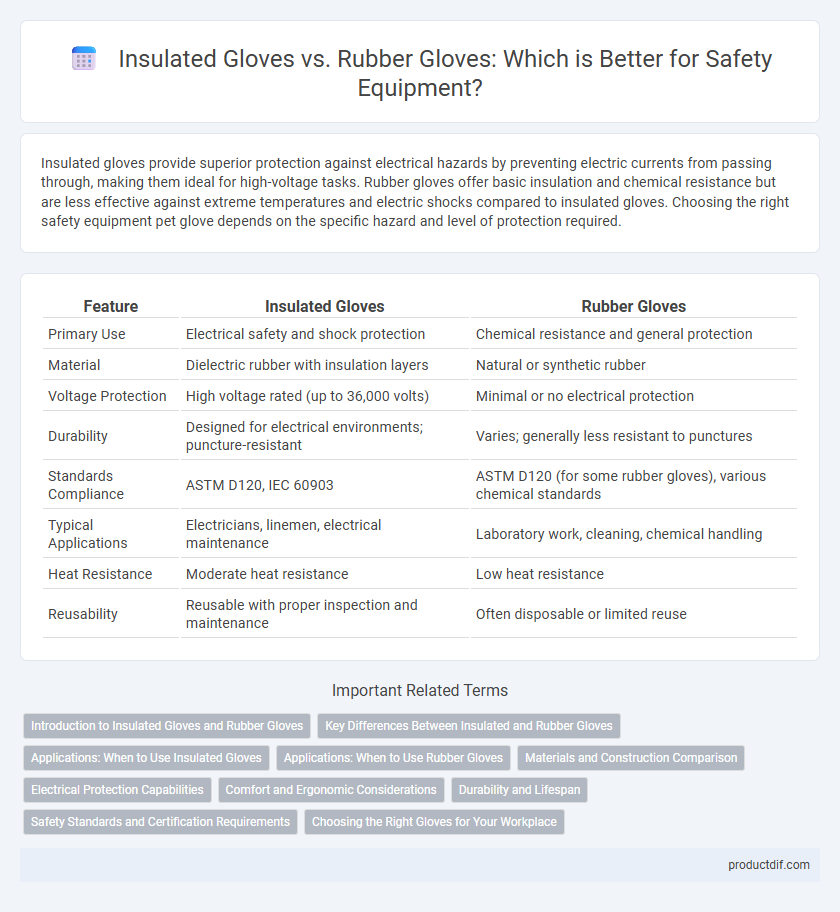
Insulated gloves provide superior protection against electrical hazards by preventing electric currents from passing through, making them ideal for high-voltage tasks. Rubber gloves offer basic insulation and chemical resistance but are less effective against extreme temperatures and electric shocks compared to insulated gloves. Choosing the right safety equipment pet glove depends on the specific hazard and level of protection required.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Insulated Gloves | Rubber Gloves |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Electrical safety and shock protection | Chemical resistance and general protection |
| Material | Dielectric rubber with insulation layers | Natural or synthetic rubber |
| Voltage Protection | High voltage rated (up to 36,000 volts) | Minimal or no electrical protection |
| Durability | Designed for electrical environments; puncture-resistant | Varies; generally less resistant to punctures |
| Standards Compliance | ASTM D120, IEC 60903 | ASTM D120 (for some rubber gloves), various chemical standards |
| Typical Applications | Electricians, linemen, electrical maintenance | Laboratory work, cleaning, chemical handling |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | Low heat resistance |
| Reusability | Reusable with proper inspection and maintenance | Often disposable or limited reuse |
Introduction to Insulated Gloves and Rubber Gloves
Insulated gloves are designed to protect workers from electrical hazards by providing a non-conductive barrier, essential in high-voltage environments. Rubber gloves, often used in industrial and medical settings, offer chemical resistance and basic electrical protection but lack the specialized insulation properties of insulated gloves. Choosing the right type depends on the specific safety requirements, such as voltage levels and exposure to hazardous materials.
Key Differences Between Insulated and Rubber Gloves
Insulated gloves are designed specifically for electrical protection, featuring layers of non-conductive materials to guard against electric shock up to certain voltage ratings. Rubber gloves, while also non-conductive, are often used for general chemical resistance and mechanical protection but may lack the specialized insulation properties required for high-voltage electrical work. Key differences include voltage protection level--insulated gloves meet stringent ASTM or IEC standards for electrical safety, whereas rubber gloves prioritize resistance to chemicals and physical hazards without guaranteed electrical insulation.
Applications: When to Use Insulated Gloves
Insulated gloves are essential for electricians and workers handling live electrical circuits, providing protection against high voltage and preventing electrical shock. These gloves are designed to maintain safety during maintenance and installation tasks in power utilities, industrial plants, and construction sites. Rubber gloves, while offering chemical and general protection, do not provide adequate insulation for high-voltage electrical work where insulated gloves are mandated.
Applications: When to Use Rubber Gloves
Rubber gloves are essential for electrical work due to their superior insulating properties that protect against electric shocks up to specified voltage levels. They are preferred in environments where workers handle live wires, electrical installations, or equipment maintenance requiring reliable dielectric protection. For chemical handling or general-purpose tasks, insulated gloves with additional protective layers may be more appropriate depending on hazard exposure.
Materials and Construction Comparison
Insulated gloves are typically made from multiple layers combining leather, rubber, and fabric to provide thermal protection and electrical insulation, whereas rubber gloves are primarily constructed from latex, neoprene, or nitrile for chemical resistance and electrical insulation. The multi-layer construction of insulated gloves includes an inner insulating liner and an outer protective shell, enhancing durability and safety in high-voltage environments. Rubber gloves generally feature a single or double rubber layer designed for flexibility and sealing against contaminants but lack the additional thermal protection found in insulated gloves.
Electrical Protection Capabilities
Insulated gloves provide superior electrical protection by meeting established ASTM D120 standards for live electrical work, ensuring dielectric strength against high-voltage shock hazards. Rubber gloves, often used as protective layering, lack the comprehensive insulation qualities of insulated gloves unless specifically rated for electrical applications. Selecting gloves certified for electrical resistance significantly reduces the risk of electrical injury in hazardous environments.
Comfort and Ergonomic Considerations
Insulated gloves provide superior thermal protection while maintaining flexibility, ensuring comfort during extended use in electrical and cold environments. Rubber gloves, though effective for electrical insulation, often lack breathability and ergonomic design, which can lead to hand fatigue and discomfort over prolonged periods. Choosing gloves with proper fit and material that allow dexterity enhances safety without compromising user comfort.
Durability and Lifespan
Insulated gloves typically offer superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to rubber gloves due to their multi-layer construction and resistance to electrical and thermal hazards. Rubber gloves, while flexible and cost-effective, tend to wear out faster under harsh conditions and require more frequent replacement to maintain safety standards. Choosing insulated gloves ensures enhanced protection and sustained performance in high-risk environments.
Safety Standards and Certification Requirements
Insulated gloves are designed to meet rigorous safety standards such as ASTM D120 and IEC 60903, ensuring protection against electrical hazards up to specific voltage levels. Rubber gloves, while also conforming to similar certifications, often require frequent testing and proper layering with leather protectors to maintain their insulating properties. Compliance with OSHA and NFPA 70E regulations is critical for both types to guarantee worker safety in electrical environments.
Choosing the Right Gloves for Your Workplace
Selecting the appropriate gloves for workplace safety is crucial, with insulated gloves offering superior protection against electrical hazards by preventing electric shock through high-voltage insulation. Rubber gloves provide excellent resistance to chemicals, punctures, and general mechanical risks, making them ideal for diverse industrial environments. Evaluating the specific hazards, voltage levels, and material compatibility in your workplace ensures optimal hand protection and compliance with safety standards.
insulated gloves vs rubber gloves Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com