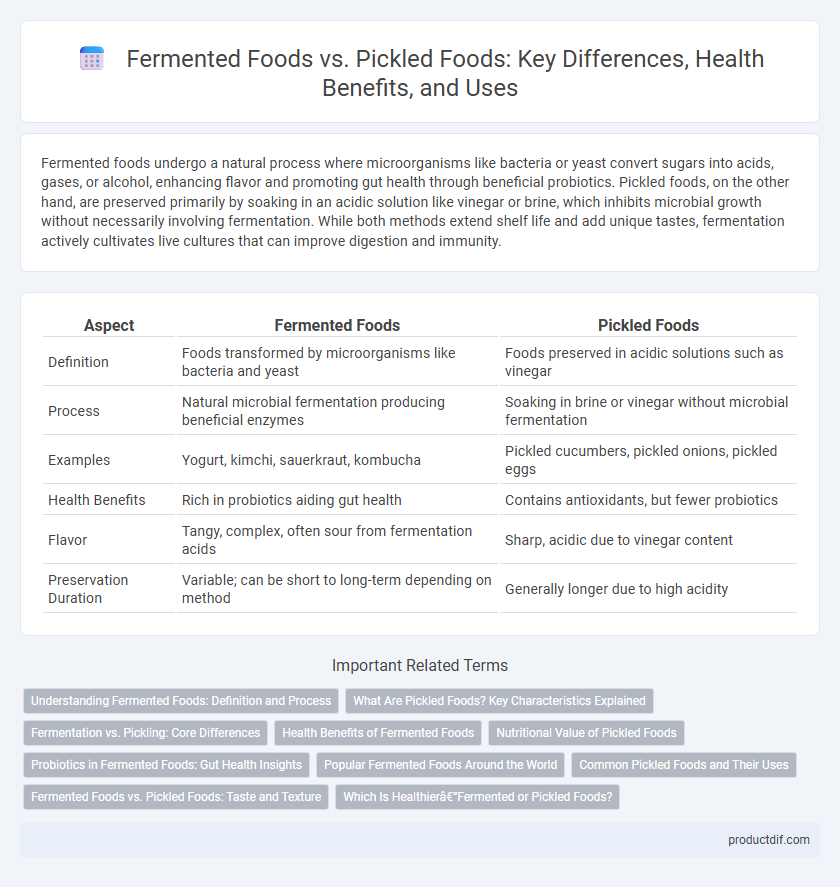
Fermented foods undergo a natural process where microorganisms like bacteria or yeast convert sugars into acids, gases, or alcohol, enhancing flavor and promoting gut health through beneficial probiotics. Pickled foods, on the other hand, are preserved primarily by soaking in an acidic solution like vinegar or brine, which inhibits microbial growth without necessarily involving fermentation. While both methods extend shelf life and add unique tastes, fermentation actively cultivates live cultures that can improve digestion and immunity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fermented Foods | Pickled Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Foods transformed by microorganisms like bacteria and yeast | Foods preserved in acidic solutions such as vinegar |
| Process | Natural microbial fermentation producing beneficial enzymes | Soaking in brine or vinegar without microbial fermentation |
| Examples | Yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, kombucha | Pickled cucumbers, pickled onions, pickled eggs |
| Health Benefits | Rich in probiotics aiding gut health | Contains antioxidants, but fewer probiotics |
| Flavor | Tangy, complex, often sour from fermentation acids | Sharp, acidic due to vinegar content |
| Preservation Duration | Variable; can be short to long-term depending on method | Generally longer due to high acidity |
Understanding Fermented Foods: Definition and Process
Fermented foods undergo a natural process where microorganisms like bacteria and yeast convert sugars into acids, gases, or alcohol, enhancing flavor and preserving the food. This biological transformation improves nutrient absorption and introduces probiotics beneficial for gut health. Unlike pickled foods that rely on vinegar or brine for preservation, fermentation leverages microbial activity to develop complex textures and tastes.
What Are Pickled Foods? Key Characteristics Explained
Pickled foods are items preserved by immersing them in an acidic solution, typically vinegar, which inhibits bacterial growth and extends shelf life. This method results in a tangy flavor profile, distinct from fermentation, which relies on beneficial bacteria producing acids naturally. Common pickled foods include cucumbers, onions, and eggs, all characterized by their crisp texture and sharp, sour taste.
Fermentation vs. Pickling: Core Differences
Fermentation involves the metabolic process where beneficial bacteria convert sugars into acids, gases, or alcohol, enhancing the nutritional profile and creating probiotics that promote gut health. Pickling primarily preserves food by immersing it in an acidic solution, typically vinegar, which inhibits microbial growth without necessarily introducing live cultures. Unlike pickling, fermentation enables the development of complex flavors and bioactive compounds through microbial activity.
Health Benefits of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods, such as yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut, are rich sources of probiotics that support gut health by enhancing the balance of beneficial bacteria. These foods contribute to improved digestion, strengthened immune function, and may reduce inflammation and the risk of certain chronic diseases. Unlike pickled foods, which are preserved mainly with vinegar, fermented foods undergo natural microbial processes that produce bioactive compounds beneficial for overall health.
Nutritional Value of Pickled Foods
Pickled foods retain many essential nutrients such as vitamins A, K, and C, along with beneficial minerals like iron and calcium, due to their preservation process. The lactic acid fermentation involved in traditional pickling enhances bioavailability of nutrients and supports gut health by promoting probiotics. Compared to other preservation methods, pickled foods offer a nutrient-rich option that aids digestion and boosts the immune system.
Probiotics in Fermented Foods: Gut Health Insights
Fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut contain live probiotics that enhance gut microbiota diversity and improve digestive health. Unlike pickled foods, which are preserved in acidic brine without live bacteria, fermented foods undergo microbial fermentation that produces beneficial bacteria essential for immune function and nutrient absorption. Incorporating fermented foods into the diet supports balanced gut flora and helps reduce inflammation-related digestive disorders.
Popular Fermented Foods Around the World
Kimchi, a staple in Korean cuisine, is a popular fermented food known for its rich probiotic content and tangy flavor. Sauerkraut, made from fermented cabbage, is widely consumed in Germany and rich in vitamins and beneficial bacteria. Other globally popular fermented foods include Japanese miso, Indian idli, and Ethiopian injera, all valued for their unique tastes and digestive health benefits.
Common Pickled Foods and Their Uses
Common pickled foods include cucumbers, olives, onions, and cabbage, each offering distinct flavors and textures that enhance culinary dishes worldwide. Pickled cucumbers serve as popular condiments in sandwiches and burgers, while pickled onions add a tangy crunch to salads and tacos. Pickled cabbage, known as sauerkraut or kimchi depending on fermentation level, is widely used in traditional European and Korean cuisine for its zest and probiotic benefits.
Fermented Foods vs. Pickled Foods: Taste and Texture
Fermented foods develop complex, tangy flavors and a natural effervescence due to beneficial bacteria producing lactic acid, resulting in a chewy or slightly soft texture. Pickled foods, preserved primarily in vinegar or brine, tend to have a sharper, more acidic taste with a crisp or crunchy bite. The fermentation process enhances probiotics and depth of flavor, distinguishing fermented foods from the simpler preservation and flavor profile of pickled foods.
Which Is Healthier—Fermented or Pickled Foods?
Fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut contain probiotics that support gut health and boost the immune system, making them generally healthier than pickled foods. Pickled foods are preserved in vinegar or brine, which may add flavor but often lack beneficial live bacteria and can be high in sodium. Choosing fermented options offers more digestive benefits and nutrient absorption compared to the primarily acidic preservation of pickled foods.
fermented foods vs pickled foods Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com