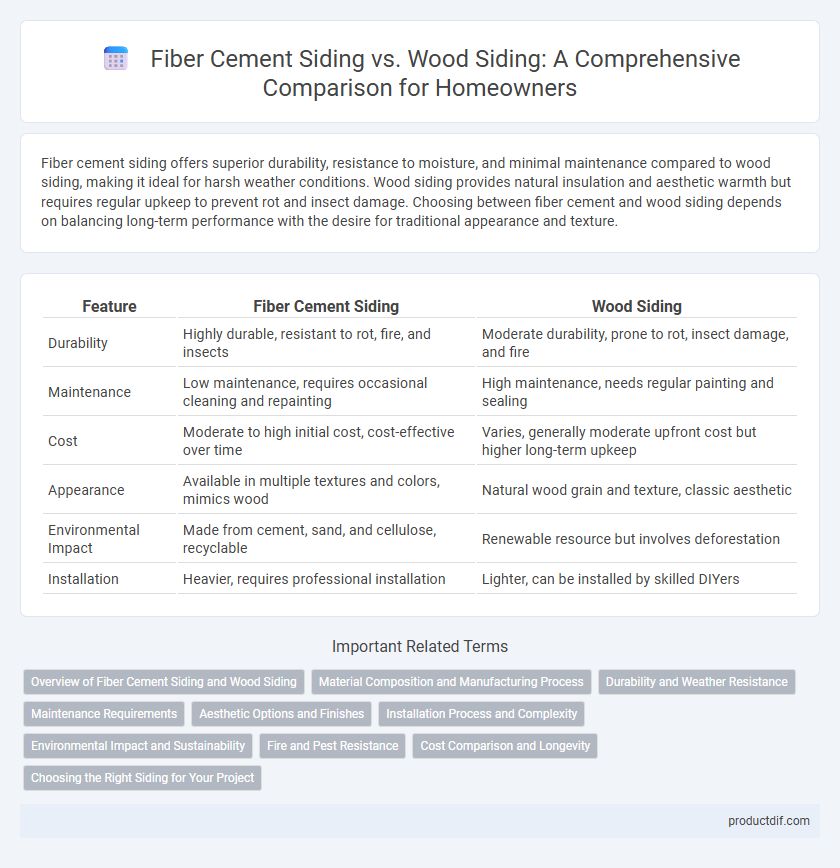
| Feature | Fiber Cement Siding | Wood Siding |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to rot, fire, and insects | Moderate durability, prone to rot, insect damage, and fire |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, requires occasional cleaning and repainting | High maintenance, needs regular painting and sealing |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial cost, cost-effective over time | Varies, generally moderate upfront cost but higher long-term upkeep |
| Appearance | Available in multiple textures and colors, mimics wood | Natural wood grain and texture, classic aesthetic |
| Environmental Impact | Made from cement, sand, and cellulose, recyclable | Renewable resource but involves deforestation |
| Installation | Heavier, requires professional installation | Lighter, can be installed by skilled DIYers |
Overview of Fiber Cement Siding and Wood Siding
Fiber cement siding is a durable, low-maintenance building material composed of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, offering resistance to fire, rot, and pests while mimicking the appearance of wood. Wood siding provides natural insulation and aesthetic warmth, but requires regular maintenance to prevent damage from moisture, insects, and decay. Fiber cement siding typically outperforms wood siding in longevity and weather resistance, making it a popular choice for modern residential construction.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Fiber cement siding consists of a mixture of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, offering enhanced durability and resistance to fire, rot, and insects compared to traditional wood siding. Wood siding is made from natural timber, typically cedar or pine, and undergoes processes such as kiln drying and planing to improve dimensional stability and finish quality. The manufacturing of fiber cement involves high-pressure molding and curing, resulting in a denser, low-maintenance product, whereas wood siding requires regular sealing and treatment to maintain its structural integrity and appearance.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Fiber cement siding offers superior durability and weather resistance compared to wood siding, as it is engineered to withstand extreme conditions like heavy rain, high winds, and hail without warping, rotting, or insect damage. Wood siding, while aesthetically pleasing, is more susceptible to moisture infiltration, decay, and termite infestation, requiring regular maintenance and protective treatments. Fiber cement's composite materials provide long-lasting performance with minimal upkeep, making it an optimal choice for climates prone to harsh weather.
Maintenance Requirements
Fiber cement siding requires minimal maintenance, resisting rot, insects, and warping, and only needs periodic cleaning and repainting every 10-15 years. Wood siding demands regular upkeep, including staining or painting every 3-7 years, plus inspections for moisture damage, insect infestations, and rot. Choosing fiber cement reduces long-term maintenance costs and labor compared to the more intensive care routine of wood siding.
Aesthetic Options and Finishes
Fiber cement siding offers a wide range of aesthetic options including wood grain textures, smooth finishes, and various color choices that resist fading and weathering over time. Wood siding provides a natural, authentic look with rich textures and can be painted or stained in numerous finishes for customized appearance, but requires regular maintenance to preserve its beauty. Homeowners seeking durable, low-maintenance siding with versatile design features often prefer fiber cement, while those wanting classic warmth and authenticity tend to choose wood.
Installation Process and Complexity
Fiber cement siding installation involves cutting heavy panels with specialized tools and securing them with nails, requiring precise measurement and protective equipment due to dust hazards. Wood siding installation is generally less complex, allowing for easier cutting and nailing with basic tools, but it demands careful moisture management to prevent warping and decay. Both materials require accurate alignment and weatherproof sealing, though fiber cement typically takes longer to install due to its density and weight.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fiber cement siding offers superior environmental benefits compared to wood siding, as it is made from sustainable raw materials like cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, reducing deforestation. Its durability and resistance to pests and rot extend the lifespan of building exteriors, minimizing the need for frequent replacements and conserving resources. Wood siding, although biodegradable, contributes to habitat loss and requires chemical treatments that can harm ecosystems, making fiber cement a more sustainable and eco-friendly option for long-term construction projects.
Fire and Pest Resistance
Fiber cement siding offers superior fire resistance due to its non-combustible composition, reducing the risk of fire damage compared to wood siding, which is highly flammable. Pest resistance is significantly better with fiber cement, as it is impervious to termites, carpenter ants, and other wood-destroying insects that commonly infest wood siding. This durability makes fiber cement siding a safer and longer-lasting option in areas prone to wildfires and pest infestations.
Cost Comparison and Longevity
Fiber cement siding typically costs between $5 to $10 per square foot, offering greater durability and lasting up to 50 years with minimal maintenance, while wood siding ranges from $4 to $7 per square foot but requires frequent upkeep and has an average lifespan of 20 to 30 years. The initial investment in fiber cement often results in long-term savings due to resistance to rot, insects, and fire, reducing replacement and repair expenses. Wood siding's lower upfront cost can increase over time due to painting, sealing, and potential damage repairs, impacting overall cost-effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Siding for Your Project
Fiber cement siding offers superior durability, resistance to fire, moisture, and pests, making it ideal for low-maintenance, long-lasting exterior cladding. Wood siding provides a natural, classic aesthetic with excellent insulation properties but requires regular maintenance to prevent rot, warping, and insect damage. Selecting the right siding depends on budget, desired appearance, climate conditions, and maintenance willingness.
Fiber Cement Siding vs Wood Siding Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com