Gypsum board offers excellent fire resistance and smooth finish, making it ideal for interior walls and ceilings, while fiber cement board provides superior durability and moisture resistance, suitable for exterior applications and areas prone to humidity. Fiber cement boards resist warping and insect damage better than gypsum, which is more susceptible to water damage and requires moisture barriers in damp environments. Choosing between the two depends on specific project needs, with gypsum board favored for ease of installation and finishing, and fiber cement board preferred for long-lasting, weather-resistant surfaces.
Table of Comparison
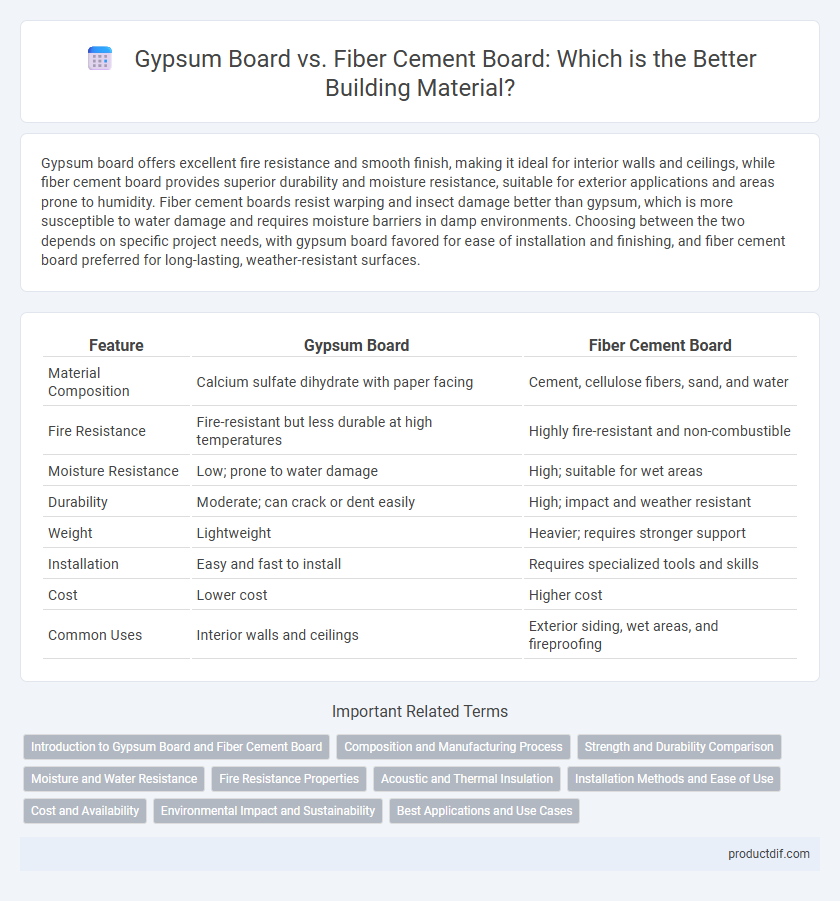
| Feature | Gypsum Board | Fiber Cement Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Calcium sulfate dihydrate with paper facing | Cement, cellulose fibers, sand, and water |
| Fire Resistance | Fire-resistant but less durable at high temperatures | Highly fire-resistant and non-combustible |
| Moisture Resistance | Low; prone to water damage | High; suitable for wet areas |
| Durability | Moderate; can crack or dent easily | High; impact and weather resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier; requires stronger support |
| Installation | Easy and fast to install | Requires specialized tools and skills |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Uses | Interior walls and ceilings | Exterior siding, wet areas, and fireproofing |
Introduction to Gypsum Board and Fiber Cement Board
Gypsum board, also known as drywall, is a lightweight construction material composed of a gypsum core sandwiched between paper layers, widely used for interior wall and ceiling applications due to its fire resistance and ease of installation. Fiber cement board consists of a mixture of cement, cellulose fibers, and sand, offering superior durability, moisture resistance, and suitability for exterior cladding and wet areas. Both materials play essential roles in modern construction, with gypsum board favored for interior finishes and fiber cement board preferred for high-moisture or exterior environments.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Gypsum board is composed mainly of calcium sulfate dihydrate pressed between thick sheets of paper, produced using a slurry of water, gypsum, and additives that hardens by drying. Fiber cement board consists of cement mixed with cellulose fibers, sand, and other reinforcing materials, formed through a process of extrusion or pressing and then cured under controlled conditions. The manufacturing of gypsum board emphasizes rapid-setting hydration, whereas fiber cement board requires curing that enhances durability and moisture resistance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Fiber cement board offers superior strength and durability compared to gypsum board, making it ideal for exterior applications and high-moisture environments. Gypsum board is more susceptible to water damage and lacks the impact resistance of fiber cement, which resists cracking and warping under stress. The dense composition of fiber cement board ensures enhanced longevity and structural integrity in demanding construction conditions.
Moisture and Water Resistance
Fiber cement board offers superior moisture and water resistance compared to gypsum board, making it ideal for high-humidity and wet areas such as bathrooms and exterior applications. Gypsum board tends to absorb water, leading to swelling, mold growth, and structural degradation if exposed to prolonged moisture. Selecting fiber cement board ensures enhanced durability and longevity in environments with frequent water exposure.
Fire Resistance Properties
Gypsum board offers exceptional fire resistance due to its non-combustible core containing chemically combined water, which releases steam to slow heat transfer and retard fire spread. Fiber cement board also provides strong fire resistance, as it is made from a mixture of cement and cellulose fibers that are inherently non-combustible and do not support flame propagation. Both materials meet stringent fire safety standards, but gypsum board is often preferred for interior applications requiring superior fire-rated assemblies.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation
Gypsum board provides effective sound absorption and moderate thermal insulation, making it suitable for interior partitions where noise reduction and temperature control are essential. Fiber cement board offers superior durability with enhanced thermal resistance and good acoustic dampening, ideal for exterior facades or high-moisture environments requiring robust insulation. Both materials support energy efficiency, but fiber cement boards excel in thermal insulation while gypsum boards are preferred for superior acoustic performance in indoor settings.
Installation Methods and Ease of Use
Gypsum board installation involves cutting sheets to size, securing them with screws or nails to metal or wood framing, and finishing with joint tape and compound for a smooth surface. Fiber cement board requires specialized tools for cutting due to its dense composition and is fastened with corrosion-resistant screws, often followed by sealing edges to prevent moisture penetration. Gypsum board is generally easier and faster to install, making it suitable for interior walls, while fiber cement board offers greater durability and moisture resistance, ideal for exterior applications.
Cost and Availability
Gypsum board offers a cost-effective solution with wide availability in most construction markets, making it a popular choice for drywall installation. Fiber cement board, while more expensive than gypsum, provides enhanced durability and moisture resistance, which justifies its higher price in specialized applications. Availability of fiber cement board is more limited compared to gypsum, often found through specialized suppliers or in regions with higher demand for weather-resistant materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum board offers lower embodied energy and is fully recyclable, contributing to reduced landfill waste, while fiber cement board involves higher energy consumption due to its cement and silica content but provides longer durability, reducing replacement frequency. Both materials have distinct environmental footprints: gypsum board's mining and reading recyclability align with circular economy principles, whereas fiber cement board offers resistance to mold and pests, decreasing chemical treatments that impact ecosystems. Selection depends on balancing embodied carbon, resource renewability, and lifecycle longevity aligned with sustainable building certifications such as LEED or BREEAM.
Best Applications and Use Cases
Gypsum board excels in interior wall and ceiling applications due to its fire resistance, ease of installation, and smooth finish ideal for painting or wallpaper. Fiber cement board is best suited for exterior siding, wet areas, and high-impact zones because of its moisture resistance, durability, and resistance to mold and rot. Choosing between gypsum board and fiber cement depends on the environment, with gypsum favored indoors and fiber cement prioritized for weather-exposed or high-humidity settings.
Gypsum board vs Fiber cement board Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com