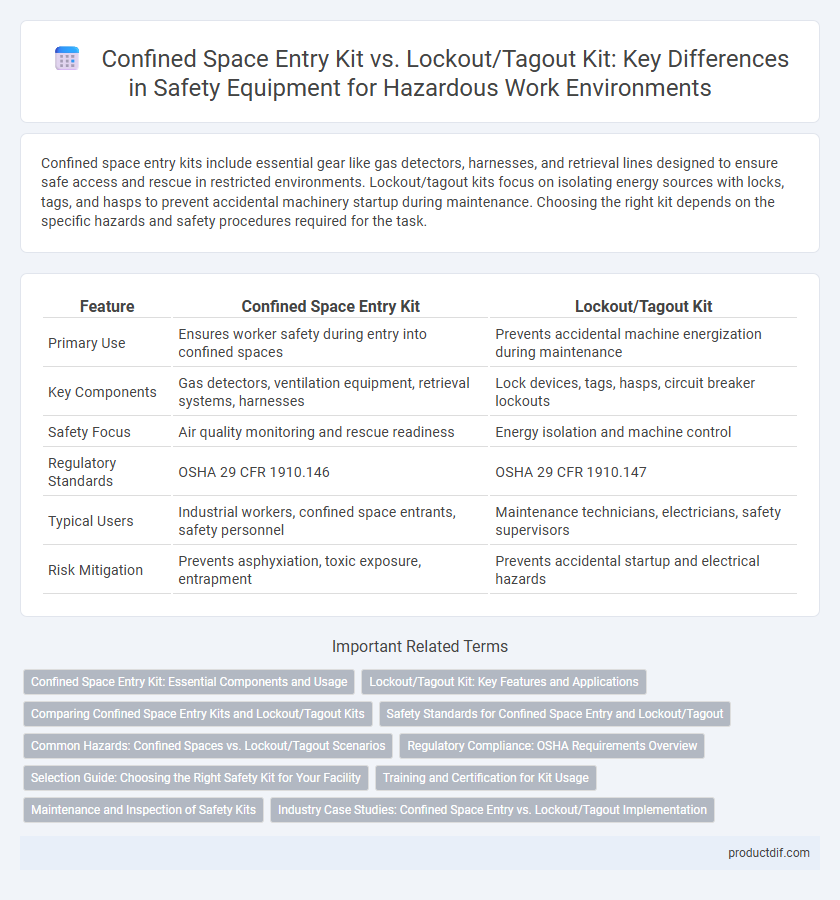
Confined space entry kits include essential gear like gas detectors, harnesses, and retrieval lines designed to ensure safe access and rescue in restricted environments. Lockout/tagout kits focus on isolating energy sources with locks, tags, and hasps to prevent accidental machinery startup during maintenance. Choosing the right kit depends on the specific hazards and safety procedures required for the task.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Confined Space Entry Kit | Lockout/Tagout Kit |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Ensures worker safety during entry into confined spaces | Prevents accidental machine energization during maintenance |
| Key Components | Gas detectors, ventilation equipment, retrieval systems, harnesses | Lock devices, tags, hasps, circuit breaker lockouts |
| Safety Focus | Air quality monitoring and rescue readiness | Energy isolation and machine control |
| Regulatory Standards | OSHA 29 CFR 1910.146 | OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 |
| Typical Users | Industrial workers, confined space entrants, safety personnel | Maintenance technicians, electricians, safety supervisors |
| Risk Mitigation | Prevents asphyxiation, toxic exposure, entrapment | Prevents accidental startup and electrical hazards |
Confined Space Entry Kit: Essential Components and Usage
A Confined Space Entry Kit includes vital components such as gas detectors, ventilation fans, harnesses, retrieval systems, and communication devices designed to ensure worker safety during entry into hazardous enclosed spaces. These kits are essential for monitoring air quality, preventing toxic exposure, and providing emergency rescue capabilities in confined spaces like tanks, sewers, or silos. Proper usage involves thorough risk assessment, continuous atmospheric testing, and adherence to safety protocols to minimize the risk of accidents or suffocation.
Lockout/Tagout Kit: Key Features and Applications
Lockout/Tagout kits contain essential devices such as padlocks, tags, hasps, and lockout devices designed to isolate energy sources and prevent accidental equipment startup during maintenance. These kits are crucial for ensuring worker safety by controlling hazardous energy in industrial environments, minimizing the risk of electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, or pneumatic injuries. Common applications include machinery repair, electrical panel servicing, and equipment lockout situations across manufacturing, construction, and maintenance sectors.
Comparing Confined Space Entry Kits and Lockout/Tagout Kits
Confined Space Entry Kits focus on providing essential tools such as gas detectors, ventilation fans, harnesses, and retrieval systems to ensure worker safety in hazardous enclosed environments. Lockout/Tagout Kits primarily include lockout devices, tags, hasps, and padlocks designed to isolate energy sources and prevent accidental startup of machinery during maintenance. Choosing between the two depends on specific safety requirements: confined space kits address atmospheric and physical hazards, while lockout/tagout kits control energy hazards to protect maintenance personnel.
Safety Standards for Confined Space Entry and Lockout/Tagout
Safety standards for confined space entry, governed by OSHA 29 CFR 1910.146, require specialized equipment such as air monitors, harnesses, and retrieval systems found in confined space entry kits to ensure worker protection in hazardous atmospheres. Lockout/tagout kits comply with OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147, emphasizing devices like padlocks, tags, and lockout hasps to control hazardous energy during equipment maintenance. Both kits are essential for workplace safety but address distinct regulatory requirements and hazard controls specific to confined spaces and energy isolation.
Common Hazards: Confined Spaces vs. Lockout/Tagout Scenarios
Confined space entry kits address hazards such as oxygen deficiency, toxic gas exposure, and risk of engulfment, ensuring worker safety in environments like tanks or underground vaults. Lockout/tagout kits focus on preventing accidental machine startup, electrical shocks, and mechanical hazards during equipment maintenance or repair, controlling energy sources effectively. Both kits target distinct but critical risks, emphasizing proper hazard identification and control measures in industrial safety protocols.
Regulatory Compliance: OSHA Requirements Overview
Confined space entry kits and lockout/tagout kits are critical for OSHA compliance, addressing distinct safety hazards in industrial environments. Confined space entry kits ensure workers are protected from atmospheric dangers and physical hazards during entry, meeting OSHA's 29 CFR 1910.146 standard. In contrast, lockout/tagout kits comply with OSHA's 29 CFR 1910.147 regulations by preventing accidental machine energization, safeguarding employees from mechanical and electrical injuries during maintenance.
Selection Guide: Choosing the Right Safety Kit for Your Facility
Selecting the right safety kit for your facility depends on the specific hazards present, with confined space entry kits designed for enclosed environments requiring respiratory protection, gas detection, and rescue equipment. Lockout/tagout kits focus on controlling hazardous energy sources during machinery maintenance, including locks, tags, and hasps to prevent accidental startup. Assessing the operational risks and regulatory compliance ensures proper kit selection to maintain worker safety and reduce workplace accidents.
Training and Certification for Kit Usage
Proper training and certification are crucial for effective use of confined space entry kits and lockout/tagout kits to ensure worker safety. Confined space entry training covers atmospheric testing, ventilation, and emergency rescue procedures specific to hazardous environments. Lockout/tagout certification emphasizes energy isolation techniques and compliance with OSHA standards to prevent accidental machinery startup during maintenance.
Maintenance and Inspection of Safety Kits
Maintenance and inspection of confined space entry kits require thorough checks of gas detectors, harnesses, and communication devices to ensure functionality and worker safety. Lockout/tagout kits demand regular verification of locks, tags, and hasps to prevent accidental energization during equipment servicing. Both kits must undergo routine evaluations following OSHA standards to guarantee compliance and operational readiness.
Industry Case Studies: Confined Space Entry vs. Lockout/Tagout Implementation
Industry case studies highlight critical differences between confined space entry kits and lockout/tagout kits in safety protocols. Confined space entry kits emphasize atmospheric testing devices, harnesses, and retrieval systems essential for enclosed environments, while lockout/tagout kits prioritize lock devices, tags, and energy-isolation tools to prevent machinery startup. Successful implementation of both kits in manufacturing and chemical plants demonstrates reduced workplace incidents by addressing distinct hazard controls within confined spaces and equipment energy sources.
Confined space entry kit vs Lockout/tagout kit Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com