OLED displays offer vibrant colors and fast refresh rates, making them ideal for dynamic hardware pet interfaces with animated features. E-ink screens excel in low power consumption and readability under direct sunlight, suitable for hardware pets that prioritize battery life and outdoor use. Choosing between OLED and e-ink hinges on whether vivid visuals or energy efficiency is the primary requirement for the device.
Table of Comparison
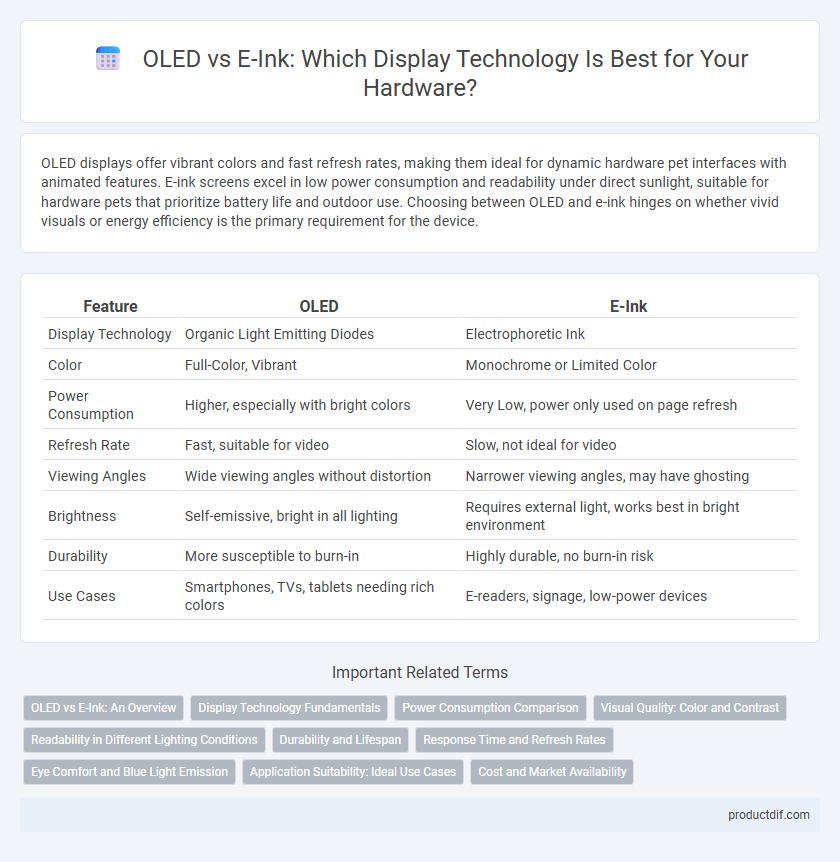
| Feature | OLED | E-Ink |
|---|---|---|
| Display Technology | Organic Light Emitting Diodes | Electrophoretic Ink |
| Color | Full-Color, Vibrant | Monochrome or Limited Color |
| Power Consumption | Higher, especially with bright colors | Very Low, power only used on page refresh |
| Refresh Rate | Fast, suitable for video | Slow, not ideal for video |
| Viewing Angles | Wide viewing angles without distortion | Narrower viewing angles, may have ghosting |
| Brightness | Self-emissive, bright in all lighting | Requires external light, works best in bright environment |
| Durability | More susceptible to burn-in | Highly durable, no burn-in risk |
| Use Cases | Smartphones, TVs, tablets needing rich colors | E-readers, signage, low-power devices |
OLED vs E-Ink: An Overview
OLED displays deliver vibrant colors and high refresh rates ideal for multimedia and dynamic content, while E-Ink screens excel in low power consumption and readability under direct sunlight, making them perfect for e-readers. OLED panels consist of organic compounds emitting light individually, enabling deep blacks and thin form factors, whereas E-Ink uses microcapsules that reflect ambient light without backlighting, contributing to longer battery life. The choice between OLED and E-Ink hinges on application needs, balancing visual performance against energy efficiency and outdoor visibility.
Display Technology Fundamentals
OLED displays utilize organic light-emitting diodes that emit light individually, resulting in higher contrast ratios, faster refresh rates, and richer color reproduction compared to e-ink screens. E-ink technology relies on electrophoretic particles suspended in microcapsules, producing a reflective, paper-like display that consumes minimal power and excels in readability under direct sunlight. The fundamental difference lies in OLED's emissive pixels versus e-ink's bistable, reflective nature, impacting applications such as smartphones requiring vibrant visuals versus e-readers prioritizing battery life and eye comfort.
Power Consumption Comparison
OLED displays consume significantly more power than e-ink screens, especially during continuous use with bright or dynamic content due to their self-emissive nature. E-ink technology requires power only when changing the displayed image, making it highly energy-efficient for static content and ideal for devices like e-readers. Consequently, e-ink panels extend battery life substantially compared to OLEDs in scenarios prioritizing power conservation.
Visual Quality: Color and Contrast
OLED displays provide superior color accuracy and vibrant contrast with true blacks achieved through individually lit pixels, enhancing visual depth and richness. E-ink screens excel in high contrast under direct sunlight and offer a paper-like reading experience but lack color reproduction, typically rendering content in grayscale. For applications prioritizing vivid imagery and dynamic visuals, OLED outperforms e-ink, which remains ideal for low-power, glare-free reading.
Readability in Different Lighting Conditions
OLED displays offer vibrant colors and high contrast, making them easy to read in low-light and indoor environments due to their self-emissive pixels. E-ink screens provide superior readability in bright sunlight by mimicking the appearance of ink on paper and reducing glare through reflected ambient light. These characteristics make OLED ideal for multimedia use indoors, while e-ink excels in outdoor reading scenarios where natural light is abundant.
Durability and Lifespan
OLED displays typically offer vibrant colors and high contrast but tend to have shorter lifespans due to organic material degradation and burn-in effects, with average durability ranging between 30,000 to 50,000 hours. E-ink screens, commonly used in e-readers, provide superior durability and longevity, often lasting over 100,000 page refresh cycles without significant wear, making them ideal for prolonged use. In terms of hardware lifespan, e-ink technology excels in energy efficiency and resilience, while OLED panels require more frequent replacement due to pixel aging.
Response Time and Refresh Rates
OLED displays boast significantly faster response times, measured in microseconds, enabling smooth motion and vibrant video playback without ghosting. E-ink screens feature slower refresh rates, often around 1 second or more, which are ideal for static images and reading but unsuitable for dynamic content. This difference makes OLED preferable for multimedia and interactive applications, while e-ink excels in low-power, glare-free devices like e-readers.
Eye Comfort and Blue Light Emission
OLED displays offer vibrant colors and high contrast but emit significant blue light, which can cause eye strain and disrupt sleep patterns during prolonged use. E-ink screens mimic the appearance of ink on paper, producing minimal blue light and reducing eye fatigue, making them ideal for extended reading sessions. For users prioritizing eye comfort and minimal blue light exposure, e-ink technology provides a superior viewing experience compared to OLED.
Application Suitability: Ideal Use Cases
OLED displays excel in vibrant color rendering and fast refresh rates, making them ideal for smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices that demand high-resolution visuals and dynamic content. E-ink screens are best suited for e-readers and low-power applications, providing sharp, easily readable text with minimal eye strain and exceptional battery life for prolonged reading sessions. Each technology optimizes user experience by aligning display strengths with specific usage scenarios in consumer electronics.
Cost and Market Availability
OLED displays generally incur higher manufacturing costs due to complex production processes and expensive materials, resulting in premium-priced devices targeted at high-end markets. E-ink technology offers significantly lower production expenses, enabling widespread adoption in affordable e-readers and budget-friendly electronic paper applications. Market availability reflects this cost disparity, with OLED dominating smartphones and tablets while e-ink holds a strong presence in dedicated e-readers and niche low-power display devices.
OLED vs e-ink Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com