Manual chisels offer precise control and tactile feedback ideal for detailed woodworking and fine carving tasks. Electric chisels increase efficiency by delivering consistent power and speed, reducing physical strain during repetitive or heavy-duty jobs. Choosing between the two depends on the project's scale, required accuracy, and user comfort preferences.
Table of Comparison
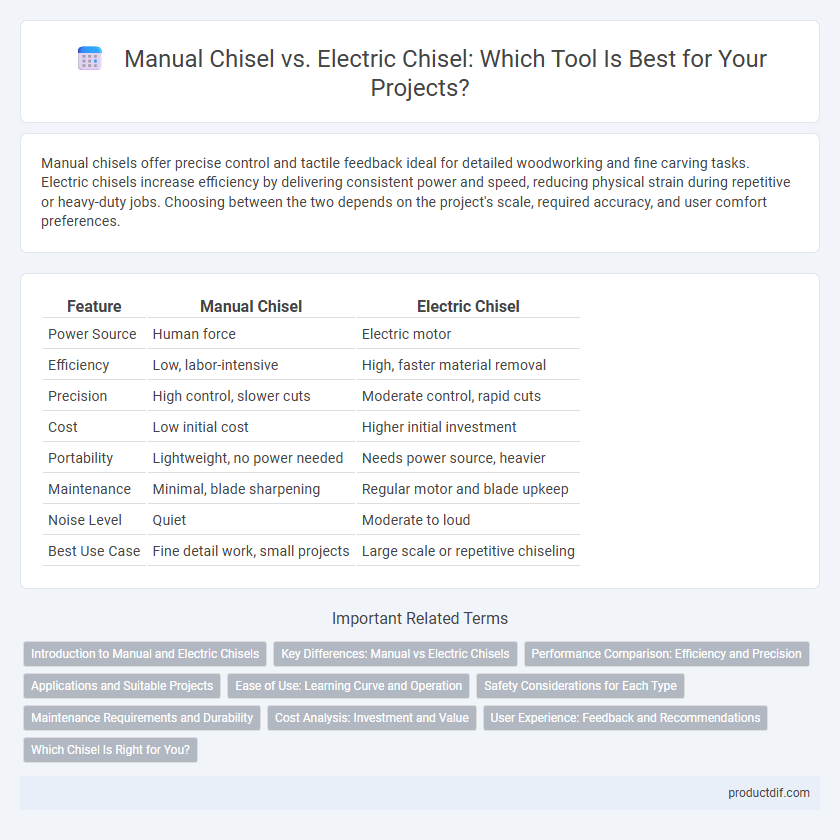
| Feature | Manual Chisel | Electric Chisel |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Human force | Electric motor |
| Efficiency | Low, labor-intensive | High, faster material removal |
| Precision | High control, slower cuts | Moderate control, rapid cuts |
| Cost | Low initial cost | Higher initial investment |
| Portability | Lightweight, no power needed | Needs power source, heavier |
| Maintenance | Minimal, blade sharpening | Regular motor and blade upkeep |
| Noise Level | Quiet | Moderate to loud |
| Best Use Case | Fine detail work, small projects | Large scale or repetitive chiseling |
Introduction to Manual and Electric Chisels
Manual chisels consist of a sharp steel blade and a handle, designed for precision woodworking and carving tasks by applying hand force. Electric chisels incorporate a motorized blade that offers increased speed and efficiency for removing material with less physical effort. Both tools are essential for different levels of carving detail and project scale in woodworking and construction.
Key Differences: Manual vs Electric Chisels
Manual chisels rely solely on hand force for precision woodworking tasks, offering superior control in detailed carving and finishing. Electric chisels, powered by motors, provide increased speed and efficiency for heavy-duty chiseling and repetitive cuts, reducing user fatigue. Key differences include power source, control level, and suitability for intricate versus large-scale projects.
Performance Comparison: Efficiency and Precision
Electric chisels deliver higher efficiency by automating repetitive motions, significantly reducing user fatigue and enabling faster material removal compared to manual chisels. Precision in electric chisels is enhanced through adjustable speed controls and consistent power output, allowing for more accurate and uniform cuts on various materials. Manual chisels offer superior tactile feedback that benefits detailed craftsmanship but generally require more skill and time to achieve similar precision and efficiency levels.
Applications and Suitable Projects
Manual chisels excel in precision woodworking, detailed carving, and small-scale projects where control and finesse are essential, making them ideal for furniture restoration and intricate joinery. Electric chisels deliver faster material removal and are better suited for large-scale demolition, heavy-duty construction, and projects requiring substantial shaping of wood or masonry. Selecting the appropriate tool depends on the project's complexity, required accuracy, and the volume of material processed.
Ease of Use: Learning Curve and Operation
Manual chisels offer straightforward handling with a minimal learning curve, relying solely on user skill and control for precise carving. Electric chisels reduce physical effort and increase efficiency but require familiarization with power settings and safety precautions to operate effectively. Choosing between the two depends on the user's experience level and the complexity of the woodworking project.
Safety Considerations for Each Type
Manual chisels offer greater control and reduced risk of injury due to the user's direct handling and slower cutting speed, making them safer for detailed or precision work. Electric chisels require stringent safety measures such as proper grounding, use of guards, and personal protective equipment to prevent accidents caused by high-speed operation and potential kickback. Users must assess the work environment and maintenance condition to mitigate hazards associated with electric chisels.
Maintenance Requirements and Durability
Manual chisels require minimal maintenance, typically limited to regular sharpening and cleaning to prevent rust, ensuring long-lasting durability even with frequent use. Electric chisels demand more intensive upkeep, including motor inspections, electrical component care, and occasional replacement of worn parts to maintain optimal performance. Durability of manual chisels generally surpasses electric models due to simpler construction and fewer mechanical failures.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Value
Manual chisels require a low initial investment, making them cost-effective for occasional use and simple woodworking tasks with minimal maintenance expenses. Electric chisels involve a higher upfront cost but provide increased efficiency, precision, and reduced labor time, potentially offering better value for professionals or frequent users. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including tool lifespan, power consumption, and productivity gains, is essential for determining the most economical choice.
User Experience: Feedback and Recommendations
Manual chisels offer precise tactile feedback, enabling craftsmen to control depth and angle accurately, which enhances intricate woodworking tasks. Electric chisels provide consistent power and speed, reducing physical strain but may sacrifice some sensitivity essential for detailed carving. Users seeking fine control and artistic precision tend to prefer manual chisels, while those prioritizing efficiency and repetitive work often recommend electric chisels.
Which Chisel Is Right for You?
Manual chisels offer precise control and are ideal for detailed woodworking or carving tasks requiring a delicate touch, while electric chisels provide increased power and efficiency for repetitive or heavy-duty projects. Choosing the right chisel depends on your specific needs, such as the type of material, project complexity, and desired speed. Consider factors like ergonomics, maintenance, and cost when deciding between manual and electric chisels to ensure optimal performance and comfort.
Manual Chisel vs Electric Chisel Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com