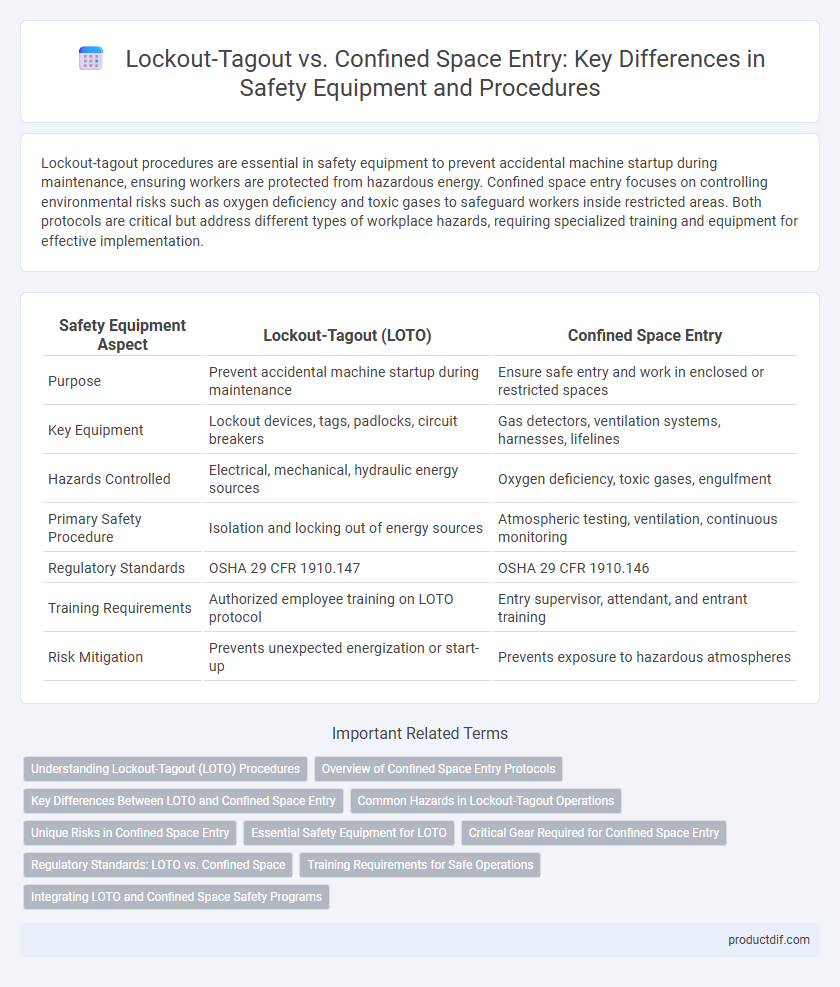
Lockout-tagout procedures are essential in safety equipment to prevent accidental machine startup during maintenance, ensuring workers are protected from hazardous energy. Confined space entry focuses on controlling environmental risks such as oxygen deficiency and toxic gases to safeguard workers inside restricted areas. Both protocols are critical but address different types of workplace hazards, requiring specialized training and equipment for effective implementation.
Table of Comparison
| Safety Equipment Aspect | Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) | Confined Space Entry |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevent accidental machine startup during maintenance | Ensure safe entry and work in enclosed or restricted spaces |
| Key Equipment | Lockout devices, tags, padlocks, circuit breakers | Gas detectors, ventilation systems, harnesses, lifelines |
| Hazards Controlled | Electrical, mechanical, hydraulic energy sources | Oxygen deficiency, toxic gases, engulfment |
| Primary Safety Procedure | Isolation and locking out of energy sources | Atmospheric testing, ventilation, continuous monitoring |
| Regulatory Standards | OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 | OSHA 29 CFR 1910.146 |
| Training Requirements | Authorized employee training on LOTO protocol | Entry supervisor, attendant, and entrant training |
| Risk Mitigation | Prevents unexpected energization or start-up | Prevents exposure to hazardous atmospheres |
Understanding Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) Procedures
Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) procedures are critical safety protocols designed to prevent accidental machine startup or energization during maintenance by isolating energy sources and applying lockout devices. Proper implementation involves identifying all energy sources, de-energizing equipment, and securing locks and tags to ensure workers cannot inadvertently activate the machinery. Understanding LOTO reduces risks of electrical shocks, mechanical injuries, and fatalities, making it essential in industries with heavy machinery and complex energy systems.
Overview of Confined Space Entry Protocols
Confined space entry protocols mandate identifying hazards, testing the atmosphere for oxygen levels and toxic gases, and ensuring continuous ventilation to maintain safe conditions. Workers must use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and secure an attendant outside the confined space for emergency communication and rescue. Lockout-tagout procedures complement these protocols by isolating hazardous energy sources to prevent accidental equipment startup during confined space operations.
Key Differences Between LOTO and Confined Space Entry
Lockout-tagout (LOTO) primarily controls hazardous energy sources to prevent accidental machine startup during maintenance, while confined space entry focuses on ensuring safe access and monitoring atmospheric conditions within enclosed or restricted spaces. LOTO involves securing energy-isolating devices with locks and tags, whereas confined space entry requires atmospheric testing, ventilation, and continuous communication. Both procedures are critical for worker safety but address fundamentally different hazards and operational environments.
Common Hazards in Lockout-Tagout Operations
Common hazards in lockout-tagout operations include unexpected machinery startup, stored energy release, and human error during lock removal. Workers face risks from electrical shocks, mechanical entanglement, and residual pressure in equipment lacking proper de-energization. Effective training and adherence to OSHA standards are critical to preventing injuries related to these hazards.
Unique Risks in Confined Space Entry
Confined space entry involves unique risks such as oxygen deficiency, toxic atmospheres, and engulfment hazards that are not addressed by lockout-tagout procedures. Unlike lockout-tagout, which focuses on controlling hazardous energy sources during equipment maintenance, confined space safety requires atmospheric testing, ventilation, and continuous monitoring to prevent asphyxiation and poisoning. Rescue plans and specialized personal protective equipment (PPE) are critical to managing the dangers inherent in confined space environments.
Essential Safety Equipment for LOTO
Essential safety equipment for Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) includes lockout devices, tags, padlocks, and circuit breaker lockouts designed to isolate hazardous energy sources and prevent accidental machine startup. In contrast to confined space entry gear, LOTO equipment focuses specifically on securing electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, and pneumatic energy controls to safeguard maintenance personnel. Proper use of LOTO devices is critical to compliance with OSHA standards and minimizing workplace injuries due to unexpected energization.
Critical Gear Required for Confined Space Entry
Critical gear required for confined space entry includes intrinsically safe gas detectors, personal protective equipment (PPE) such as full-body harnesses with retrieval lines, and respiratory protection like supplied-air or self-contained breathing apparatuses. Lockout-tagout primarily focuses on isolating energy sources to prevent accidental machine start-up, whereas confined space entry demands specialized gear to address atmospheric hazards, physical entrapment risks, and rescue readiness. Proper use of this critical equipment is essential to comply with OSHA regulations and ensure worker safety in confined environments.
Regulatory Standards: LOTO vs. Confined Space
Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) safety equipment compliance is governed by OSHA standard 29 CFR 1910.147, which mandates control of hazardous energy during machinery servicing to prevent accidental startup. Confined space entry is regulated under OSHA's 29 CFR 1910.146, requiring specific protocols such as atmospheric testing and permit systems to protect workers inside spaces with limited entry or ventilation. Both standards emphasize employee training and risk assessment, but LOTO focuses on energy isolation while confined space regulations prioritize safe entry and rescue procedures.
Training Requirements for Safe Operations
Lockout-tagout training requires workers to understand energy control procedures, identification of hazardous energy sources, and proper use of locking and tagging devices to prevent accidental machine startup. Confined space entry training emphasizes hazard recognition, communication protocols, atmospheric testing, ventilation, and emergency rescue techniques. Both training programs are essential for compliance with OSHA standards to ensure worker safety in different high-risk environments.
Integrating LOTO and Confined Space Safety Programs
Integrating Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) and Confined Space Entry safety programs enhances workplace hazard control by ensuring energy sources are effectively isolated before personnel enter confined spaces. Combining these protocols minimizes risks of unexpected equipment startup and hazardous atmospheres, providing comprehensive protection against mechanical, electrical, and environmental dangers. Implementing joint training, coordinated procedures, and synchronized permits strengthens compliance with OSHA standards and promotes a unified safety culture.
Lockout-tagout vs Confined space entry Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com