Dip switches provide reliable, low-profile manual configuration settings for electronic devices, allowing multiple binary options to be selected simultaneously. Push buttons offer tactile feedback for momentary or maintained user input, ideal for triggering functions or resetting hardware. While dip switches are best for fixed configuration, push buttons excel in interactive control scenarios.
Table of Comparison
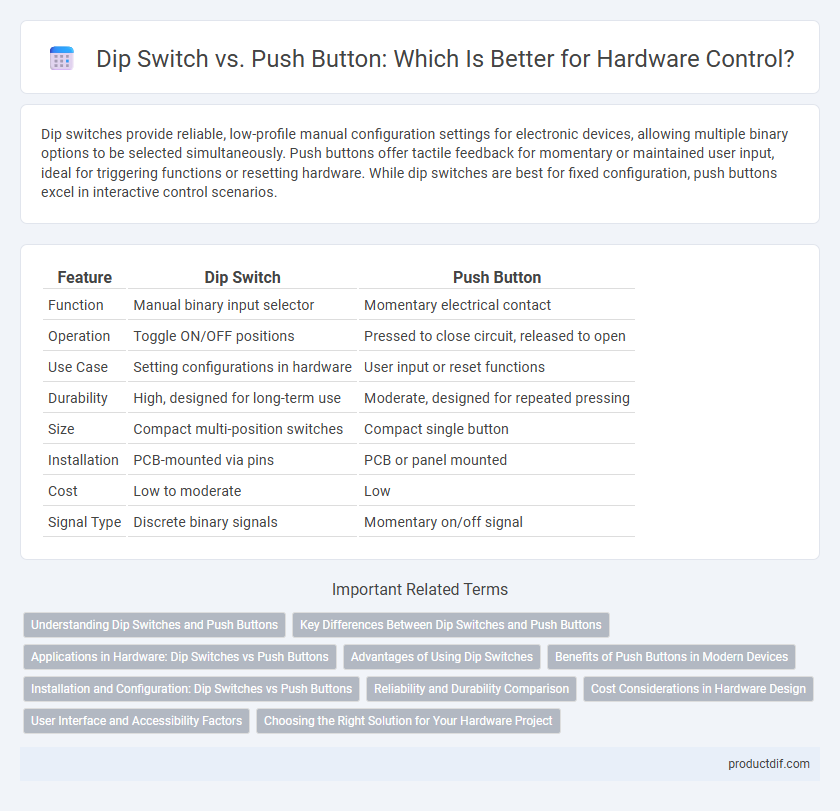
| Feature | Dip Switch | Push Button |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Manual binary input selector | Momentary electrical contact |
| Operation | Toggle ON/OFF positions | Pressed to close circuit, released to open |
| Use Case | Setting configurations in hardware | User input or reset functions |
| Durability | High, designed for long-term use | Moderate, designed for repeated pressing |
| Size | Compact multi-position switches | Compact single button |
| Installation | PCB-mounted via pins | PCB or panel mounted |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Low |
| Signal Type | Discrete binary signals | Momentary on/off signal |
Understanding Dip Switches and Push Buttons
Dip switches are compact, manual electric switches that allow configuration settings on circuit boards by toggling individual switches between ON and OFF positions, providing precise control over hardware functions. Push buttons are momentary contact switches that complete or interrupt circuits only while pressed, commonly used for user inputs and immediate commands in electronic devices. Both components serve distinct control purposes: dip switches for persistent configuration and push buttons for transient user interactions.
Key Differences Between Dip Switches and Push Buttons
Dip switches provide multiple switch positions for setting configurations and are often used for binary or hexadecimal input in hardware devices, allowing for on/off toggles in a compact form. Push buttons serve as momentary switches that complete a circuit only while pressed, used primarily for initiating actions like resets or user inputs. Unlike dip switches which maintain their state until changed, push buttons return to their default state immediately after being released, making their operation fundamentally different in hardware applications.
Applications in Hardware: Dip Switches vs Push Buttons
Dip switches are commonly used in hardware for setting configurations or selecting modes on circuit boards, offering a reliable way to make multiple binary choices without software intervention. Push buttons serve as user inputs in devices requiring momentary activation, such as reset switches, power buttons, or manual controls in consumer electronics. Hardware designs often integrate dip switches for fixed operational settings, while push buttons handle dynamic user interactions or immediate command inputs.
Advantages of Using Dip Switches
Dip switches offer compact, reliable, and cost-effective solutions for setting configurations in electronic devices, providing precise control without the need for additional software or power. Their non-volatile nature ensures settings remain intact during power loss, making them ideal for hardware customization and troubleshooting. Unlike push buttons, dip switches minimize accidental changes and support multiple binary options in a simple, space-efficient format.
Benefits of Push Buttons in Modern Devices
Push buttons offer enhanced durability and faster response times compared to dip switches, making them ideal for modern devices requiring quick and reliable user inputs. Their compact design supports sleek and ergonomic product interfaces, improving user experience in consumer electronics and industrial equipment. Integration with microcontrollers and digital circuits is simplified with push buttons, enabling advanced functionality and programmability in smart devices.
Installation and Configuration: Dip Switches vs Push Buttons
Dip switches require manual adjustment by toggling small switches to configure settings, making them ideal for fixed or rarely changed configurations during installation. Push buttons offer dynamic control, allowing users to easily change settings or trigger functions without internal hardware modification, suitable for frequent adjustments or user interface operations. Installation of dip switches typically involves soldering onto a PCB, while push buttons are mounted for easy access, emphasizing different use cases in hardware design.
Reliability and Durability Comparison
Dip switches offer superior reliability in hardware configurations due to their robust mechanical design, which minimizes the risk of accidental toggling and electrical contact failures. Push buttons, while convenient for frequent user interactions, generally exhibit lower durability under continuous use because their moving parts are more susceptible to wear and mechanical fatigue. In industrial and long-term applications, dip switches provide consistent performance and stability, making them the preferred choice for environments demanding high reliability and extended operational lifespan.
Cost Considerations in Hardware Design
Dip switches are generally more cost-effective than push buttons due to their simpler mechanical design and lower manufacturing costs, making them ideal for budget-conscious hardware projects. Push buttons often incur higher expenses because of their complex assembly, tactile feedback mechanisms, and increased durability requirements in industrial applications. Choosing between dip switches and push buttons hinges on balancing initial hardware costs with long-term maintenance and reliability factors.
User Interface and Accessibility Factors
Dip switches offer a tactile interface allowing users to set hardware configurations without software, suitable for environments requiring durable, discrete inputs. Push buttons provide immediate feedback and ease of operation with a single press, enhancing accessibility for users needing quick and straightforward interactions. User interface design benefits from push buttons in applications demanding frequent changes, while dip switches excel in stable settings with infrequent adjustments.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Hardware Project
Dip switches offer reliable, low-cost configuration options for hardware projects requiring multiple binary settings, ideal for permanent or semi-permanent setups. Push buttons provide tactile control for temporary user inputs, enabling real-time interactions and resets in devices with frequent manual operations. Selecting between dip switches and push buttons depends on the need for persistent configuration versus dynamic input, power consumption considerations, and the desired user experience in the hardware design.
Dip switch vs Push button Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com