Assembly tools are designed to join or fit components together efficiently, ensuring precise alignment and secure fastening. Disassembly tools focus on safely separating parts without causing damage, often featuring mechanisms to undo fasteners or pry components apart. Choosing the right tool depends on the task, as assembly tools optimize construction while disassembly tools facilitate repair or recycling processes.
Table of Comparison
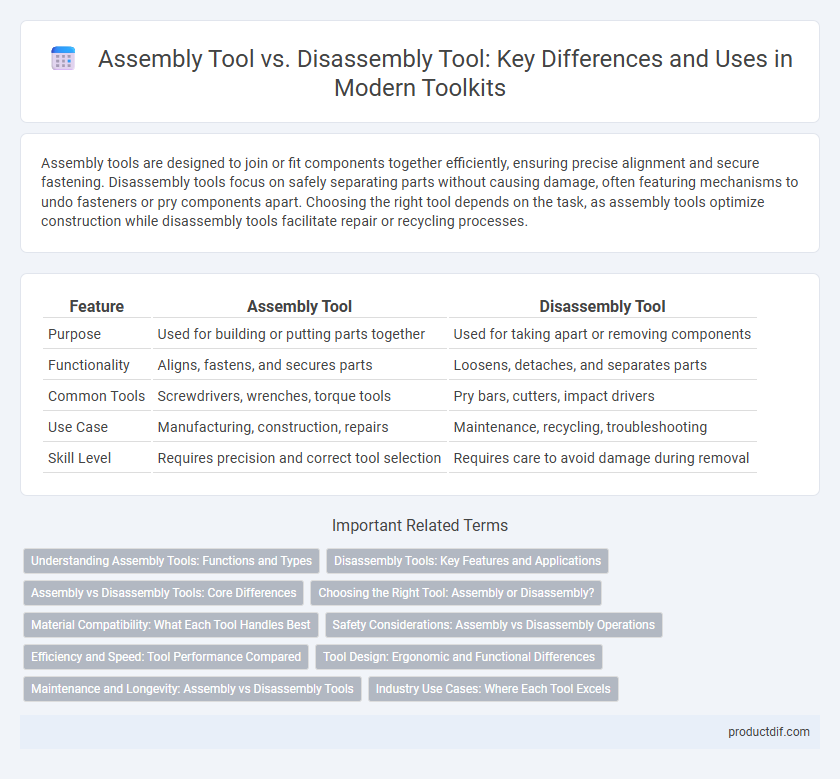
| Feature | Assembly Tool | Disassembly Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Used for building or putting parts together | Used for taking apart or removing components |
| Functionality | Aligns, fastens, and secures parts | Loosens, detaches, and separates parts |
| Common Tools | Screwdrivers, wrenches, torque tools | Pry bars, cutters, impact drivers |
| Use Case | Manufacturing, construction, repairs | Maintenance, recycling, troubleshooting |
| Skill Level | Requires precision and correct tool selection | Requires care to avoid damage during removal |
Understanding Assembly Tools: Functions and Types
Assembly tools, such as screwdrivers, wrenches, and hammers, are specifically designed to join components securely during manufacturing or repair processes. These tools enable precise fitting, fastening, and alignment of parts to ensure structural integrity and functional performance. Different types of assembly tools include manual, pneumatic, and electric variants, each suited for specific materials and applications.
Disassembly Tools: Key Features and Applications
Disassembly tools are designed specifically to efficiently and safely take apart components without causing damage, featuring precision tips, adjustable torque settings, and ergonomic handles to enhance user control. Common applications include electronics repair, automotive maintenance, and machinery overhaul where careful separation of parts is crucial. These tools often incorporate features like non-slip grips and multi-function heads to accommodate various fasteners and materials during the disassembly process.
Assembly vs Disassembly Tools: Core Differences
Assembly tools are designed to efficiently join components together, typically featuring mechanisms like screwdrivers, clamps, and torque wrenches that ensure precise fitting and secure fastening. Disassembly tools focus on safely separating parts without causing damage, including pry bars, pullers, and crowbars specifically engineered for controlled force application. The core differences lie in their purpose and design: assembly tools prioritize alignment and fastening, whereas disassembly tools emphasize leverage and separation.
Choosing the Right Tool: Assembly or Disassembly?
Selecting the right tool hinges on the task's nature: assembly tools are designed for constructing, fastening, and securing components, while disassembly tools specialize in loosening, prying, and dismantling parts. Using an assembly tool like a torque wrench or screw gun ensures precision and efficiency during build processes, whereas disassembly tools such as pry bars, impact drivers, and extractor sets reduce damage risk when removing fasteners or components. Understanding the specific mechanical requirements and material conditions guides the optimal choice between assembly and disassembly tools, enhancing workflow and tool longevity.
Material Compatibility: What Each Tool Handles Best
Assembly tools excel in compatibility with materials like metal fasteners, plastic components, and wood, designed to securely join parts without causing damage or deformation. Disassembly tools specialize in safely separating materials such as glued joints, riveted metals, and snap-fit plastics, minimizing wear and preserving material integrity. Choosing the right tool depends on the specific material properties and the required precision for either joining or separating components.
Safety Considerations: Assembly vs Disassembly Operations
Assembly tools require careful handling to prevent injuries caused by pinching or crushing forces during component fitting, emphasizing the use of ergonomic grips and protective gloves. Disassembly tools demand attention to potential sudden releases of tension or stored energy in parts, necessitating safeguards like safety glasses and controlled force application. Both operations benefit significantly from clear workspace organization and adherence to manufacturer safety guidelines to minimize accident risks.
Efficiency and Speed: Tool Performance Compared
Assembly tools are engineered to enhance efficiency and speed by streamlining component integration through precise torque control and ergonomic design, significantly reducing operational time. Disassembly tools prioritize rapid and safe extraction of parts, often featuring specialized mechanisms like impact drivers or leverage arms that minimize damage and effort. In comparing tool performance, assembly tools excel in repetitive, high-precision tasks, whereas disassembly tools optimize speed in breakdown processes, making each indispensable depending on workflow requirements.
Tool Design: Ergonomic and Functional Differences
Assembly tools prioritize ergonomic grips and precision to enhance user control and reduce fatigue during repetitive tasks, often featuring mechanisms that facilitate fasteners' secure placement. Disassembly tools emphasize leverage, durability, and access to tight or obscured fasteners, with designs that minimize risk of component damage while maximizing force application. Functional differences manifest in torque control, handle design, and tool tip geometry, tailored to assembly's constructive needs versus disassembly's deconstructive challenges.
Maintenance and Longevity: Assembly vs Disassembly Tools
Assembly tools are designed to efficiently join components, ensuring precise alignment and secure fastening, which enhances the overall durability of equipment during maintenance. Disassembly tools focus on safely separating parts without causing damage, preserving the integrity of components for prolonged use and reducing wear. Utilizing the correct tool for assembly or disassembly minimizes equipment strain, extending the operational lifespan and optimizing maintenance effectiveness.
Industry Use Cases: Where Each Tool Excels
Assembly tools excel in manufacturing industries requiring precision and repeatability, such as automotive and electronics production, where efficient component joining is critical. Disassembly tools are vital in maintenance, repair, and recycling sectors, enabling safe and systematic breakdown of products like machinery and appliances. Each tool optimizes workflow by tailoring functionality to either construction or deconstruction processes in industrial applications.
Assembly tool vs Disassembly tool Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com