Manual tools offer greater precision and control for detailed tasks, making them ideal for fine craftsmanship and repairs without power dependency. Electric tools significantly increase efficiency and reduce physical effort, enabling users to complete large or repetitive jobs quickly and with consistent power output. Choosing between manual and electric tools depends on the specific project requirements, portability needs, and the user's skill level.
Table of Comparison
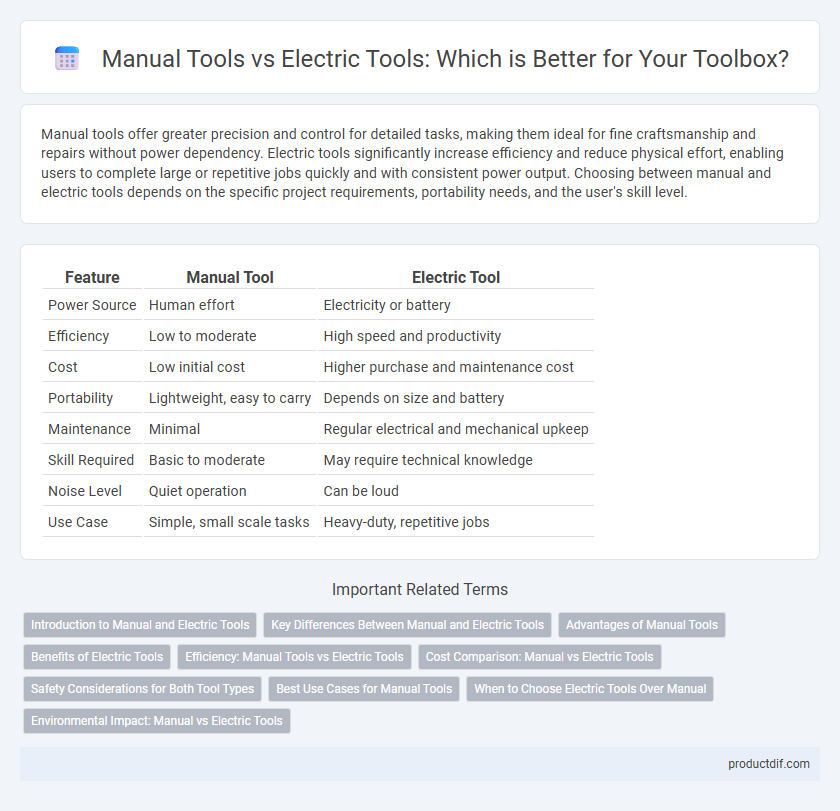
| Feature | Manual Tool | Electric Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Human effort | Electricity or battery |
| Efficiency | Low to moderate | High speed and productivity |
| Cost | Low initial cost | Higher purchase and maintenance cost |
| Portability | Lightweight, easy to carry | Depends on size and battery |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular electrical and mechanical upkeep |
| Skill Required | Basic to moderate | May require technical knowledge |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | Can be loud |
| Use Case | Simple, small scale tasks | Heavy-duty, repetitive jobs |
Introduction to Manual and Electric Tools
Manual tools rely on human power and skill for operation, offering precise control and portability without the need for electricity. Electric tools use a motor powered by batteries or an electrical outlet, providing increased speed and efficiency for heavy-duty tasks. Understanding the differences in power source, functionality, and application helps choose the appropriate tool for specific projects.
Key Differences Between Manual and Electric Tools
Manual tools rely on human strength and skill for operation, offering precision and control without the need for power sources. Electric tools use motorized power, enabling faster, more consistent performance and reducing physical effort. Key differences include efficiency, ease of use, maintenance requirements, and suitability for various tasks and scales of work.
Advantages of Manual Tools
Manual tools offer precise control and enhanced safety, reducing the risk of accidents due to their slower and more deliberate operation. They require no power source, making them highly reliable and cost-effective for use in remote locations or during power outages. The simplicity of manual tools ensures easier maintenance and longer durability compared to electric alternatives.
Benefits of Electric Tools
Electric tools offer significant benefits over manual tools, including increased efficiency and reduced physical effort, allowing users to complete tasks faster and with less fatigue. Their precision and power enable consistent performance in demanding applications such as drilling, cutting, and fastening. Battery-powered models provide portability and convenience, making them ideal for both professional contractors and DIY enthusiasts.
Efficiency: Manual Tools vs Electric Tools
Manual tools require physical effort and more time to complete tasks, often suitable for precision work and small projects but less efficient for extensive or repetitive jobs. Electric tools significantly increase efficiency by providing consistent power, reducing user fatigue, and speeding up task completion, making them ideal for large-scale or heavy-duty projects. Choosing between manual and electric tools depends on the nature of the work, with electric tools offering superior efficiency in productivity and time management.
Cost Comparison: Manual vs Electric Tools
Manual tools generally have a lower upfront cost compared to electric tools, making them more budget-friendly for basic tasks. Electric tools, while more expensive initially, offer greater efficiency and reduced labor time, potentially lowering long-term operational costs. When considering maintenance, manual tools typically incur fewer expenses since they lack complex components that require repairs or battery replacements.
Safety Considerations for Both Tool Types
Manual tools reduce the risk of electric shock and typically offer greater control, minimizing accidental injuries if used properly. Electric tools, while more efficient, require strict adherence to safety protocols such as grounding, regular inspection for damaged cords, and the use of personal protective equipment. Understanding the operational differences and hazards of each tool type is essential to prevent accidents and ensure safe handling in various work environments.
Best Use Cases for Manual Tools
Manual tools excel in precision tasks such as carving, fine woodworking, and detailed crafting where control and delicacy are paramount. They are ideal for environments lacking power sources or requiring quiet operation, such as remote outdoor settings or noise-sensitive workshops. Tasks involving small adjustments, intricate assembly, or maintenance work benefit from the tactile feedback and simplicity of manual tools.
When to Choose Electric Tools Over Manual
Electric tools offer superior efficiency and speed for tasks requiring repetitive motion or high precision, making them ideal for large projects or professional use. They reduce physical strain and increase productivity by providing consistent power, especially useful in woodworking, metalworking, and home improvement. When accuracy, time-saving, and ease of use are priorities, electric tools outperform manual alternatives significantly.
Environmental Impact: Manual vs Electric Tools
Manual tools significantly reduce environmental impact by eliminating the need for electricity or batteries, resulting in zero carbon emissions during operation. Electric tools, while enhancing efficiency and power, contribute to carbon footprints through energy consumption and battery disposal challenges. Choosing manual tools supports sustainability and reduces long-term ecological damage compared to the environmental costs associated with manufacturing, operating, and disposing of electric tools.
Manual Tool vs Electric Tool Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com