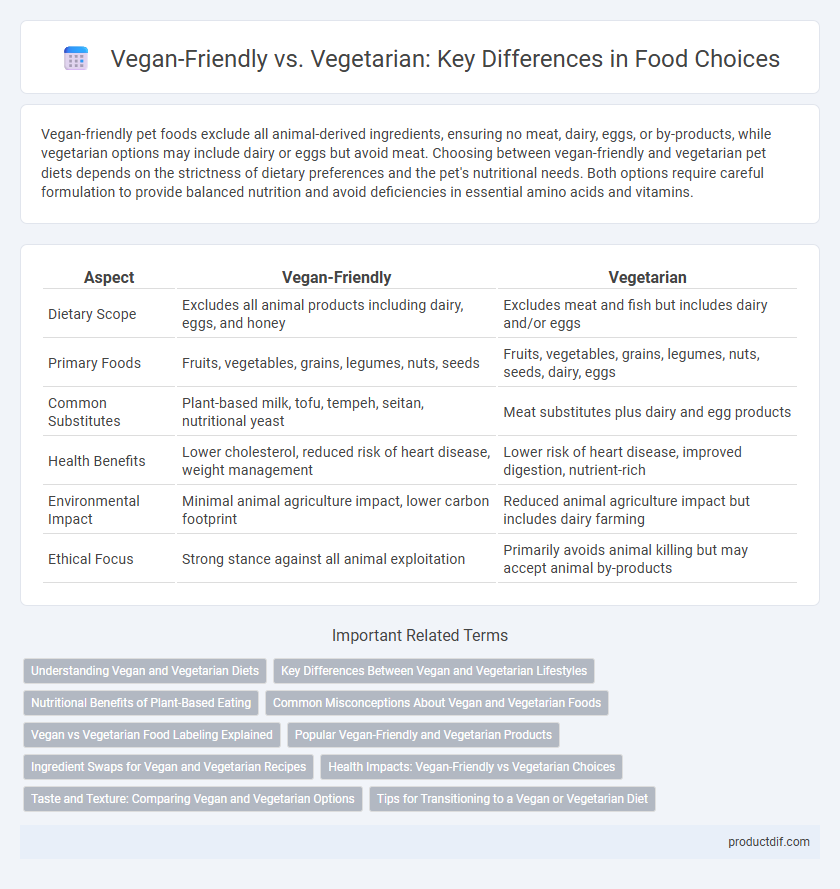
Vegan-friendly pet foods exclude all animal-derived ingredients, ensuring no meat, dairy, eggs, or by-products, while vegetarian options may include dairy or eggs but avoid meat. Choosing between vegan-friendly and vegetarian pet diets depends on the strictness of dietary preferences and the pet's nutritional needs. Both options require careful formulation to provide balanced nutrition and avoid deficiencies in essential amino acids and vitamins.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Vegan-Friendly | Vegetarian |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary Scope | Excludes all animal products including dairy, eggs, and honey | Excludes meat and fish but includes dairy and/or eggs |
| Primary Foods | Fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, seeds | Fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, dairy, eggs |
| Common Substitutes | Plant-based milk, tofu, tempeh, seitan, nutritional yeast | Meat substitutes plus dairy and egg products |
| Health Benefits | Lower cholesterol, reduced risk of heart disease, weight management | Lower risk of heart disease, improved digestion, nutrient-rich |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal animal agriculture impact, lower carbon footprint | Reduced animal agriculture impact but includes dairy farming |
| Ethical Focus | Strong stance against all animal exploitation | Primarily avoids animal killing but may accept animal by-products |
Understanding Vegan and Vegetarian Diets
Vegan diets exclude all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and honey, emphasizing plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and legumes to promote ethical, environmental, and health benefits. Vegetarian diets eliminate meat and fish but often include dairy and eggs, offering more dietary flexibility while still focusing on plant-derived nutrients and protein sources. Both diets vary in nutritional considerations, with vegans needing to ensure adequate intake of vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids through fortified foods or supplements.
Key Differences Between Vegan and Vegetarian Lifestyles
Vegan and vegetarian lifestyles differ primarily in dietary restrictions, with vegans excluding all animal products including dairy, eggs, and honey, while vegetarians may consume dairy and eggs but avoid meat, poultry, and fish. Beyond diet, vegans often avoid animal-derived products in clothing, cosmetics, and household items, reflecting a broader ethical commitment to animal rights. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for nutritional planning, ethical considerations, and product labeling in the food industry.
Nutritional Benefits of Plant-Based Eating
Vegan-friendly diets eliminate all animal products, providing high fiber, antioxidants, and lower saturated fat, which supports heart health and weight management. Vegetarian diets include dairy and eggs, offering additional protein, calcium, and vitamin B12 sources integral for bone health and energy metabolism. Both plant-based approaches promote reduced risk of chronic diseases, enhanced digestive health, and improved nutrient density by emphasizing fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and whole grains.
Common Misconceptions About Vegan and Vegetarian Foods
Many people mistakenly believe vegan and vegetarian diets only differ by the exclusion of meat, but vegans also avoid all animal-derived products such as dairy, eggs, and honey. Another common misconception is that vegetarian and vegan foods are nutritionally deficient, though both diets can provide all essential nutrients when well-planned with sources like legumes, nuts, and fortified plant-based foods. Despite popular belief, vegan and vegetarian foods are widely available and diverse, ranging from dairy-free cheeses to plant-based meats, debunking the myth that these diets are restrictive or bland.
Vegan vs Vegetarian Food Labeling Explained
Vegan food labels indicate products free from all animal-derived ingredients, including dairy, eggs, and honey, catering to strict plant-based diets. Vegetarian labels often allow dairy and eggs but exclude meat, fish, and poultry, reflecting a more flexible dietary choice. Clear labeling helps consumers identify suitable products quickly, supporting dietary preferences and ethical choices.
Popular Vegan-Friendly and Vegetarian Products
Popular vegan-friendly products include plant-based meat substitutes, such as Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods, which replicate the taste and texture of animal products without using any animal-derived ingredients. Vegetarian options often involve dairy and egg-containing products like cheese varieties, yogurt, and egg-based dishes that provide essential nutrients and protein. Both categories feature a wide range of fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds that form the foundation of balanced, nutrient-rich diets.
Ingredient Swaps for Vegan and Vegetarian Recipes
Ingredient swaps in vegan recipes often replace dairy with plant-based alternatives such as almond milk, coconut yogurt, or cashew cheese, ensuring the dish remains entirely free of animal products. Vegetarian recipes might use eggs and dairy as protein sources, which vegans substitute with flaxseed eggs, tofu, or nutritional yeast for texture and flavor enhancement. These strategic ingredient adjustments maintain nutrient balance and culinary integrity while catering to specific dietary preferences within vegan and vegetarian cooking.
Health Impacts: Vegan-Friendly vs Vegetarian Choices
Vegan-friendly diets eliminate all animal products, leading to lower cholesterol levels and reduced risk of heart disease compared to vegetarian diets, which may include dairy and eggs. Both diets can provide adequate nutrients when well-planned, but vegans need to ensure sufficient intake of vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids to prevent deficiencies. Studies show that vegan diets often result in lower body mass index and improved insulin sensitivity, contributing to better metabolic health than some vegetarian options.
Taste and Texture: Comparing Vegan and Vegetarian Options
Vegan and vegetarian foods offer distinct taste and texture experiences due to their varying use of animal products. Vegan options rely on plant-based ingredients like legumes, nuts, and soy, often delivering rich, hearty textures and bold flavors through spices and fermentation. Vegetarian dishes typically include dairy and eggs, resulting in creamier textures and milder, more familiar flavors that cater to a wider range of palates.
Tips for Transitioning to a Vegan or Vegetarian Diet
Gradually introduce plant-based proteins such as lentils, tofu, and chickpeas to replace animal products while ensuring balanced nutrition. Focus on incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds to meet essential vitamins and minerals like B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids. Plan meals ahead, experiment with new recipes, and consider supplements to support a healthy transition to a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle.
Vegan-friendly vs Vegetarian Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com